Abstract
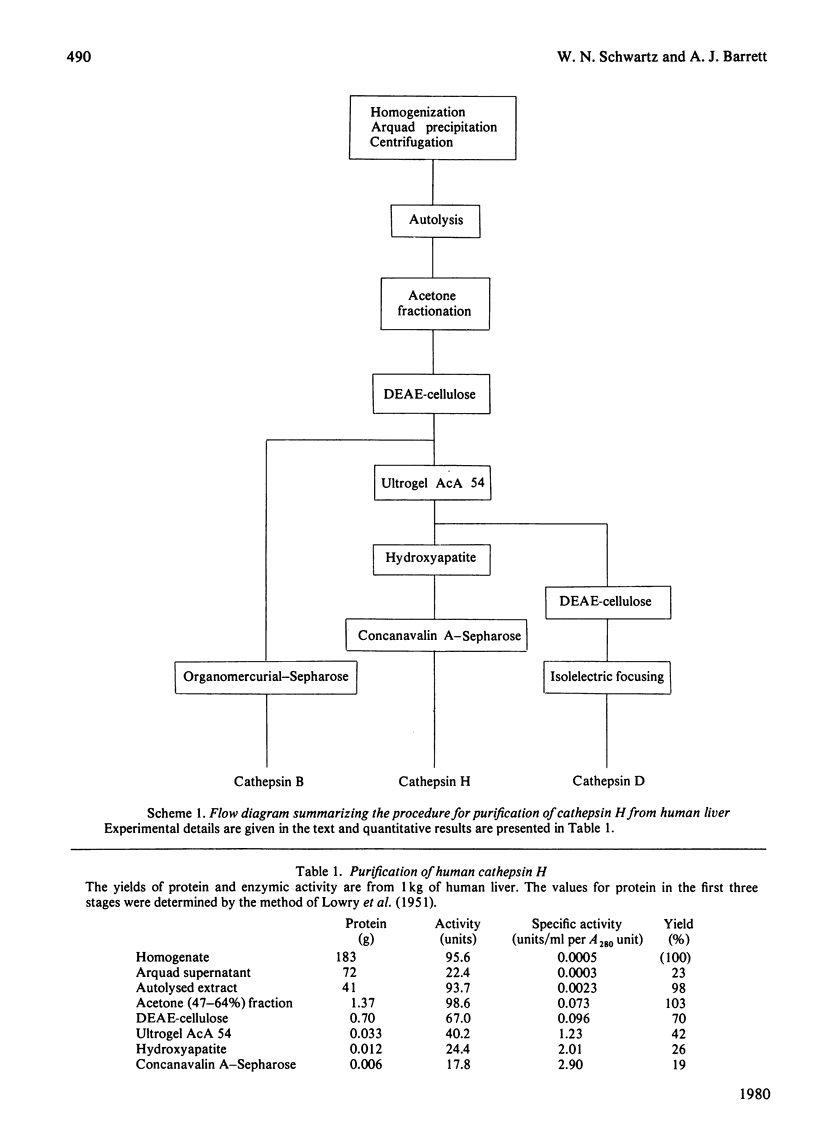
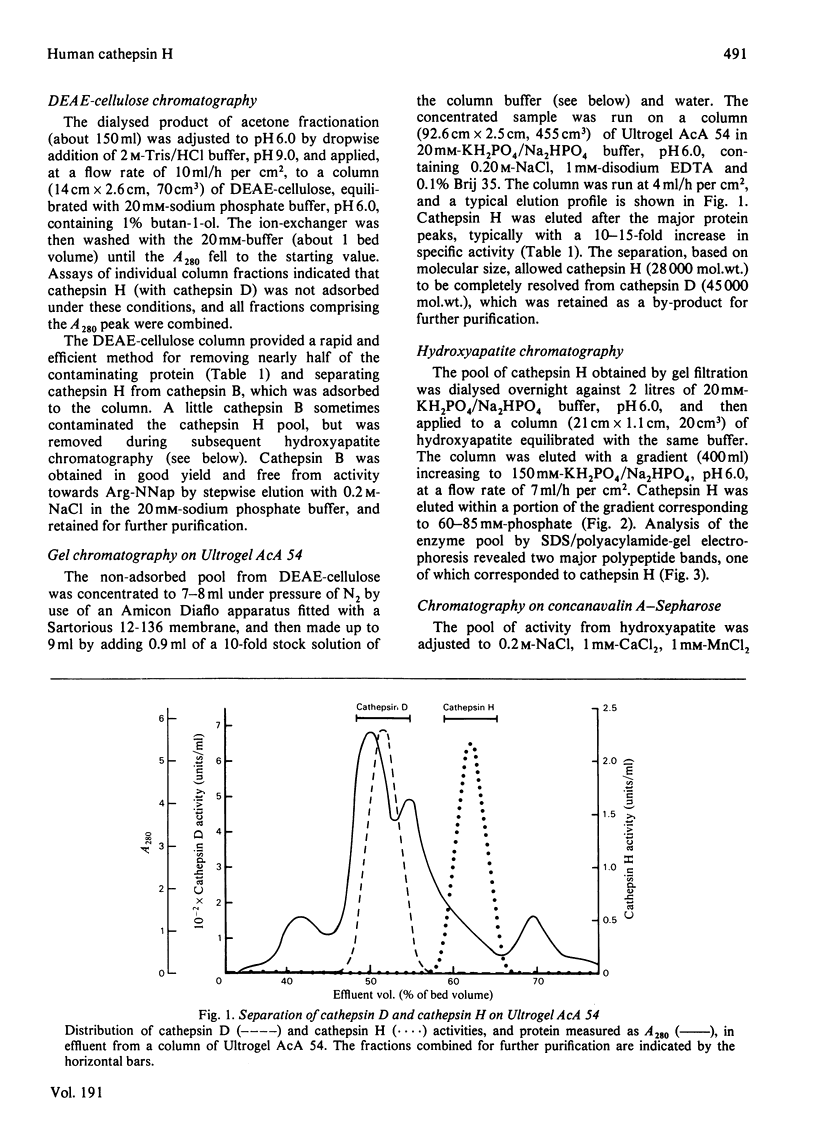
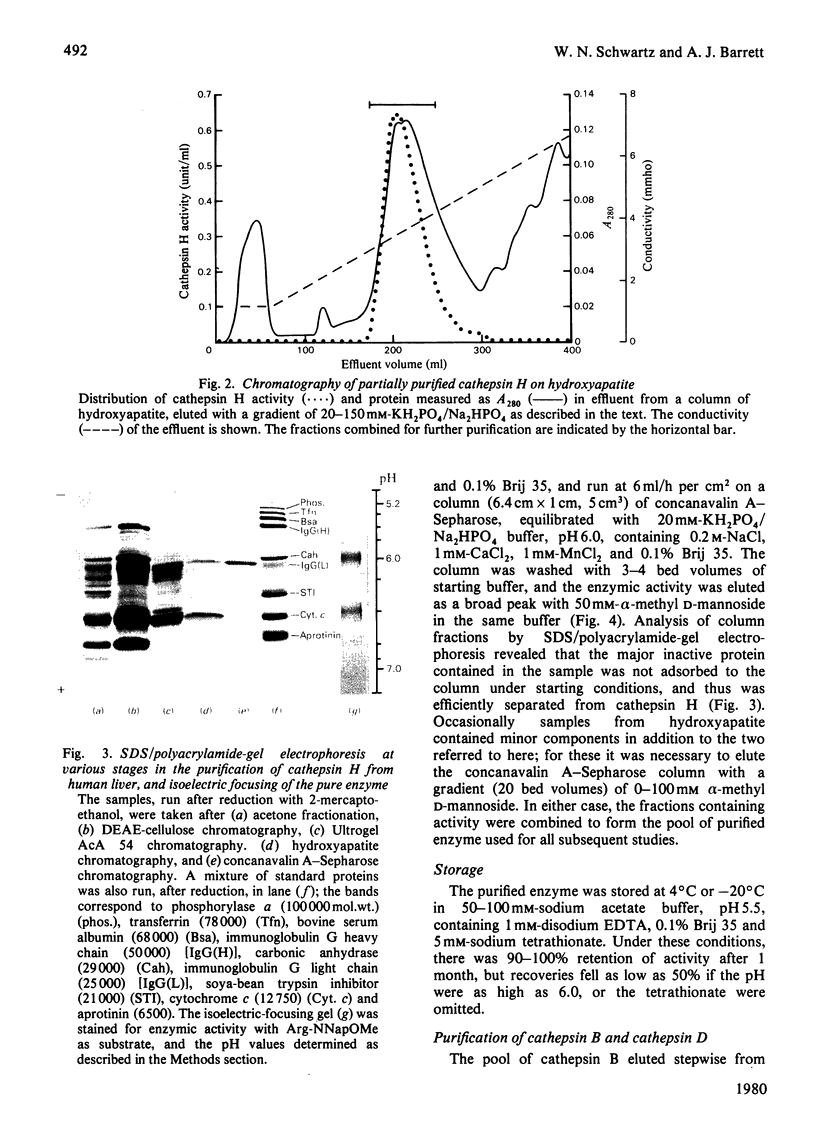
Cathepsin H was purified from human liver by a method involving autolysis and acetone fractionation, and chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, Ultrogel AcA 54, hydroxyapatite and concanavalin A-Sepharose. The procedure allowed for the simultaneous isolation of cathepsin B and cathepsin D. Cathepsin H was shown to consist of a single polypeptide chain of 28 000 mol.wt., and affinity for concanavalin A-Sepharose indicated that it was a glycoprotein. The enzyme existed in multiple isoelectric forms, the two major forms having pI values of 6.0 and 6.4; it hydrolysed azocasein (pH optimum 5.5), benzoylarginine 2-naphthylamide (Ba-Arg-NNap), leucyl 2-naphthylamide (Arg-NNap), (pH optimum 6.8). Arg-NNap and Arg-NMec, unlike Bz-Arg-NNap-, were not hydrolysed by human cathepsin B. Cathepsin H was similar to cathepsin B in being irreversibly inactivated by exposure to alkaline pH. Sensitivity to chemical inhibitors by 1 microM-leupeptin, which gave essentially complete inhibition of the other lysosomal cysteine proteinases, cathepsins B and L.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J. A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):280–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. An improved color reagent for use in Barrett's assay of Cathepsin B. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cathepsin D. Purification of isoenzymes from human and chicken liver. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1170601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Fluorimetric assays for cathepsin B and cathepsin H with methylcoumarylamide substrates. