Abstract
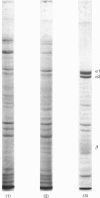
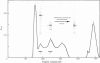
Purification of the (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase has been improved 2-fold the respect to both purity and yield over the previous method [Peterson, Ewing, Hootman & Conte (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253, 4762-4770] by using Lubrol WX and non-denaturing concentrations of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS). The enzyme was purified 200-fold over the homogenate. The preparation had a specific activity of about 600 mumol of Pi/h per mg of protein, and was about 60% pure according to quantification of Coomassie Blue-stained SDS/polyacrylamide gels. The yield of purified enzyme was about 10 mg of protein per 100g of dry brine-shrimp (Artemia salina) cysts. The method is highly suitable for purification either on a small scale (10-25g of dry cysts) or on a large scale (900g of dry cysts) and methods are described for both. The large (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase subunit (alpha-subunit) was isolated in pure form by SDS-gel filtration on Bio-Gel A 1.5m. The small subunit (beta-subunit) was eluted with other contaminating proteins on the Bio-Gel column, but was isolated in pure form by extraction from SDS/polyacrylamide gels. The amino acid and carbohydrate compositions of both subunits are reported. The alpha-subunit contained 5.2% carbohydrate by weight, and the beta-subunit 9.2%. Sialic acid was absent from both subunits.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell M. V., Sargent J. R. The partial purification of sodium-plus-potassium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from the gills of Anguilla anguilla and its inhibition by orthovanadate. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):431–438. doi: 10.1042/bj1790431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill L., Peterson G. L., Hokin L. E. The large subunit of (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus is a glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):488–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. Purification and properties of the enzyme from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Aug;163(2):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90537-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:731–752. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings D. F., Reynolds J. A. Molecular weight of (Na+,K+)ATPase from shark rectal gland. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):817–821. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E., Dahl J. L., Deupree J. D., Dioxon J. F., Hackney J. F., Perdue J. F. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. X. Purification of the enzyme from the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2593–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B. E., Wagner H., Jr, smith T. W. Sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of the nasal salt gland of the duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Purification, characterization, and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of the phosphorylating polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4365–4371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Properties of the two polypeptides of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7642–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Purification of the sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane L. K., Copenhaver J. H., Jr, Lindenmayer G. E., Schwartz A. Purification and characterization of and (3H)ouabain binding to the transport adenosine triphosphatase from outer medulla of canine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7197–7200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P. J., Hokin L. E. Microheterogeneity of the glycoprotein subunit of the (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91820-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S. Inactivation by detergents of the proline transport system in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli and its reactivation by bovine serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone J. R., Hackney J. F., Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Molecular properties of purified (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosine triphosphatases and their subunits from the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias and the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4178–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplified method for analysis of inorganic phosphate in the presence of interfering substances. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jan;84(1):164–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90495-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L., Ewing R. D., Conte F. P. Membrane differentiation and de Nova synthesis of the (Na+ + k+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase during development of Artemia salina nauplii. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L., Ewing R. D., Hootman S. R., Conte F. P. Large scale partial purification and molecular and kinetic properties of the (Na + K)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from Artemia salina nauplii. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4762–4770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J., Schwartz A. Improved purification and partial characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase from cardiac muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 20;401(2):184–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Neuberger M. R., Liu T. Y. Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Purification from brain of an intrinsic membrane protein fraction enriched in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 20;508(3):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation, and difference in affinity for strophanthidin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6060–6067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. H., MacRae T. H., Wahba A. J. The use of Artemia salina for developmental studies: preparation of embryos, tRNA, ribosomes and initiation factor 2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:298–311. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]