Abstract
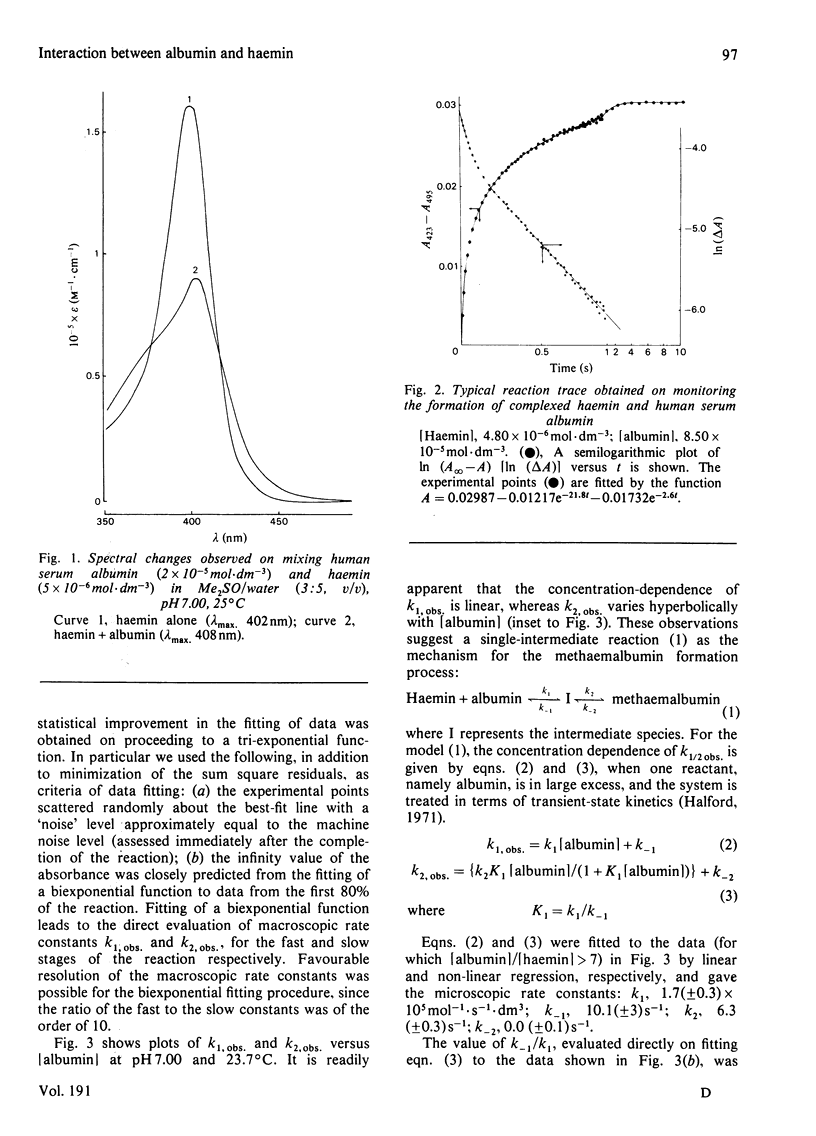
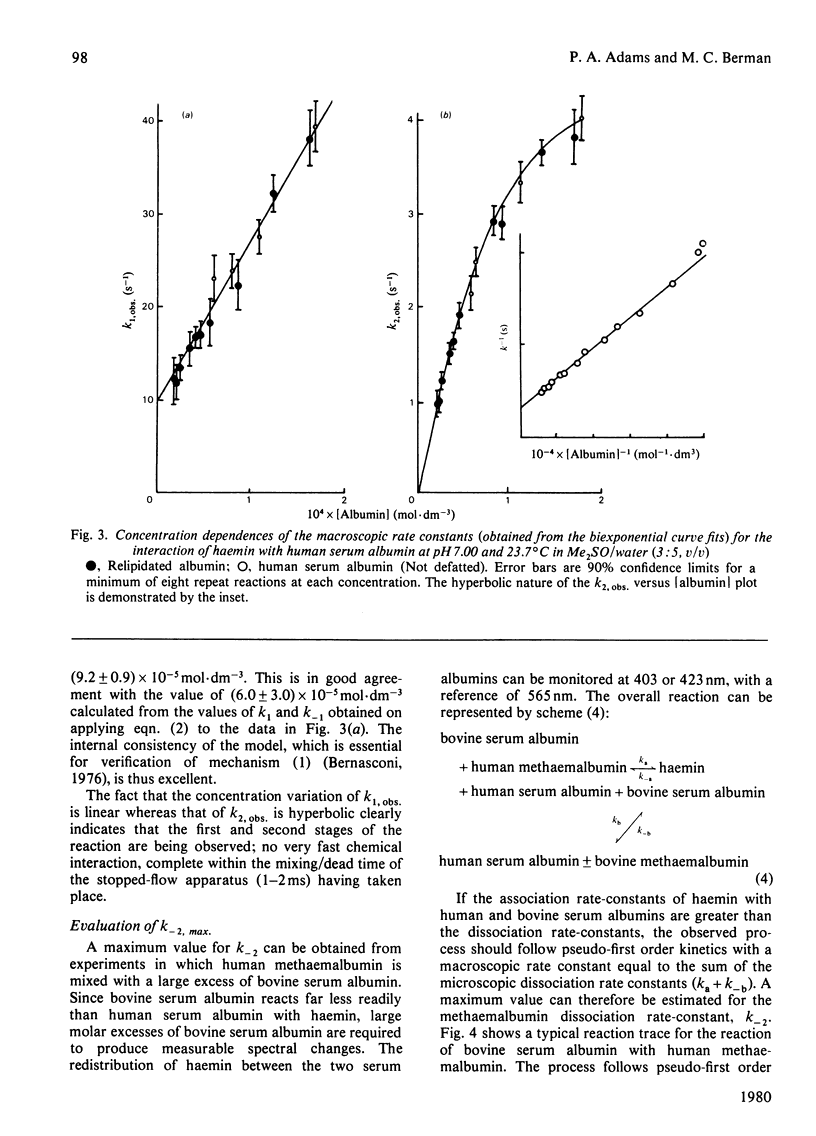
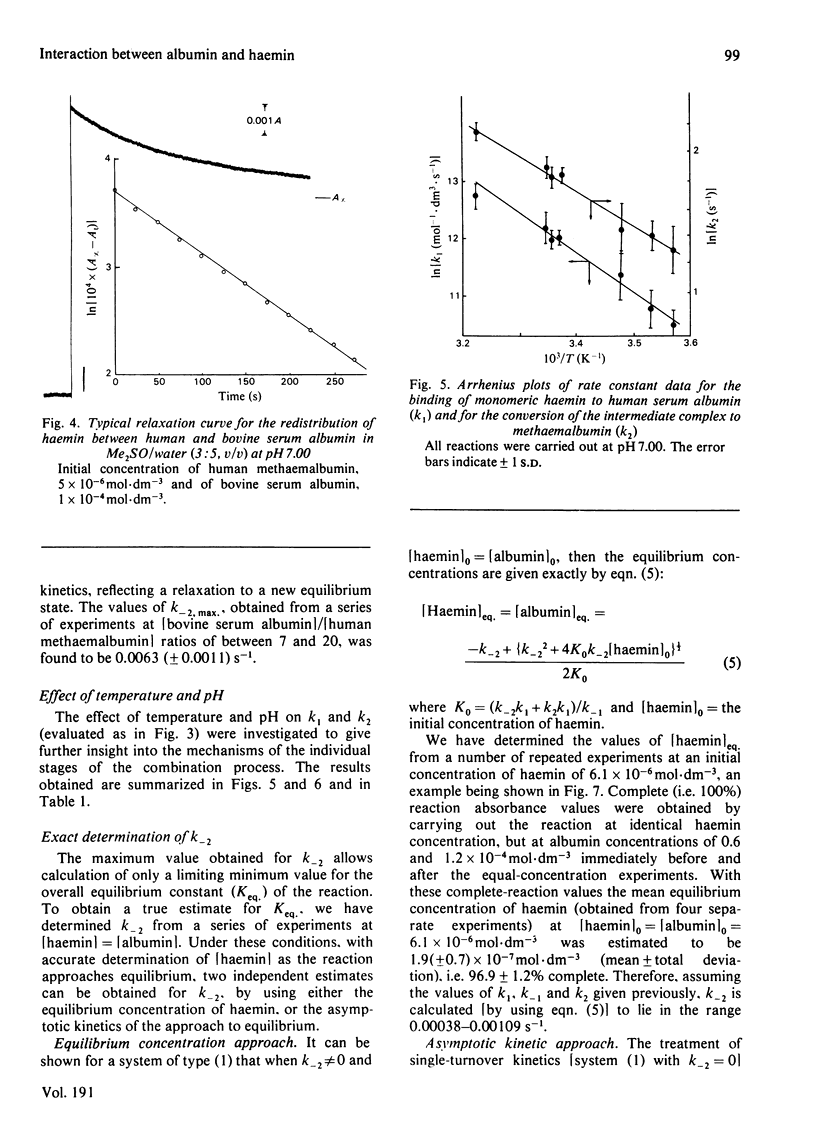
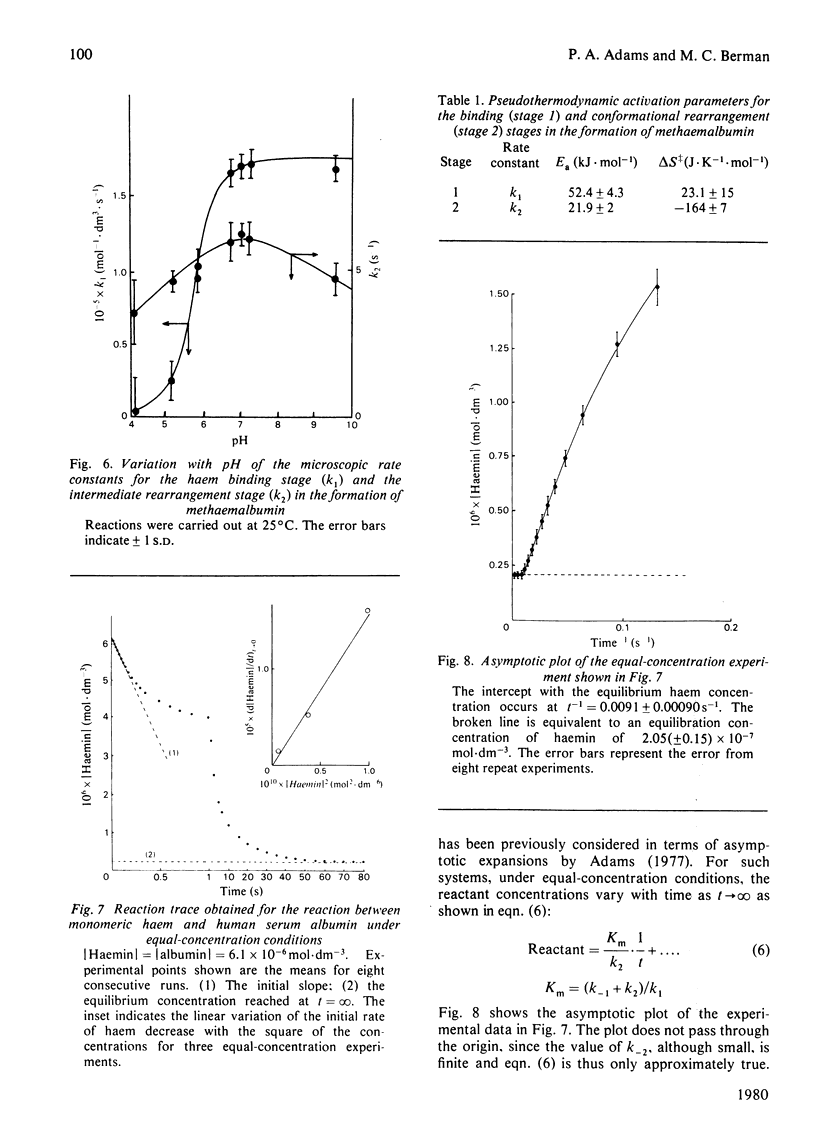
The interaction of human serum albumin with monomeric haemin has been investigated by detailed kinetic analysis in dimethyl sulphoxide/water (3:5, v/v). The results obtained under conditions of albumin saturation of haemin and under pseudo-single turnover conditions indicate that methaemalbumin is formed in a two-stage, single-intermediate process. The initial association between the haemin and human serum albumin is a chemically controlled process (k1 = 1.7 X 10(5) mol-1 . s-1 . dm3 at 24 degrees C); the variation of K1 with pH exhibited a well defined pK of 5.9. The overall equilibrium constant, calculated by using microscopic rate constants, is 1.1 (+/- 0.5) X 10(8) mol-1 at 24 degrees C. The data and conclusions are consistent with a general binding mechanism for albumin in which intermediate formation is followed by an entropy-controlled internalization of the ligand.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaven G. H., Chen S. H., d' Albis A., Gratzer W. B. A spectroscopic study of the haemin--human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 1;41(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Lantzke I. R. Solution structures of ferrihaem in some dipolar aprotic solvents and their binary aqueous mixtures. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):279–285. doi: 10.1042/bj1150279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier G. S., Pratt J. M., De Wet C. R., Tshabalala C. F. Studies on haemin in dimethyl sulphoxide/water mixtures. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj1790281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D., Stroupe S. D. Kinetics and mechanism of bilirubin binding to human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4370–4377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. An analysis of transient kinetics. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):319–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1250319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T. Porphyrin-binding proteins in serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:624–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr G. R., Pasternack R. F. The interaction of some water-soluble porphyrins and metalloporphyrins with human serum albumin. Bioinorg Chem. 1977;7(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W. The rate of access to the organic ligand-binding region of serum albumin is entropy controlled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. O., Peisach J. A model compound study of the CO-adduct of cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7495–7498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


