Abstract
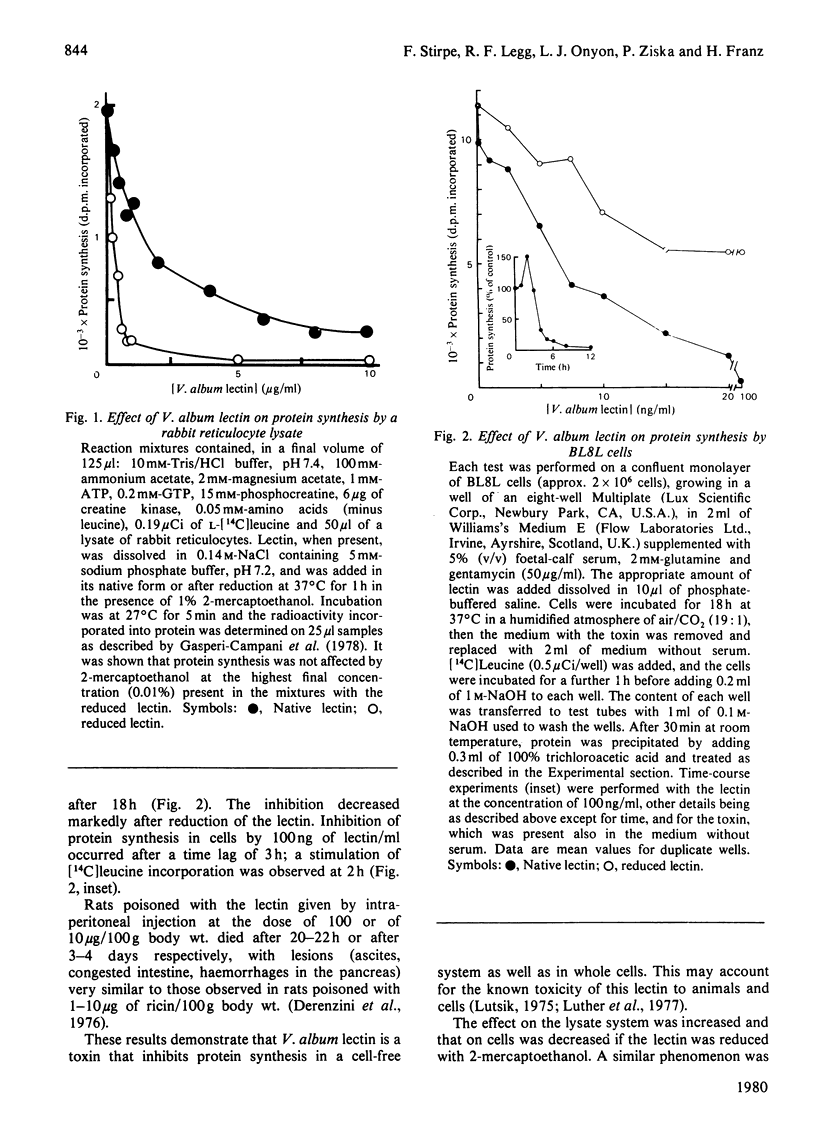
1. The haemagglutinating and toxic lectin from Viscum album L. (mistletoe) inhibits protein synthesis in a lysate of rabbit reticulocytes, with an ID50 (concentration giving 50% inhibition) of 2.6 microgram/ml. This effect is enhanced (ID50 0.21 microgram/ml) if the lectin is reduced with 2-mercaptoethanol. 2. The lectin inhibits protein synthesis also in BL8L cells in culture. Inhibition occurs after a lag time of 3 h. The ID50 is 7 ng/ml, and increases after reduction of the lectin. 3. This and the gross lesions observed in rats poisoned with V. album lectin indicate this is a toxin very similar to ricin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri L., Lorenzoni E., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by a lectin from Momordica charantia and by other haemagglutinins. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):633–635. doi: 10.1042/bj1820633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri L., Zamboni M., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by proteins from the seeds of Momordica charantia (bitter pear melon). Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):443–452. doi: 10.1042/bj1860443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz H., Haustein B., Luther P., Kuropka U., Kindt A. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von Inhaltsstoffen der Mistel (Viscum album L.). I. Affinitätschromatographie von Mistelrohextrakt an fixierten Plasmaproteinen. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(1):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Bonetti E., Stirpe F. Modeccin, the toxin of Adenia digitata. Purification, toxicity and inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):491–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1740491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judah D. J., Legg R. F., Neal G. E. Development of resistance to cytotoxicity during aflatoxin carcinogenesis. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):343–345. doi: 10.1038/265343b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Tserng K. Y., Chen C. C., Lin L. T., Tung T. C. Abrin and ricin: new anti-tumour substances. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):292–293. doi: 10.1038/227292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luther P., Franz H., Haustein B., Bergmann K. C. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von Inhaltsstoffen der Mistel (Viscum album L.). II. Wirkung von agglutinierenden und zytotoxischen Fraktionen auf Mäuse-Aszites-Tumorzellen. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(1):119–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Treatment of abrin and ricin with -mercaptoethanol opposite effects on their toxicity in mice and their ability to inhibit protein synthesis in a cell-free system. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):48–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refsnes K., Haylett T., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Modeccin--a plant toxin inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1176–1183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltvedt E. Structure and toxicity of pure ricinus agglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 21;451(2):536–548. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Bonetti E. Inhibition of protein synthesis by modeccin, the toxin of Modecca digitata. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 20;85(1):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziska P., Franz H. Affinity chromatography of human serum proteins using matrix bound lectins from Viscum album and Vicia faba. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1979;38(4):697–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziska P., Franz H., Kindt A. The lectin from viscum album L. purification by biospecific affinity chromatography. Experientia. 1978 Jan 15;34(1):123–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01921941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


