Abstract
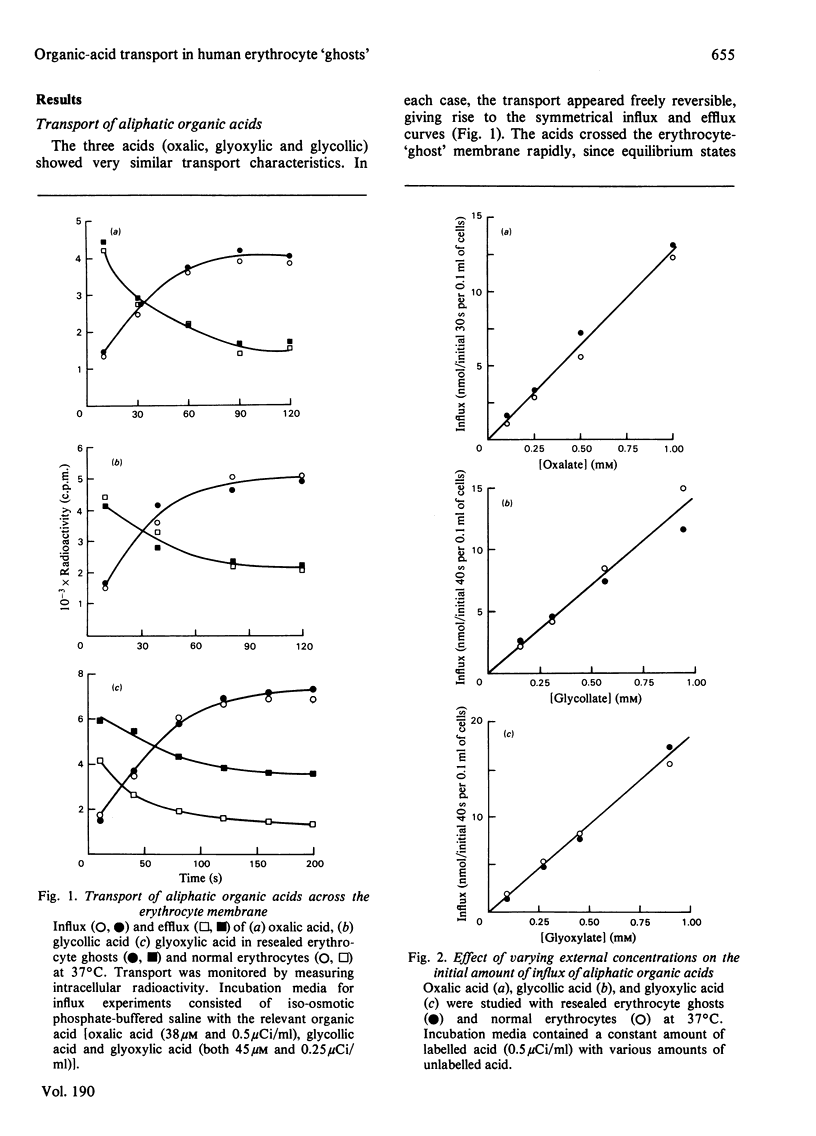
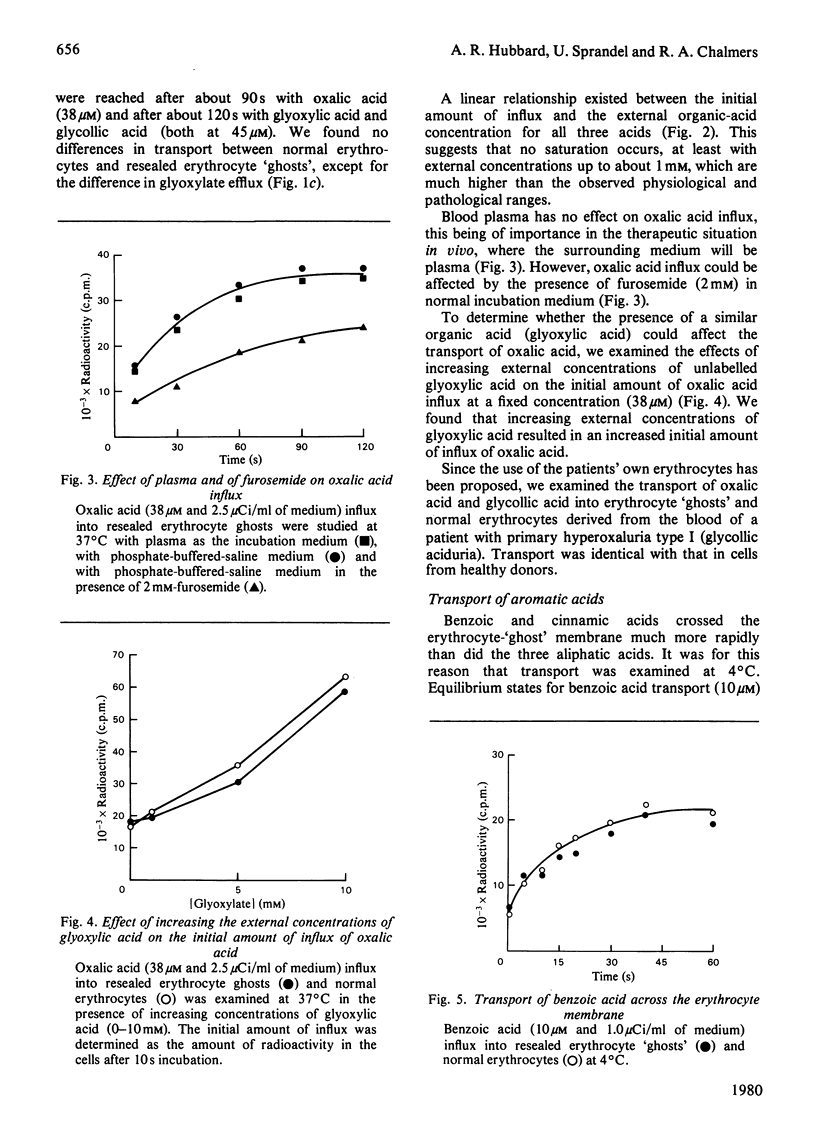
The transport of organic acids across the membrane of resealed haemoglobin-containing erythrocyte 'ghosts' prepared by a dialysis technique has been studied. The present work forms part of studies directed towards the use of erythrocyte cellular carriers in enzyme-replacement therapy of inherited metabolic diseases. Oxalic acid, glycollic acid and glyoxylic acid were taken as representative of aliphatic acids of low molecular mass and benzoic and cinnamic acids as representative of unsubstituted aromatic acids. These selected acids are important in the diseases with which the present work is concerned. Comparison of influx and efflux transport characteristics showed that erythrocyte 'ghosts' retain transport properties closely similar to those of normal erythrocytes. Rapid transport was observed with all organic acids studied and there was a linear relationship between initial amount of influx and external concentration of aliphatic acid. Saturation of the transport system was not observed up to 1 mM external concentration, and the presence of plasma in the external medium had no effect on transport characteristics. Transport in intact erythrocytes and prepared erythrocyte 'ghosts' from patients with hyperoxaluria was also studied.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert L., Motais R. Molecular features of organic anion permeablity in ox red blood cell. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(1):159–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousin J. L., Motais R. The role of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors on anion permeability into ox red blood cells. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):61–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G. L., Villacorte D. G., Beutler E. High-yield entrapment of proteins into erythrocytes. Biochem Med. 1977 Oct;18(2):220–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. E., Stamp T. C. Treatment of primary hyperoxaluria. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Dec;45(244):735–745. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.244.