Abstract
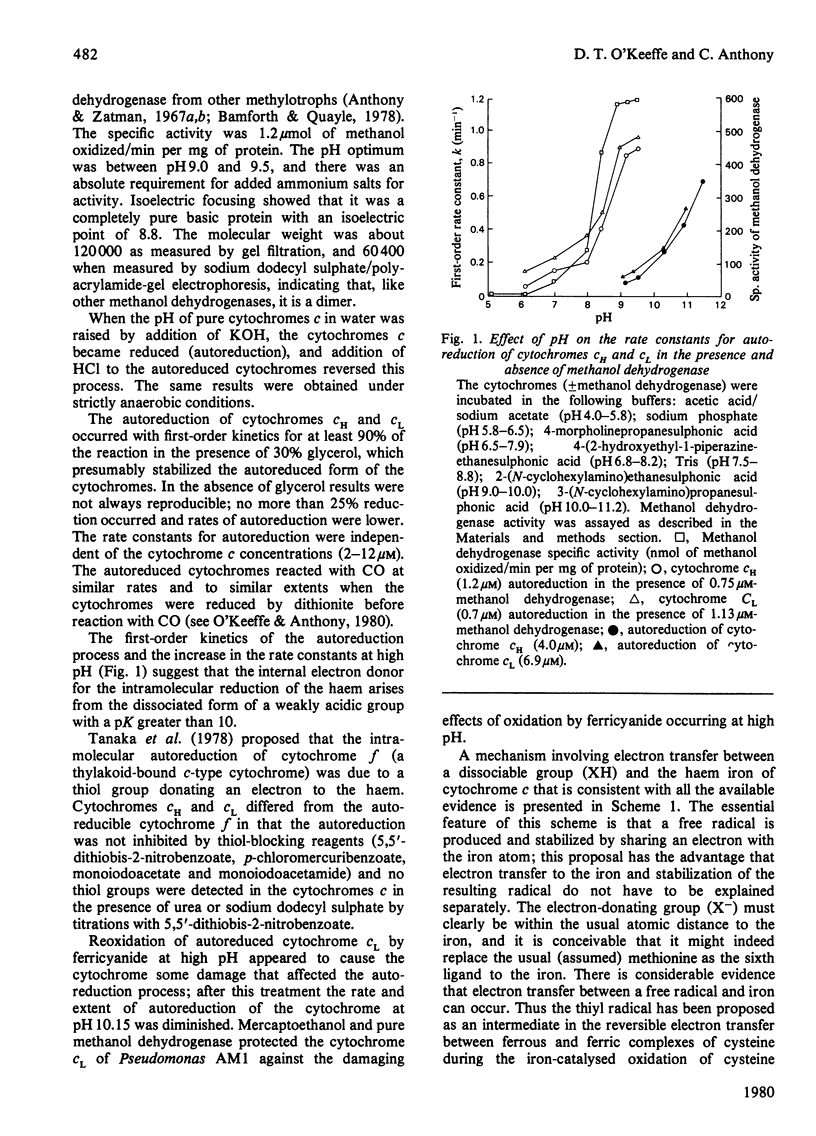
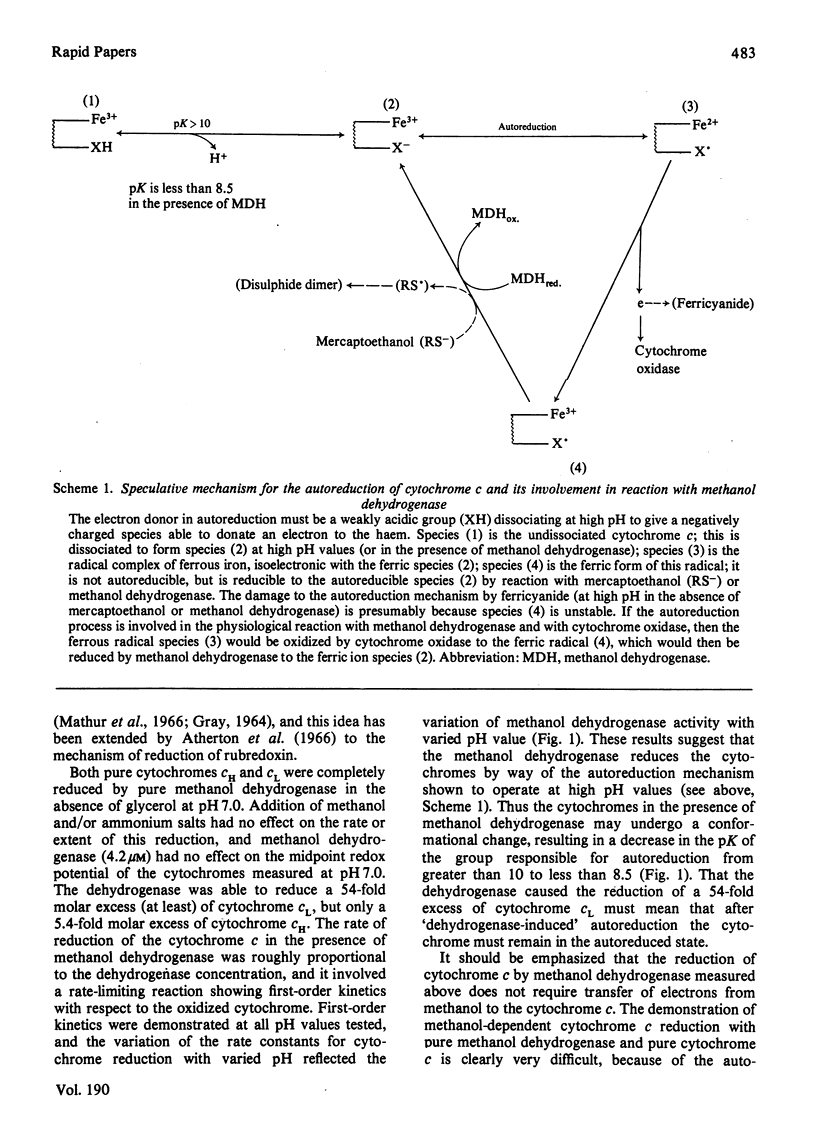
Cytochromes cH and cL were autoreduced at high pH (pK greater than 10) and the autoreduced cytochromes reacted with CO. The autoreduction was first-order with respect to oxidized cytochrome c and was reversible by lowering the pH. Pure methanol dehydrogenase reduced cytochrome c (in the absence of methanol) by lowering the pK for autoreduction to less than 8.5. A mechanism is proposed for the autoreduction of cytochrome c and its involvement in the reaction with methanol dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony C. The microbial metabolism of C1 compounds. The cytochromes of Pseudomaonas AM1. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):289–298. doi: 10.1042/bj1460289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. Purification and properties of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):953–959. doi: 10.1042/bj1040953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. The prosthetic group of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27: a new oxidoreductase prosthetic group. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):960–969. doi: 10.1042/bj1040960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton N. M., Garbett K., Gillard R. D., Mason R., Mayhew S. J., Peel J. L., Stangroom J. E. Spectroscopic investigation of rubredoxin and ferredoxin. Nature. 1966 Nov 5;212(5062):590–593. doi: 10.1038/212590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamforth C. W., Quayle J. R. Aerobic and anaerobic growth of Paracoccus denitrificans on methanol. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):91–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00407934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Jr Studies on methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium X. Isolation of an oxidized form of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):213–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1870213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Jr The prosthetic group of methanol dehydrogenase. Purification and some of its properties. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):221–226. doi: 10.1042/bj1870221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Westerling J. Purification and properties of methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 9;524(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netrusov A. I., Anthony C. The microbial metabolism of C1 compounds. Oxidative phosphorylation in membrane preparations of Pseudomonas AM1. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):353–360. doi: 10.1042/bj1780353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury S. A., Forrest H. S., Cruse W. B., Kennard O. A novel coenzyme from bacterial primary alcohol dehydrogenases. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):843–844. doi: 10.1038/280843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Takahashi M. A., Asada K. Isolation of monomeric cytochrome f from Japanese radish and a mechanism of autoreduction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7397–7403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerling J., Frank J., Duine J. A. The prosthetic group of methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium X: electron spin resonance evidence for a quinone structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