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):909–912. doi: 10.1042/bj1870909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):809–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1310809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Protein degradation in health and disease. Introduction: the classification of proteinases. Ciba Found Symp. 1979;(75):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Poole B. Fractionation of the rat liver enzymes that hydrolyze benzoyl-arginine-2-naphthylamide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 26;397(2):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. E., Barrett A. J., Hembry R. M. Preparation of antibody fragments: conditions for proteolysis compared by SDS slab-gel electrophoresis and quantitation of antibody yield. J Immunol Methods. 1978;21(3-4):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. F., Pennington R. J. Separation of cathepsin B1 and related enzymes from rat skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 25;577(2):253–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen M., Hopsu-Havu V. K. alpha-N-benzoylarginine-2-naphthylamide hydrolase (cathepsin B1 ?) from rat skin. II. Purification of the enzyme and demonstration of two inhibitors in the skin. Acta Chem Scand B. 1975;29(7):772–780. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.29b-0772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P., Broghammer U. Intrazellulärer Proteinabbau. VII. Kathepsin L und H: Zwei neue Proteinasen aus Rattenleberlysosomen. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1976;35(3-4):285–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P. Cathepsin L. A new proteinase from rat-liver lysosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P., Hanson H. Cathepsin H: an endoaminopeptidase from rat liver lysosomes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(2):185–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. G. Human cathepsin B. Application of the substrate N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-arginyl-L-arginine 2-naphthylamide to a study of the inhibition by leupeptin. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):447–453. doi: 10.1042/bj1890447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks N., Datta R. K., Lajtha A. Partial resolution of brain arylamidases and aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2882–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Ellis S. On the substrate specificity of cathepsins B1 and B2 including a new fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin B1. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1269–1276. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Kalnitsky G. Separation of a new alpha-N-benzoylarginine-beta-naphthylamide hydrolase from cathepsin B1. Purification, characterization, and properties of both enzymes from rabbit lung. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4319–4326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Kalnitsky G. alpha-N-benzoylarginine-beta-naphthylamide hydrolase, an aminoendopeptidase from rabbit lung. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):369–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén B. Studies on the histochemical "leucine aminopeptidase" reaction. VI. The selective demonstration of cathepsin B activity by means of the naphythylamide reaction. Histochemie. 1968;15(2):150–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00306365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Hansén L., Sjösten A. Staining of proteins after isoelectric focusing in gels by new procedures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Green G. D., Shaw E. A comparison of the behavior of chymotrypsin and cathepsin B towards peptidyl diazomethyl ketones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 28;89(4):1354–1360. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]