Abstract
Z-discs were isolated from Lethocerus (waterbug) flight muscle by removing the contractile proteins from myofibrils with a solution of high ionic strength. Sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS)/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis confirmed a previous report that major Z-disc proteins had subunit mol.wts of 200 000, 180 000, 105 000, 95 000, 42 000 and 35 000. A protein of subunit mol.wt 25 000 was found in once-washed Z-discs but was degraded or was removed by successive washes. In addition, a protein of high molecular weight (less than 300 000) was found in Z-discs. Proteins of subunit mol.wts. 42 000, 35 000 and 25 000 were individually sliced from SDS/polyacrylamide gels and eluted. Amino acid analysis showed that the 35 000-subunit-mol.wt. protein was not, as was previously suggested, tropomyosin, but was a distinct Z-disc protein rich in proline. Calculations based on the amino acid analysis showed that this protein contained substantial hydrophobic regions. Preliminary investigations into the isoelectric point and a method of isolation of the 35 000-subunit-mol.wt. Z-disc protein are described. This protein was found in slices cut from SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoretograms of whole myofibrils. The protein of 42 000 subunit mol.wt. was shown by amino acid analysis to be actin and the 25 000-subunit-mol.wt. Z-disc protein was proline-rich.
Full text
PDF


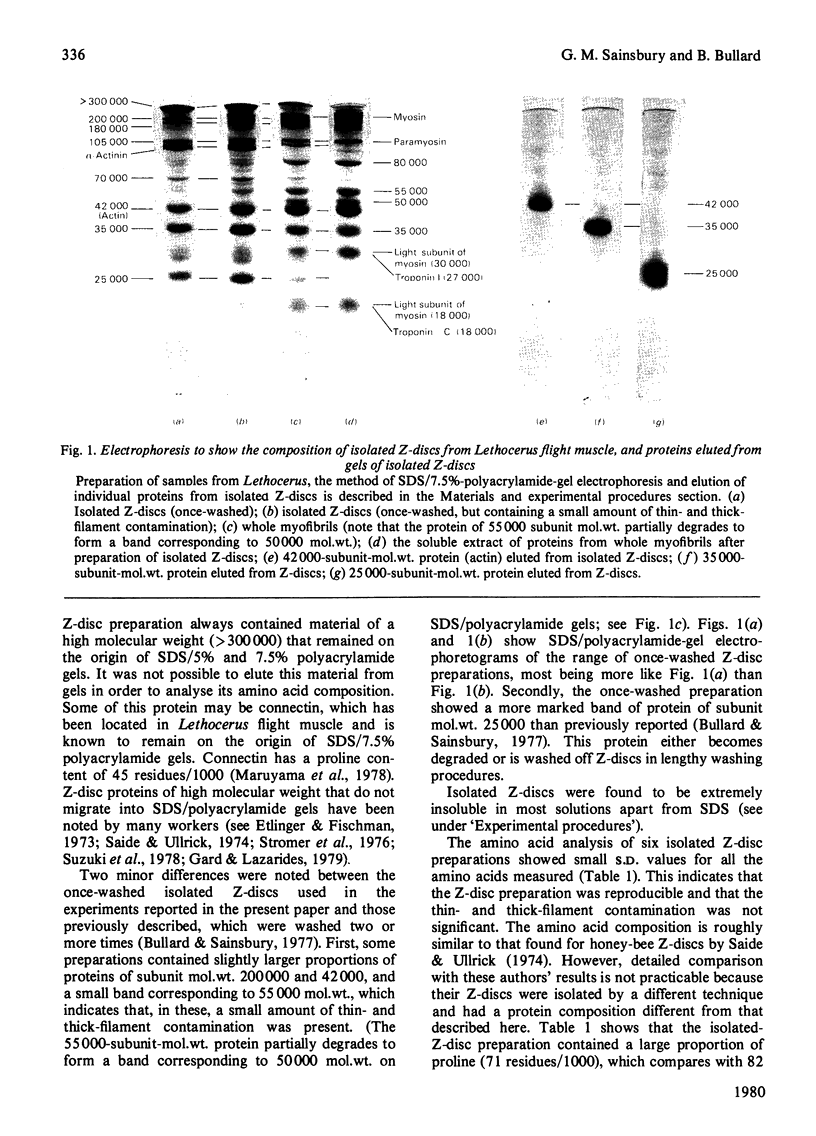

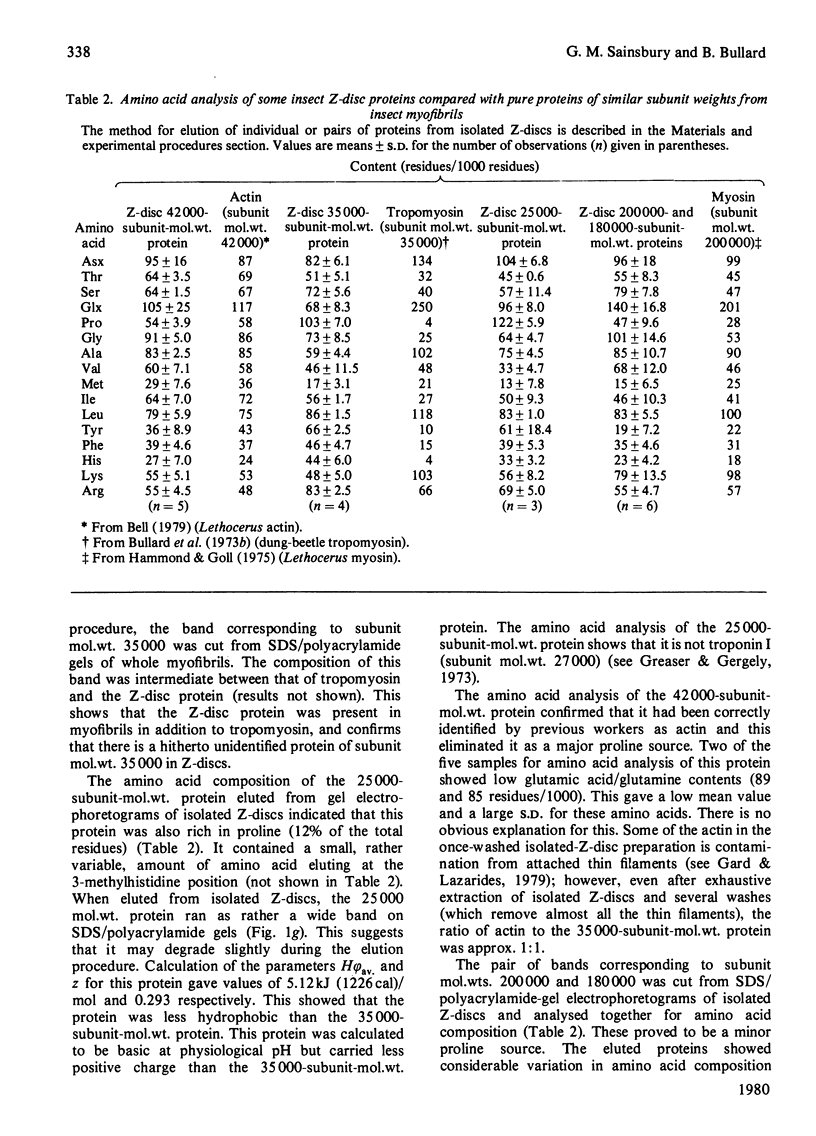

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrantes F. J. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor : different compositions evidenced by statistical analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow C. C. On the average hydrophobicity of proteins and the relation between it and protein structure. J Theor Biol. 1967 Aug;16(2):187–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Dabrowska R., Winkelman L. The contractile and regulatory proteins of insect flight muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):277–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1350277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Hammond K. S., Luke B. M. The site of paramyosin in insect flight muscle and the presence of an unidentified protein between myosin filaments and Z-line. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):417–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Luke B., Winkelman L. The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Sainsbury G. M. The proteins in the Z line of insect flight muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):399–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1610399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORSI A., PERRY S. V. Some observations on the localization of myosin, actin and tropomyosin in the rabbit myofibril. