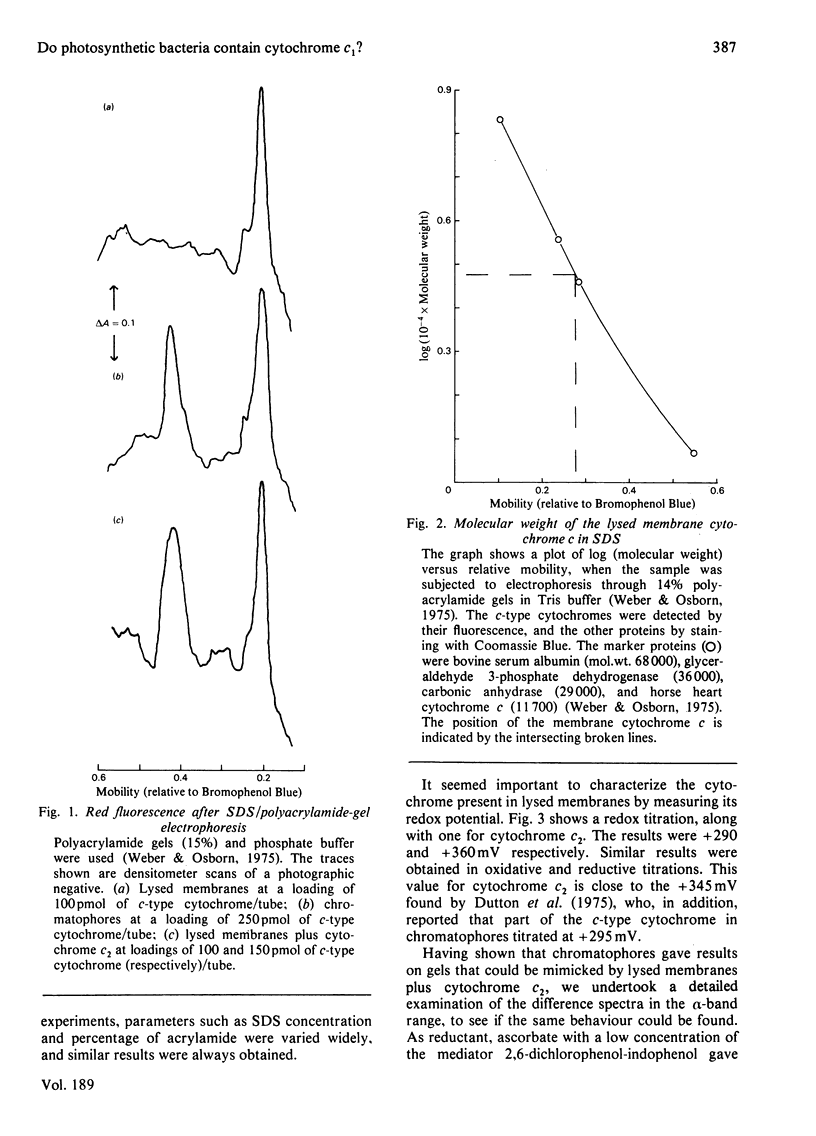
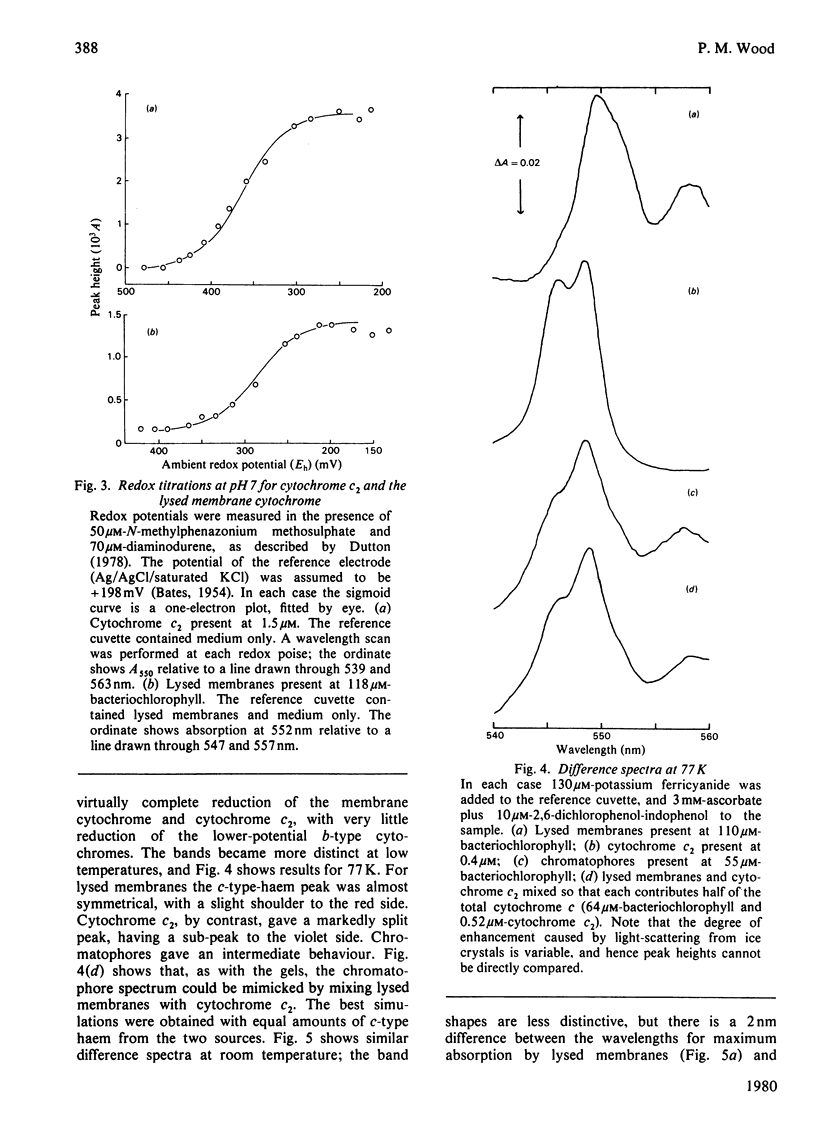
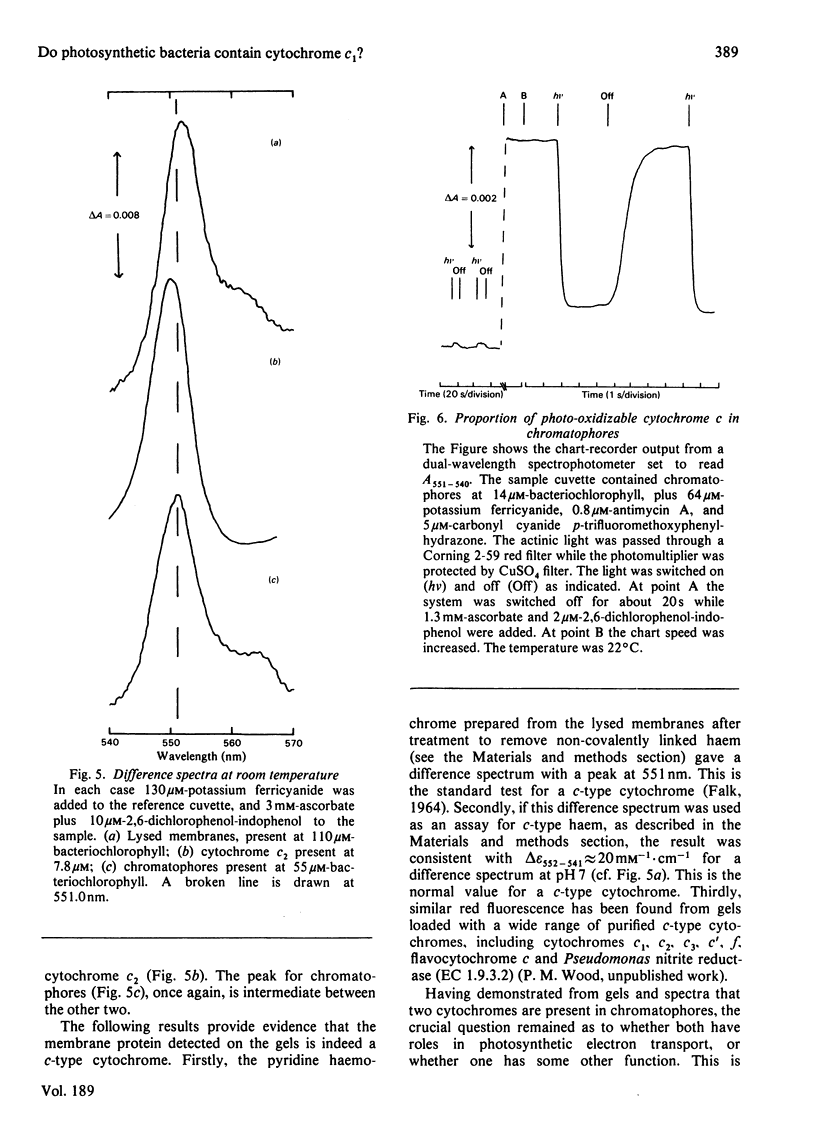
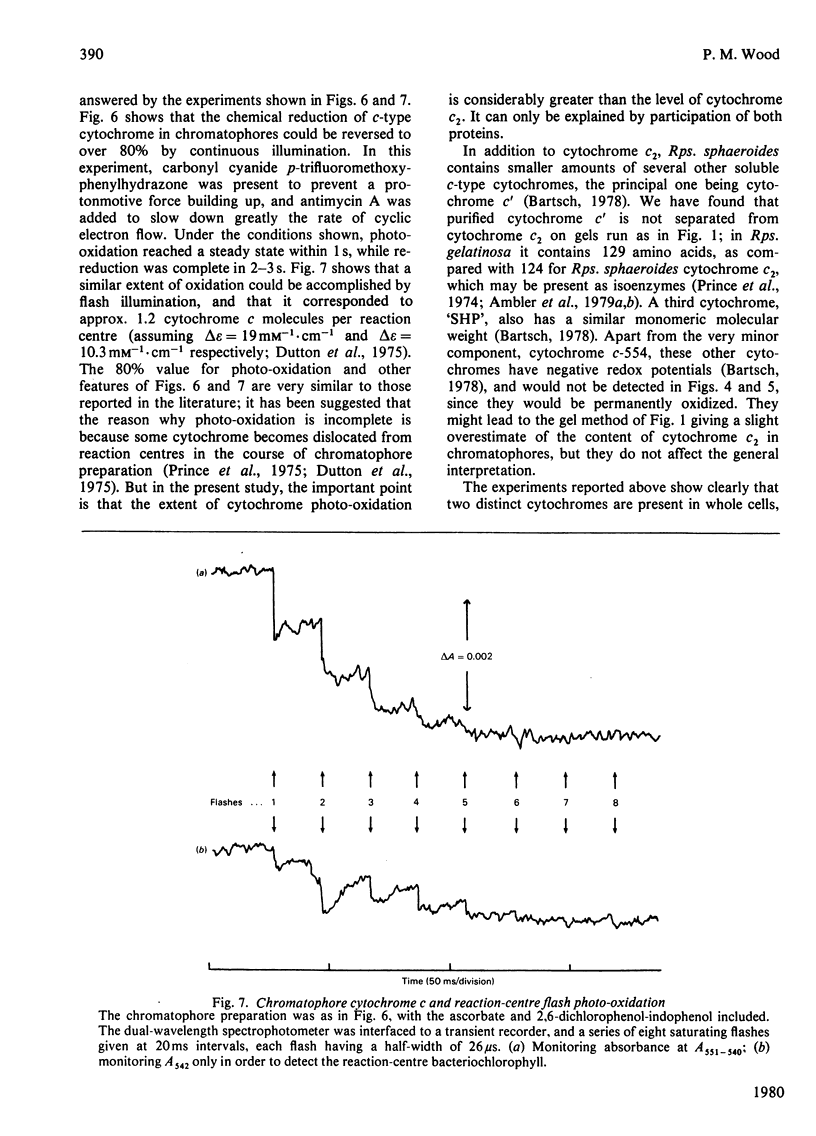
Abstract
A method is described for characterizing, c-type cytochromes in bacterial membrane preparations according to molecular weight on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Applied to the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides this technique is used, together with spectroscopic measurements, to demonstrate that a membrane-bound cytochrome c of mol.wt. 30000 is active in photosynthetic electron transport in addition to the well-known soluble cytochrome, cytochrome c2. The membrane cytochrome has a midpoint potential (E'0) at pH 7 of +290 mV, as compared with +360 mV for purified cytochrome c2. Its alpha-band has a peak near 552 nm, as compared with 550 nm for cytochrome c2. Evidence is presented that chromatophores contain roughly equal amounts of the two cytochromes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Daniel M., Hermoso J., Meyer T. E., Bartsch R. G., Kamen M. D. Cytochrome c2 sequence variation among the recognised species of purple nonsulphur photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):659–660. doi: 