Abstract
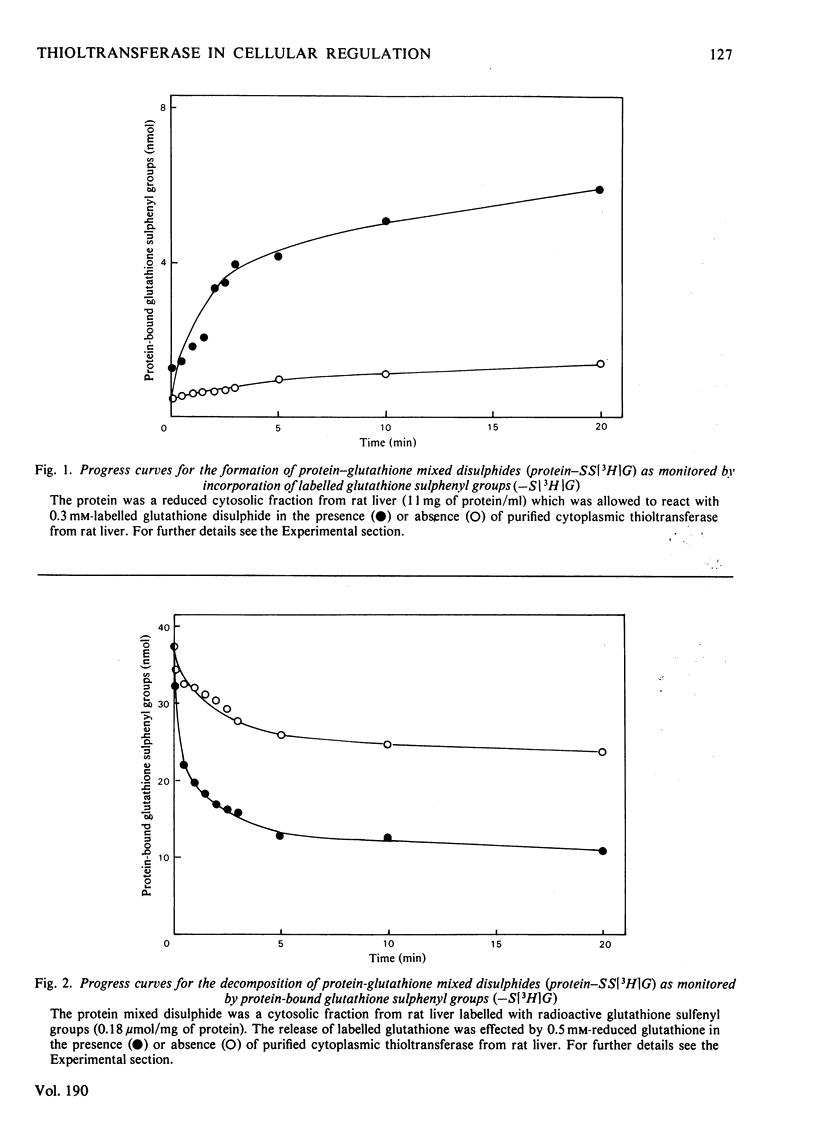
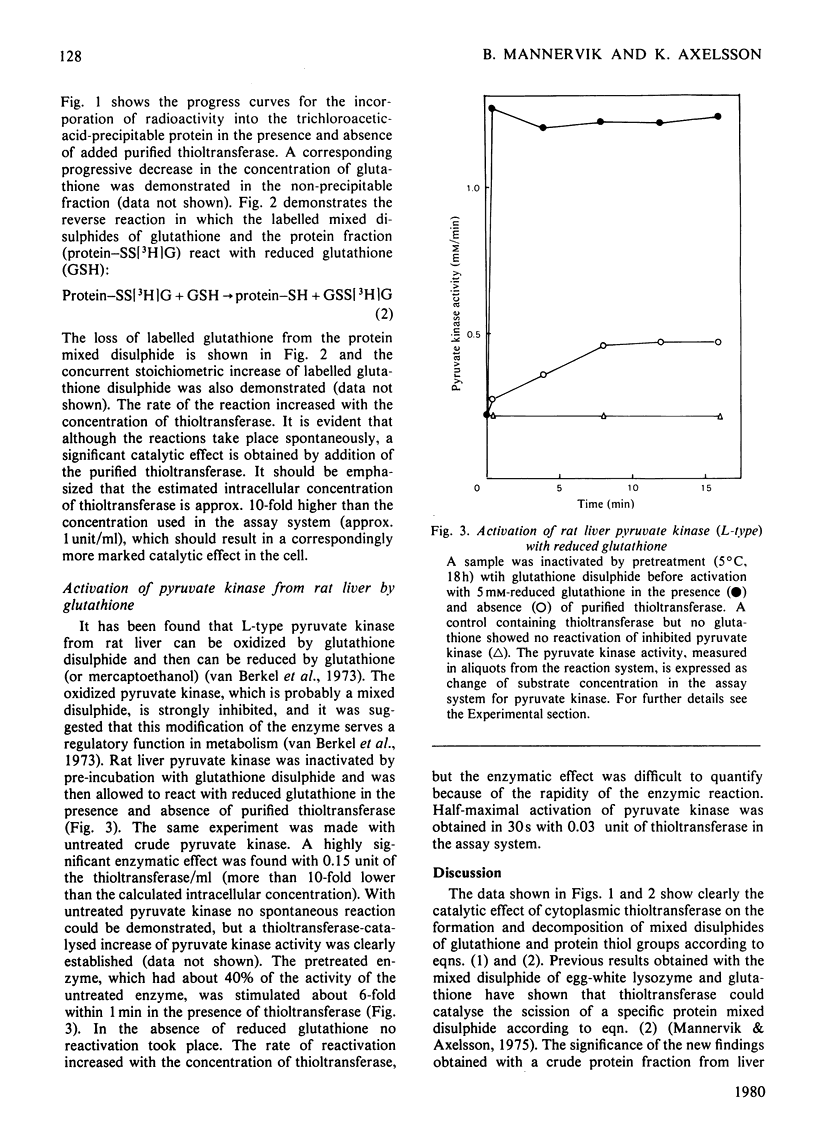
Cytoplasmic thioltransferase purified from rat liver [Axelsson, Eriksson & Mannervik (1978) Biochemistry 17, 2978--2984] catalyses the formation and decomposition of mixed disulphides of proteins and glutathione. The enzyme was found to catalyse the reversible thiol-disulphide interchange between glutathione disulphide and a crude thiol-containing protein fraction from rat liver. This finding indicates a role of the thioltransferase in the regulation of the 'glutathione status' of the cell. Specifically, it was found that thioltransferase catalyses the reactivation of pyruvate kinase from rat liver that had previously been inactivated by glutathione disulphide. It is suggested that thioltransferase may have a general role in regulatory processes involving thiol-disulphide interchange.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson K., Eriksson S., Mannervik B. Purification and characterization of cytoplasmic thioltransferase (glutathione:disulfide oxidoreductase) from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2978–2984. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Mannervik B. A possible role of cytoplasmic thioltransferase in the intracellular degradation of disulfide-containing proteins. Acta Chem Scand B. 1980;34(2):139–140. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.34b-0139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Mannervik B. Synthesis of a mixed disulfide of egg white lysozyme and glutathione - a model substrate for enzymatic reduction of protein mixed disulfides. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 15;53(1):40–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba A., Lee E., Matsuda T., Kihara T., Iwata H. Reversible inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity of rat brain caudate nucleus by oxidized glutathione. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):1204–1210. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDJARN L., BREMER J. The inhibitory effect at the hexokinase level of disulphides on glucose metabolism in human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:286–291. doi: 10.1042/bj0840286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest M. J., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver glycogen synthetase. Reversible inactivation of glycogen synthetase D by sulfhydryl-disulfide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1550–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner M., Hollenberg P. F., Coon M. J. Mechanism of action of pyruvate kinase. Role of sulfhydryl groups in catalytic activity as determined by disulfide interchange. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8114–8121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Larsson A., Meister A. Inhibition of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase by cystamine: an approach to a therapy of 5-oxoprolinuria (pyroglutamic aciduria). