Abstract
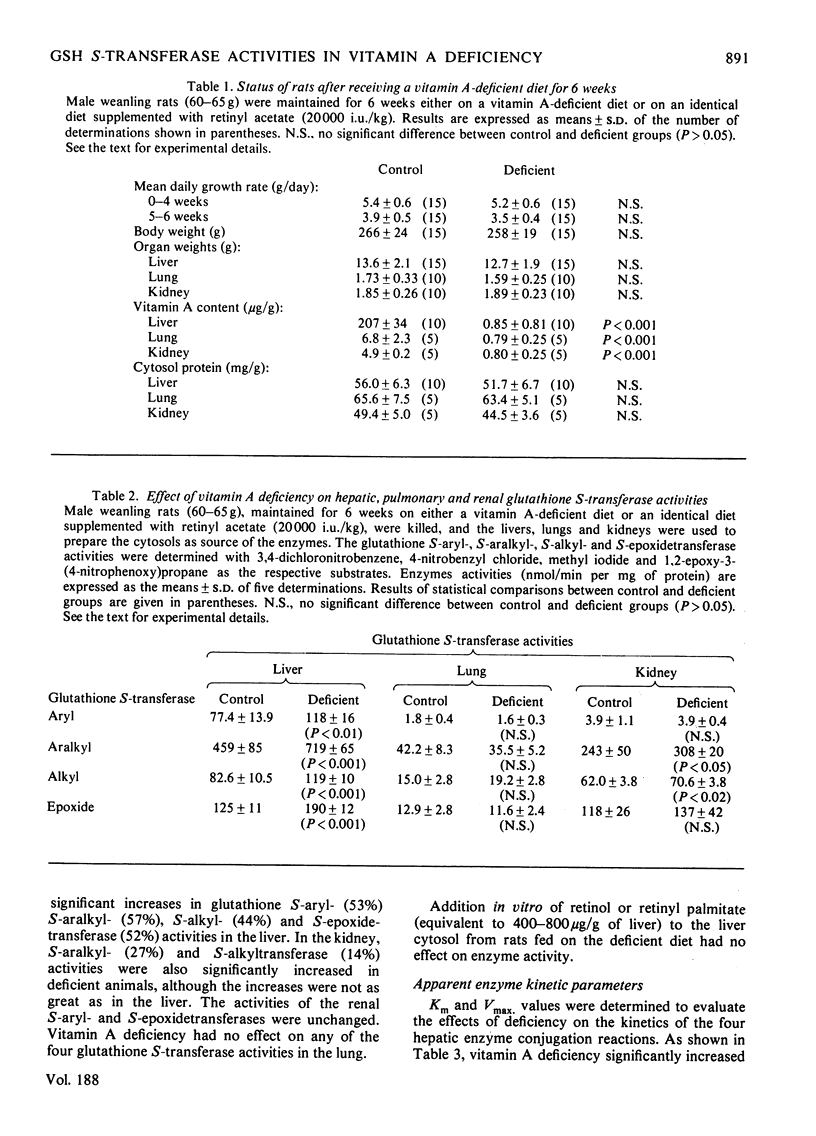
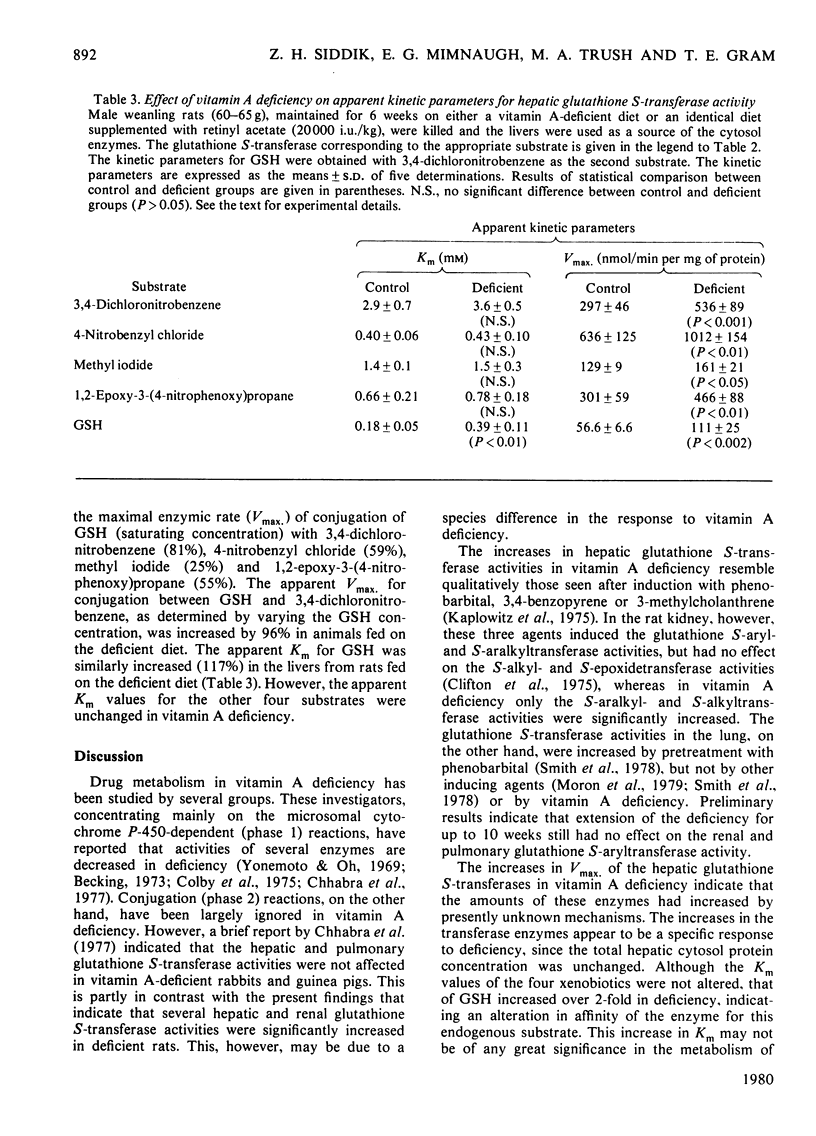
Feeding male weanling rats on a vitamin A-deficient diet for 6 weeks resulted in significant increases (44-57%) in glutathione S-aryl-, S-aralkyl- S-alkyl- and S-epoxidetransferase activities in the liver cytosol. Only the S-aralkyl- (27%) and S-alkyltransferase (14%) activities were significantly increased in the kidney as a result of deficiency. There was no effect on any of the pulmonary glutathione S-transferase activities. The increases in hepatic transferase activities were due primarily to increases (25-96%) in the apparent Vmax. There were no changes in the apparant Km of any of the four drug substrates employed. With 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene as the second substrate, the apparent Km for glutathione was increased by over 2-fold in vitamin A-deficient livers as compared with controls. The relationship between these results and enhanced susceptibility to chemical carcinogens in vitamin A deficiency is briefly discussed, and comparison is made between the effects of this nutritional state and pretreatment with drug inducers on the glutathione S-transferases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baars A. J., Jansen M., Breimer D. D. The influence of phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on glutathione S-transferase activity of rat liver cytosol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(21):2487–2497. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becking G. C. Vitamin A status and hepatic drug metabolism in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;51(1):6–11. doi: 10.1139/y73-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Batzinger R. P., Ou S. Y., Bueding E., Cha Y. N., Talalay P. Elevation of hepatic glutathione S-transferase activities and protection against mutagenic metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene by dietary antioxidants. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4486–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton G., Kaplowitz N., Wallin J. D., Kuhlenkamp J. Drug induction and sex differences of renal glutathione S-transferases in the rat. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):259–262. doi: 10.1042/bj1500259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby H. D., Kramer R. E., Greiner J. W., Robinson D. A., Krause R. F., Canady W. J. Hepatic drug metabolism in retinol-deficient rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Sep 1;24(17):1645–1646. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjellstedt T. A., Allen R. H., Duncan B. K., Jakoby W. B. Enzymatic conjugation of epoxides with glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3702–3707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta V. M., Kaufman D. G., Harris C. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B., Saffiotti U. Vitamin A deficiency enhances binding of benzo(a)pyrene to tracheal epithelial DNA. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):48–49. doi: 10.1038/247048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover P. L., Sims P. Conjugations with glutathione. Distribution of glutathione S-aryltransferase in vertebrate species. Biochem J. 1964 Mar;90(3):603–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0900603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K. Studies on glutathione S-alkyltransferase of the rat. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):44–56. doi: 10.1042/bj0980044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Kuhlekamp J., Clifton G. Drug induction of hepatic glutathione S-transferases in male and female rats*. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):351–356. doi: 10.1042/bj1460351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moron M. S., Depierre J. W., Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 4;582(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Maguire J. H., Ball L. M., Bend J. R. Pulmonary metabolism of epoxides. Fed Proc. 1978 Sep;37(11):2480–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. J., Ohl V. S., Litwack G. Ligandin, the glutathione S-transferases, and chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis: a review. Cancer Res. 1977 Jan;37(1):8–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Dunlop N. M., Newton D. L., Smith J. M. Prevention of chemical carcinogenesis by vitamin A and its synthetic analogs (retinoids). Fed Proc. 1976 May 1;35(6):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto T., O M. On the functional site of vitamin A. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1969 Sep 10;15(3):254–260. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.15.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


