Abstract
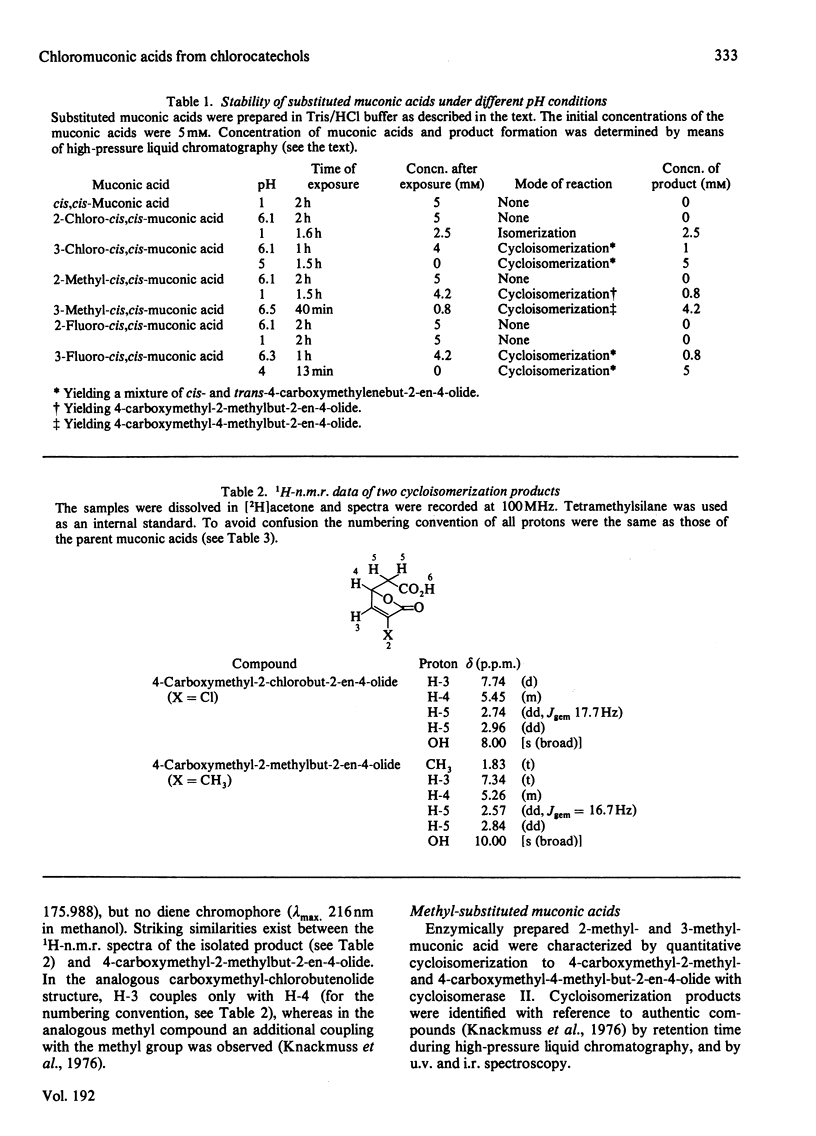
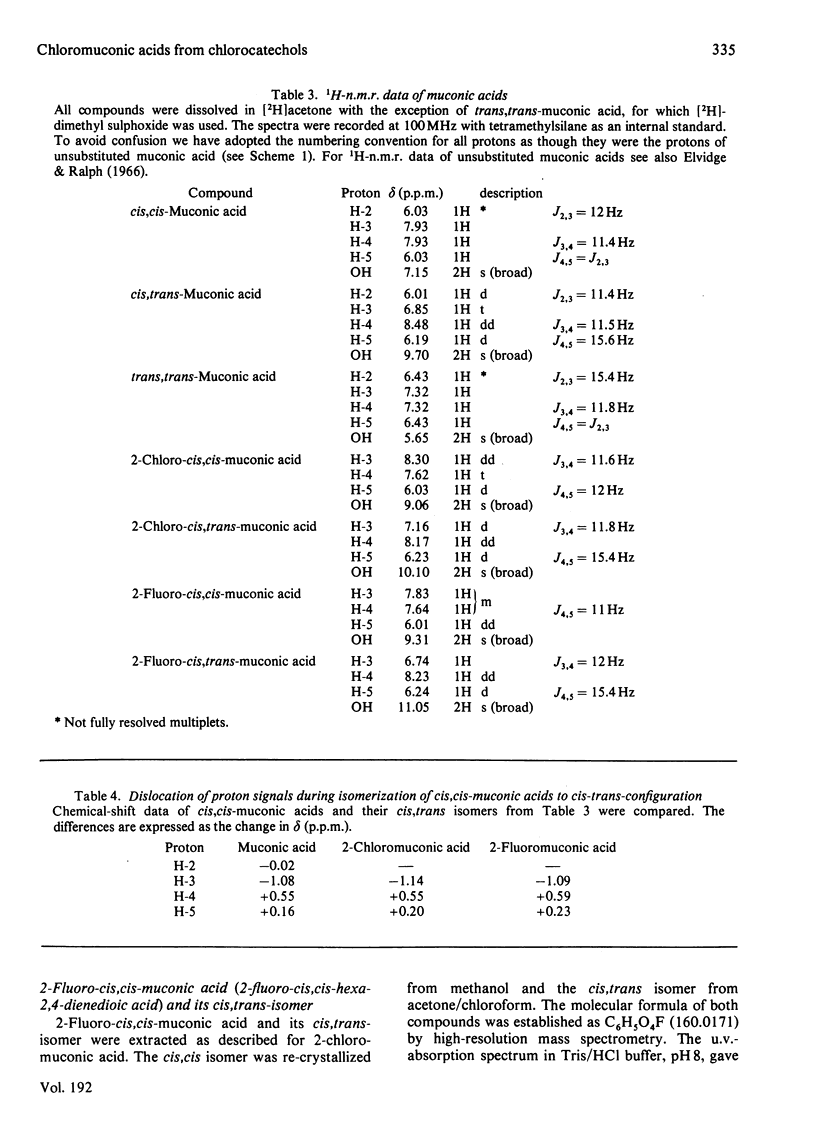
Substituted muconic acids were prepared from the corresponding catechols by pyrocatechase II from Pseudomonas sp. B13. The stabilities of substituted muconic acids were compared under different pH conditions. 3-Substituted cis, cis-muconic acids cycloisomerized readily in slightly acidic solutions, whereas 2-chloro- and 2-fluoro-cis,cis-muconic acids were stable under these conditions and could be isolated as crystalline compounds. They were isomerized to the cis, trans-form in highly acidic solution (pH 1), particularly when heated to 80 degrees C. Cycloisomerization of 2-chloro-cis,cis-muconic acid in 75% (v/v) H2SO4 yields 4-carboxymethyl-2-chloro-but-2-en-4-olide (4-chloro-2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-3H-furan-2-ylacetic acid). THe cis,cis-configuration of 2-chloromuconic acid was certified by 1H n.m.r. spectroscopy and by enzymic cycloisomerization. Although the cis,cis-configuration of 2-fluoromuconic acid was confirmed by corresponding spectroscopic data, it was not cycloisomerized by crude extracts or cycloisomerase II preparations from Pseudomonas sp. B13.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate-grown pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):73–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1740073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesser K. H., Schmidt E., Knackmuss H. J. Adaptation of Alcaligenes eutrophus B9 and Pseudomonas sp. B13 to 2-Fluorobenzoate as Growth Substrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.68-73.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Moss P., Fernley H. N. Bacterial metabolism of 4-chlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1220509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Ring-fission, lactonizing and delactonizing enzymes. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):533–542. doi: 10.1042/bj1220533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B., Blakley E. R. The metabolism of p-fluorobenzoic acid by a Pseudomonas sp. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Aug;17(8):1015–1023. doi: 10.1139/m71-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke D., Fritsche W. Mikrobielle Dechlorierung von Pesticiden und anderen Umweltchemikalien. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1978;18(5):365–382. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630180509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knackmuss H. J., Hellwig M. Utilization and cooxidation of chlorinated phenols by Pseudomonas sp. B 13. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00689343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Enzymes of the catechol pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3795–3799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. The mechanism of formation of beta-ketoadipic acid by bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):821–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Conversion of chlorinated muconic acids into maleoylacetic acid. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):339–347. doi: 10.1042/bj1920339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A., Hellwig M., Dorn E., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Critical Reactions in Fluorobenzoic Acid Degradation by Pseudomonas sp. B13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):58–67. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.58-67.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