10.1038/278659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D. Anomalies in amino acid sequences of small cytochromes c and cytochromes c' from two species of purple photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):661–662. doi: 10.1038/278661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini-Melandri A., Jones O. T., Hauska G. Cytochrome c2--an electron carrier shared by the respiratory and photosynthetic electron transport chain of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 15;86(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall S., Noack N., Wu M., Loewenberg J. R. A simple colorimetric method for determination of protein. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ien L. T., Aur R. J., Stagner S., Cavallo K., Wood A., Goff J., Pitner S., Hustu H. O., Seifert M. J., Simone J. V. Long-term neurological implications of somnolence syndrome in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Neurol. 1980 Sep;8(3):273–277. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty A., Gray J. C. Synthesis of cytochrome f by isolated pea chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Petty K. M., Bonner H. S., Morse S. D. Cytochrome c2 and reaction center of Rhodospeudomonas spheroides Ga. membranes. Extinction coefficients, content, half-reduction potentials, kinetics and electric field alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 17;387(3):536–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L. Redox potentiometry: determination of midpoint potentials of oxidation-reduction components of biological electron-transfer systems. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:411–435. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. N., Jones O. T. The kinetics of flash-induced electron flow in bacteriochlorophyll-less membranes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides reconstituted with reaction centres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 8;545(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M. B. Detection of cytochromes on sodium dodecylsulphate-polyacrylamide gels by their intrinsic fluorescence. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jul;74(1):132–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90316-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., FROHWIRT N. Spectrum of horse-heart cytochrome c. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):570–572. doi: 10.1042/bj0710570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Baccarini-Melandri A., Hauska G. A., Melandri B. A., Crofts A. R. Asymmetry of an energy transducing membrane the location of cytochrome c2 in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 15;387(2):212–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Cogdell R. J., Crofts A. R. The photo-oxidation of horse heart cytochrome c and native cytochrome c2 by reaction centres from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides R26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 23;347(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:778–785. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whale F. R., Jones O. T. The cytochrome system of heterotrophically-grown Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 3;223(1):146–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Periplasmic location of the terminal reductase in nitrite respiration. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80757-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. The roles of c-type cytochromes in algal photosynthesis. Extraction from algae of a cytochrome similar to higher plant cytochrome f. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):605–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