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harisch G., Schole J. Der Glutathionstatus der Rattenleber in Abhängigkeit vom Lebensalter und von akuter Belastung. Z Naturforsch C. 1974 May-Jun;29(5-6):261–266. doi: 10.1515/znc-1974-5-614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrap K. R., Jackson R. C., Riches P. G., Smith C. A., Hill B. T. The occurrence of protein-bound mixed disulfides in rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 17;310(1):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Glutathione-dependent synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides. Characterization of the enzymatic mechanism of Escherichia coli glutaredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3672–3678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T., Binkley F. Cyclic AMP-dependent control of the rat hepatic glutathione disulfide-sulfhydryl ratio. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 23;498(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J., Binkley F. Glutathione dependent control of protein disulfide-sulfhydryl content by subcellular fractions of hepatic tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):192–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Kosower E. M. The glutathione status of cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:109–160. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Axelsson K. Reduction of disulphide bonds in proteins mixed disulphides catalysed by a thioltransferase in rat liver cytosol. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):785–788. doi: 10.1042/bj1490785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modig H. Cellular mixed disulphides between thiols and proteins, and their possible implication for radiation protection. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Feb;17(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Horecker B. L., Pontremoli S. Regulatory sulfhydryl groups and activation by homocystine in liver fructose diphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Traniello S., Enser M., Shapiro S., Horecker B. L. Regulation of fructose diphosphatase activity by disulfide exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):286–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazu T., Tokutake S., Usami M. Inactivation of phosphorylase phosphatase by a factor from rabbit liver and its chemical characterization as glutathione disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7376–7382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuboi S., Hayasaka S. Control of -aminolevulinate synthetase activity in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. II. Requirement of a disulfide compound for the conversion of the inactive form of fraction I to the active form. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel J. C., Koster J. F., Hülsmann W. C. Two interconvertible forms of L-type pyruvate kinase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):118–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


