Abstract
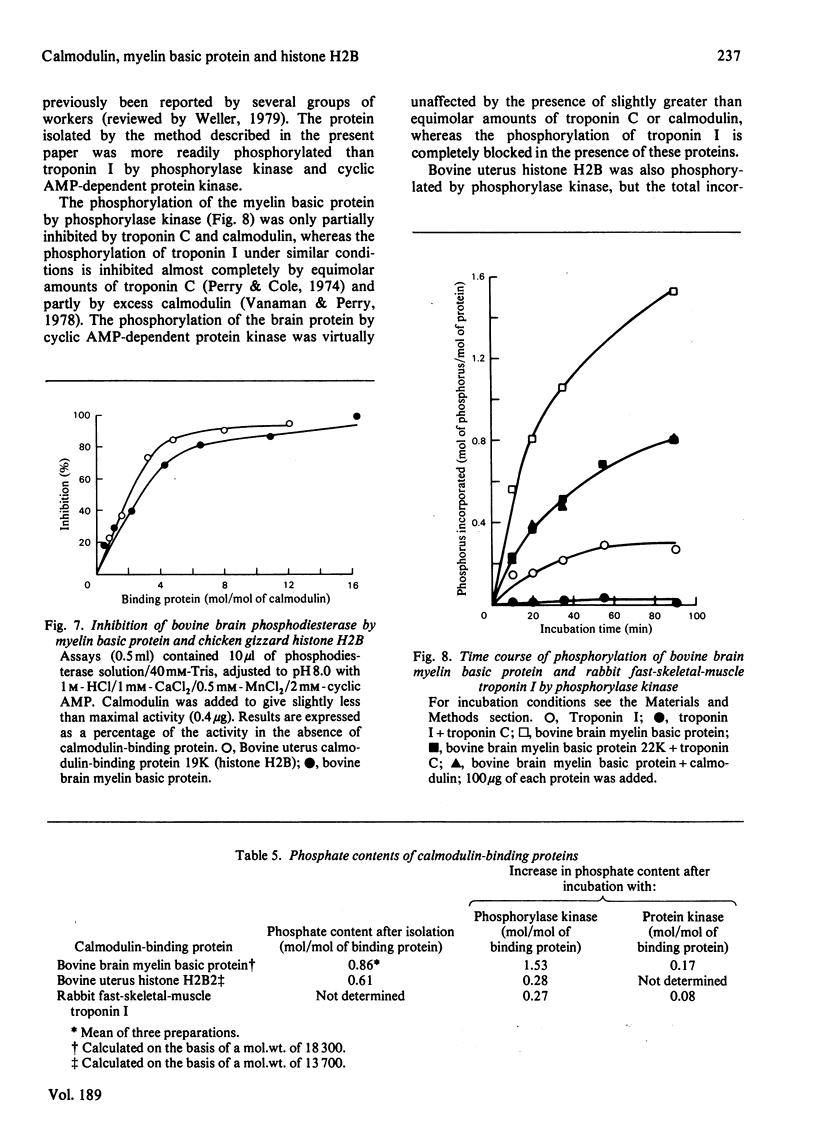
1. A calmodulin-binding protein of apparent mol.wt. 19 000 has been purified from chicken gizzard. Similar proteins have been isolated from bovine uterus, rabbit skeletal muscle and rabbit liver. 2. These proteins migrated as an equimolar complex with bovine brain calmodulin on electroporesis on polyacrylamide gels in the presence of Ca2+ and 6M-urea. The complex was dissociated in the presence of EGTA. 2. The chicken gizzard calmodulin-binding protein has been shown to be identical with chicken erythrocyte histone H2B on the basis of partial amino acid sequence determination. 4. The calmodulin-binding proteins of apparent mol.wt. 22 000 isolated previously from bovine brain [Grand & Perry (1979) Biochem. J. 183, 285-295] has been shown, on the basis of partial amino-acid-sequence determination, to be identical with myelin basic protein. 5. The activation of bovine brain phosphodiesterase by calmodulin is inhibited by excess bovine uterus calmodulin-binding protein (histone H2B). 6. The phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by phosphorylase kinase is partially inhibited, whereas the phosphorylation of uterus calmodulin-binding protein (histone H2B) is unaffected by calmodulin or troponin C. 7. The subcellular distribution of myelin basic protein and calmodulin suggests that the two proteins do not exist as a complex in vivo.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Kemp B. E., Dunkley P. R., Murray A. W. Phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):569–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1350569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Demonstration of an activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 6;38(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation of troponin I from cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1490525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhoot G. K., Gell P. G., Perry S. V. The localization of the different forms of troponin I in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easley C. W. Combinations of specific color reactions useful in the peptide mapping technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 13;107(2):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Wakabayashi T., Ebashi F. Troponin and its components. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):441–445. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath R. M., Vincenzi F. F. Phosphodiesterase protein activator mimics red blood cell cytoplasmic activator of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. The preparation of calmodulins from barley (Hordeum sp.) and basidiomycete fungi. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):755–760. doi: 10.1042/bj1850755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