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):12–17. doi: 10.1042/bj0680012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Cohen C., Longley W. Tropomyosin: crystal structure, polymorphism and molecular interactions. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):87–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Specific fluorescent labeling of chicken myofibril Z-line proteins catalyzed by guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):336–347. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M. A., Schroeter J. P., Sass R. L. Optical diffraction of the Z lattice in canine cardiac muscle. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):818–836. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Purification and properties of the components from troponin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2125–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond K. S., Goll D. E. Purification of insect myosin and alpha-actinin. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1510189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Endo M., Ebashi S. Localization of 6S component of a alpha-actinin at Z-band. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):630–632. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A. Some aspects of the structural organization of the myofibril as revealed by antibody--staining methods. J Cell Biol. 1966 Mar;28(3):505–525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. E., Shay J. W., Biesele J. J. Urea extraction of Z bands, intercalated disks, and desmosomes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Aug;24(3):181–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. M., Goll D. E., Arakawa N., Stromer M. H. Purification and properties of alpha-actinin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):296–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saide J. D., Ullrick W. C. Purification and properties of the isolated honeybee Z-disc. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):671–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. High-resolution preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: fluorescent visualization and electrophoretic elution-concentration of protein bands. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer M. H., Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H., Rice R. V. The effect of various protein fractions on Z- and M-line reconstitution. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):167–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer M. H., Tabatabai L. B., Robson R. M., Goll D. E., Zeece M. G. Nemaline myopathy, an integrated study: selective extraction. Exp Neurol. 1976 Feb;50(2):402–421. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