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBEL O., PASSOW H. [The permeability of erythrocyte membranes for organic anions. On the problem of diffusion through the pores]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:378–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson A., Zarembski P. M. Oxalic acid metabolism in man: a review. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968 Oct 21;2(2):115–132. doi: 10.1007/BF02279201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. R., Sprandel U., Chalmers R. A. Transport of oxalic acid, glycollic acid, glyoxylic acid and benzoic acid by resealed erythrocyte 'ghosts' prepared by a dialysis technique [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):958–960. doi: 10.1042/bst0070958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihler G. M., Glew R. H., Schnure F. W. Enzyme loading of erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2663–2666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihler G., Lantzy A., Purpura J., Glew R. H. Enzymatic degradation of uric acid by uricase-loaded human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):595–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI108129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprandel U., Hubbard A. R., Chalmers R. A. In vitro studies on resealed erythrocyte ghosts as protein carriers. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1979 Jul 20;175(3):239–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01851280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprandel U., Hubbard A. R., Chalmers R. A. Membrane transport in resealed haemoglobin-containing human erythrocyte 'ghosts' prepared by a dialysis procedure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W. Oxaluria. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1973 Jan;7(2):161–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W., Purkiss P., Chalmers R. A. A new variant form of phenylketonuria. Q J Med. 1979 Jul;48(191):403–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U., Riemann F., Pilwat G. Enzyme loading of electrically homogeneous human red blood cell ghosts prepared by dielelctric breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):460–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