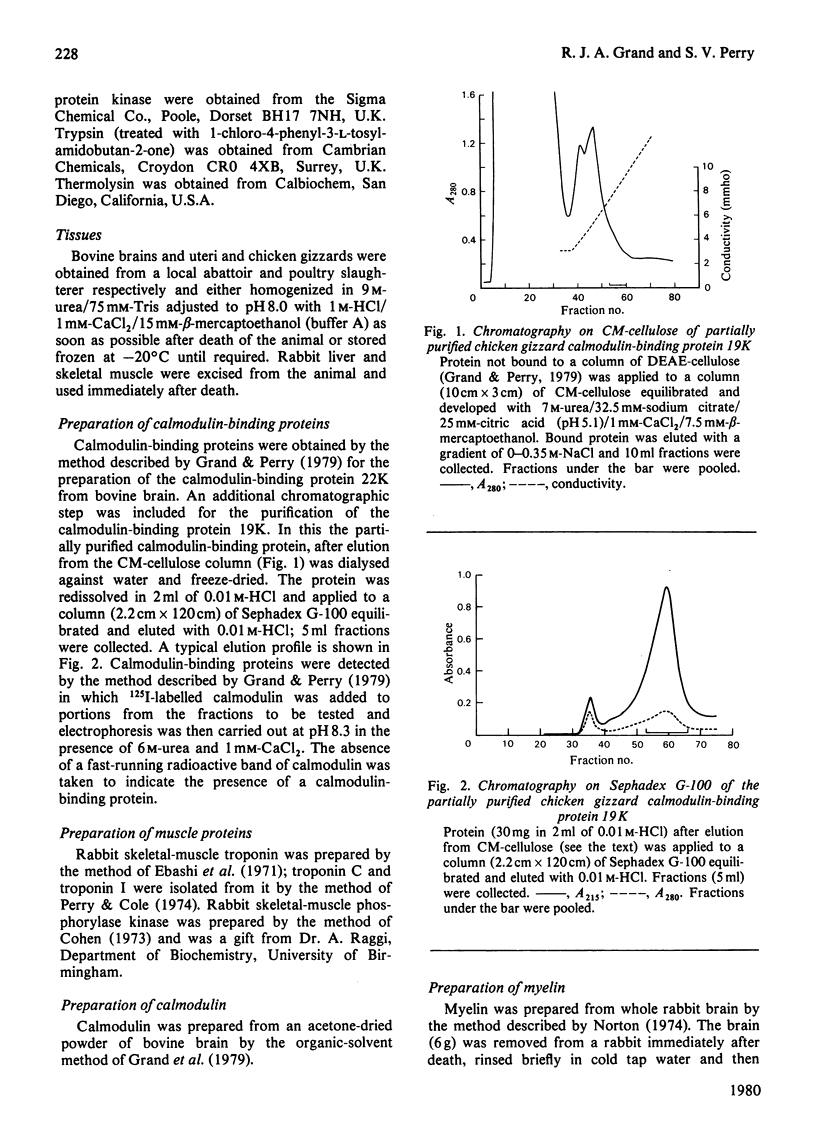
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. Calmodulin-binding proteins from brain and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):285–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1830285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Smith J. F. Rapid sequence analysis of small peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Perry S. V. The interaction of the calcium-binding protein (troponin C) with bivalent cations and the inhibitory protein (troponin I). Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):145–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1370145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
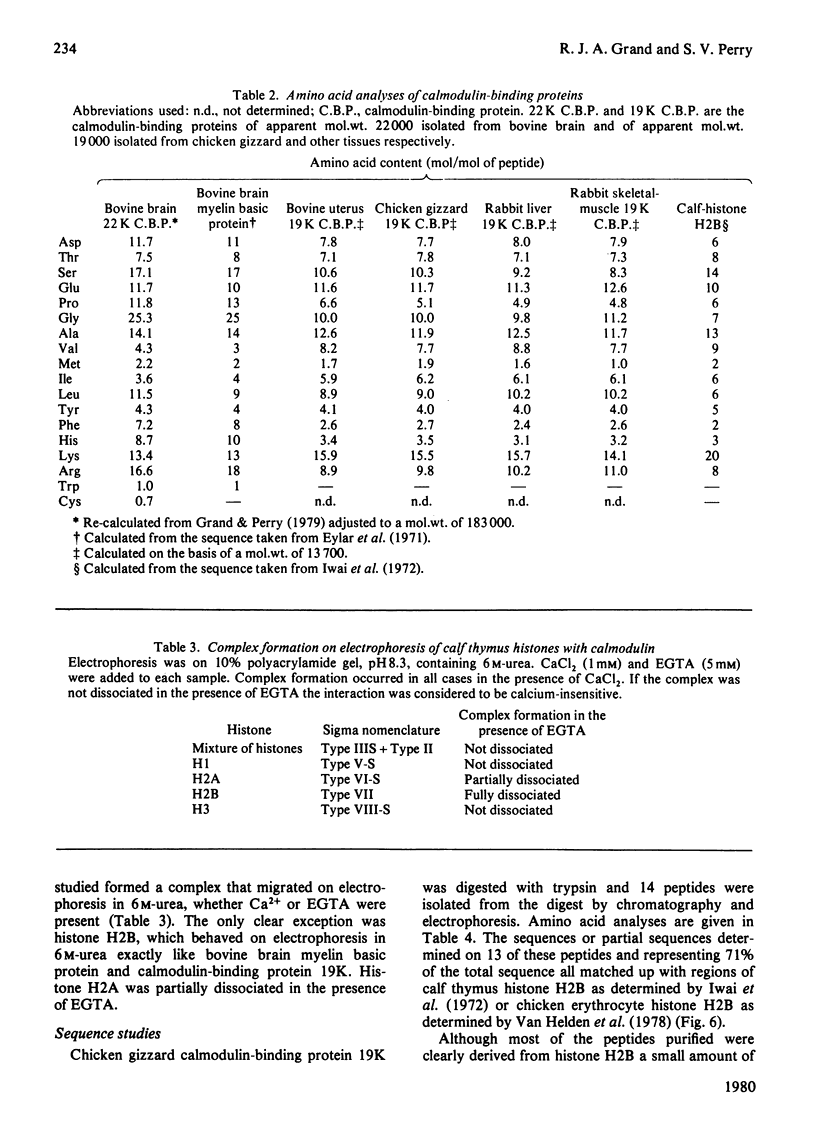
- Iwai K., Hayashi H., Ishikawa K. Calf thymus lysine- and serine-rich histone. 3. Complete amino acid sequence and its implication for interactions of histones with DNA. J Biochem. 1972 Aug;72(2):357–367. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R. Calcium dependent phosphodiesterase activity and its activating factor (PAF) from brain studies on cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase (3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavis P. C., Rosenfeld S. S., Gergely J., Grabarek Z., Drabikowski W. Proteolytic fragments of troponin C. Localization of high and low affinity Ca2+ binding sites and interactions with troponin I and troponin T. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5452–5459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kakiuchi S. In vitro and in vivo phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by exogenous and endogenous adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in brain. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2769–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. Calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase of rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1790089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T. Isolation of myelin from nerve tissue. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:435–444. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez de Lores A., Alberici M., De Robertis E. Ultrastructural and enzymic studies of cholinergic and non-cholinergic synaptic membranes isolated from brain cortex. J Neurochem. 1967 Feb;14(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb05897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Desai R., Waisman D. M., Wang J. H. Purification and subunit structure of bovine brain modulator binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4276–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry J. M., Górecka A., Aksoy M. O., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. Roles of calcium and phosphorylation in the regulation of the activity of gizzard myosin. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4411–4418. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoake J. A., Song S. Y., Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Distribution and developmental changes of the enzyme and its protein activator in mammalian tissues and cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 25;341(2):402–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):375–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1530375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo T. S., Wang T. H., Wang J. H. Purification and properties of the protein activator of bovine heart cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):588–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden P., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., Von Holt C. Histone H2B variants from the erythrocytes of an amphibian, a reptile and a bird. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 28;533(1):278–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Desai R. Modulator binding protein. Bovine brain protein exhibiting the Ca2+-dependent association with the protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4175–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Harrelson W. G., Jr, Keller P. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. Structural similarities between the Ca2+-dependent regulatory proteins of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Characterization of a region of the primary sequence of troponin C involved in calcium ion-dependent interaction with troponin I. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj1730449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. A method for purifying methionine-containing peptides by radioactive labelling. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(3):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Trayer I. P. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Separation and biological activity of the components of inhibitory-factor preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1270215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The preparation and properties of the components of troponin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoman L. C., Olson M. O., Sugano N., Jordan J. J., Taylor D. W., Starbuck W. C., Busch H. Amino acid sequence of the center of the arginine-lysine-rich histone from calf thymus. The total sequence. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6018–6023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]