Abstract
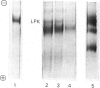
Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of immunoprecipitates of liver cytosol with anti-(L-type pyruvate kinase) serum revealed proteins of mol.wt. 56 000 and 42 000 in addition to the heavy and light chains. The ratio of the 56 000 mol.wt. to the 42 000 mol.wt. protein increased under dietary conditions that resulted in an increase in the apparent specific activity of hepatic pyruvate kinase. The 42 000 mol.wt. protein was removed from immunoprecipitates if the liver cytosol was partially purified by pH precipitation and (NH4)2SO4 fractionation before addition of the antiserum. This technique may be used to analyse the formation of pure L-type pyruvate kinase in liver. By using H14CO3-labelling, the t1/2 of L-type pyruvate kinase was estimated as 75 +/- 1.7 h in post-weaned high-carbohydrate-diet-fed rats. Before weaning there was little immunoreactive pyruvate kinase in rat liver cytosol. Induction began between 6 and 24 h after weaning and reached a maximum value 120 h after weaning. When clearly enhanced total pyruvate kinase activity was first observed at 24 h post-weaning, the apparent specific activity of hepatic pyruvate kinase was considerably lower than the specific activity of the pure isolated enzyme. When the induction of L-type pyruvate kinase was monitored by the incorporation of L-[4,5-3H]leucine, the maximum rate of synthesis occurred 24--48 h after weaning. After this period synthesis declined, indicating a relatively slow turnover of the enzyme once the enzyme concentration was established in the liver.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström G., Ekman P., Dahlqvist U., Humble E., Engström L. Subtilisin-catalyzed removal of phosphorylated site of pig liver pyruvate kinase without inactivation of the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström G., Ekman P., Humble E., Engström L. Proteolytic modification of pig and rat liver pyruvate kinase type L including phosphorylatable site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90580-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. B., Cimbala M. A., Foster J. L., Morgan R. A. Hepatic pyruvate kinase. Regulation by glucagon, cyclic adenosine 3'-5'-monophosphate, and insulin in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3756–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Cottam G. L. Turnover of liver pyruvate kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):426–433. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus T. H., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Modulation of the phosphorylation state of rat liver pyruvate kinase by allosteric effectors and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7855–7864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway G. A., Jr, Weber G. Effects of hormonal and nutritional changes on rates of synthesis and degradation of hepatic phosphofructokinase isozymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway G. A., Leung G. L., Thrasher J. R., Cooper M. D. Turnover of hepatic phosphofructokinase in normal and diabetic rats. Role of insulin and peptide stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7460–7463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekman P., Dahlqvist U., Humble E., Engström L. Comparative kinetic studies on the L-type pyruvate kinase from rat liver and the enzyme phosphorylated by cyclic 3', 5'-AMP-stimulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 8;429(2):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström L. The regulation of liver pyruvate kinase by phosphorylation--dephosphorylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;13:28–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feliú J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Hormonal control of pyruvate kinase activity and of gluconeogenesis in isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felíu J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Regulation in vitro and in vivo of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent inactivation of rat-liver pyruvate kinase type L. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. L., Blair J. B. Acute hormonal control of pyruvate kinase and lactate formation in the isolated rat hepatocyte. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Aug;189(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. R., McCully V., Cottam G. L. Evidence for a proteolytic modification of liver pyruvate kinase in fasted rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jul;195(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90357-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
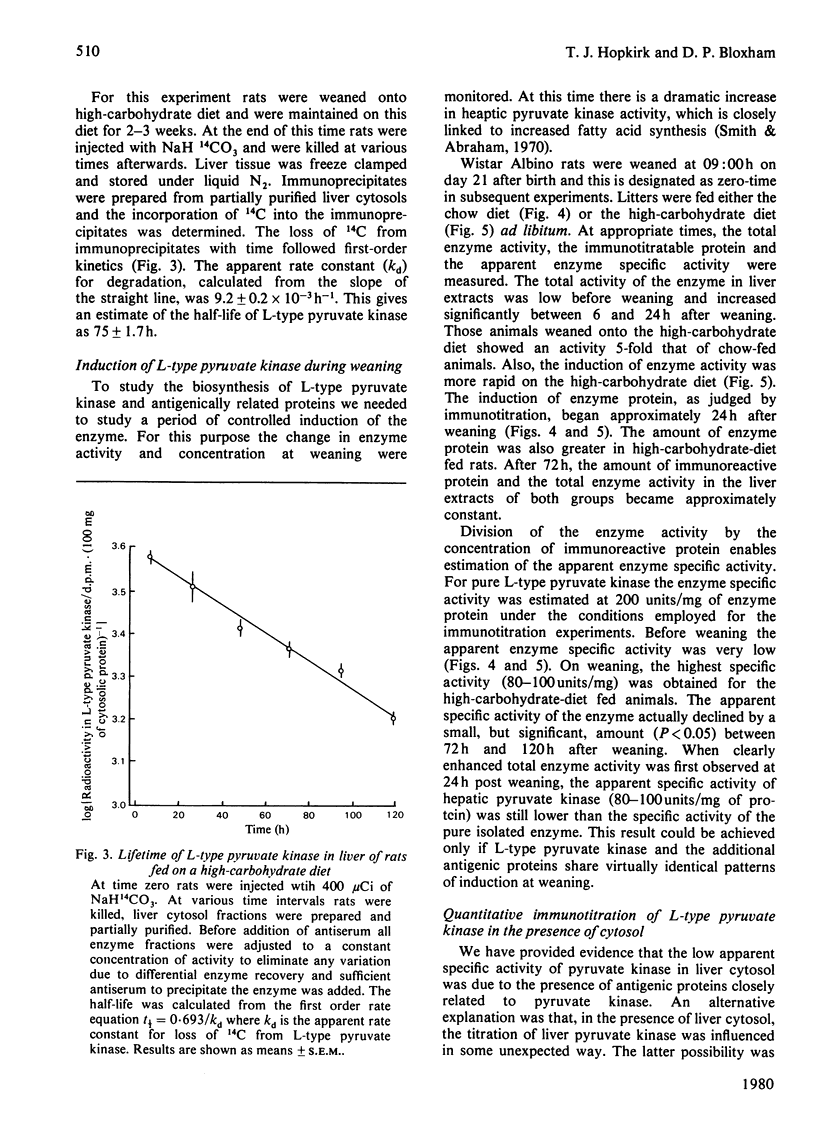
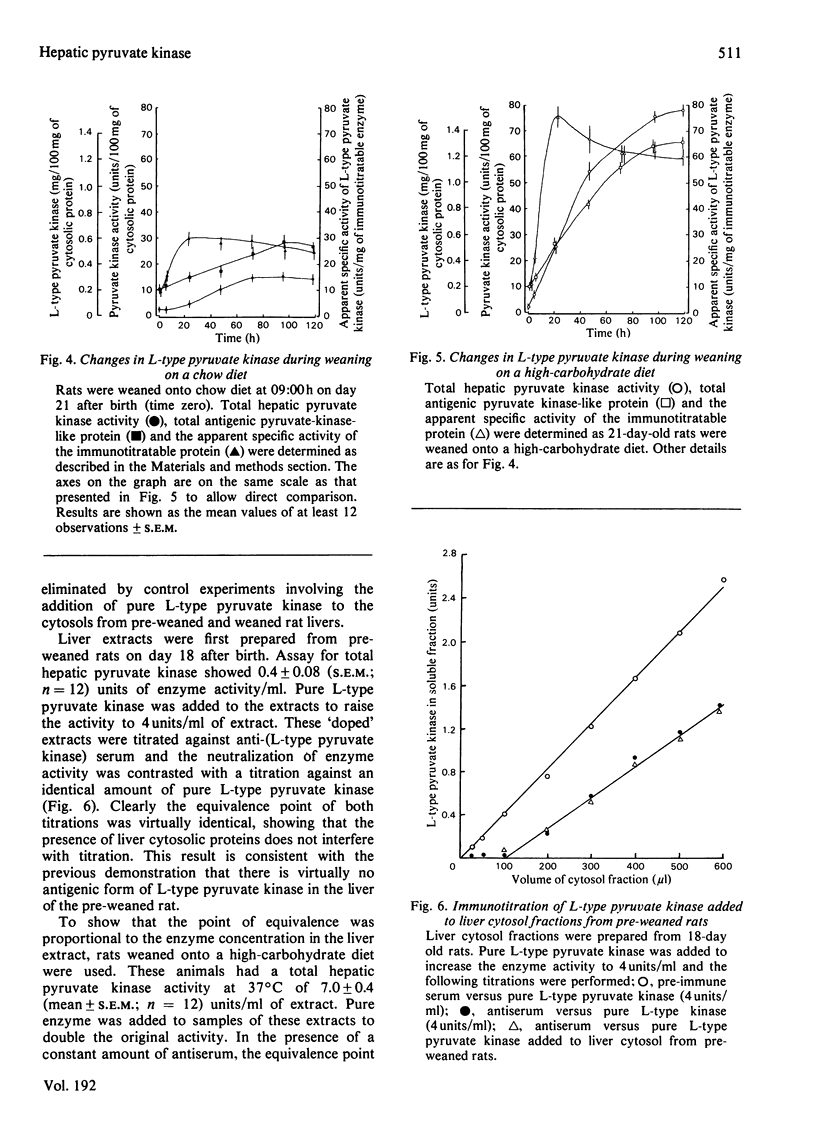
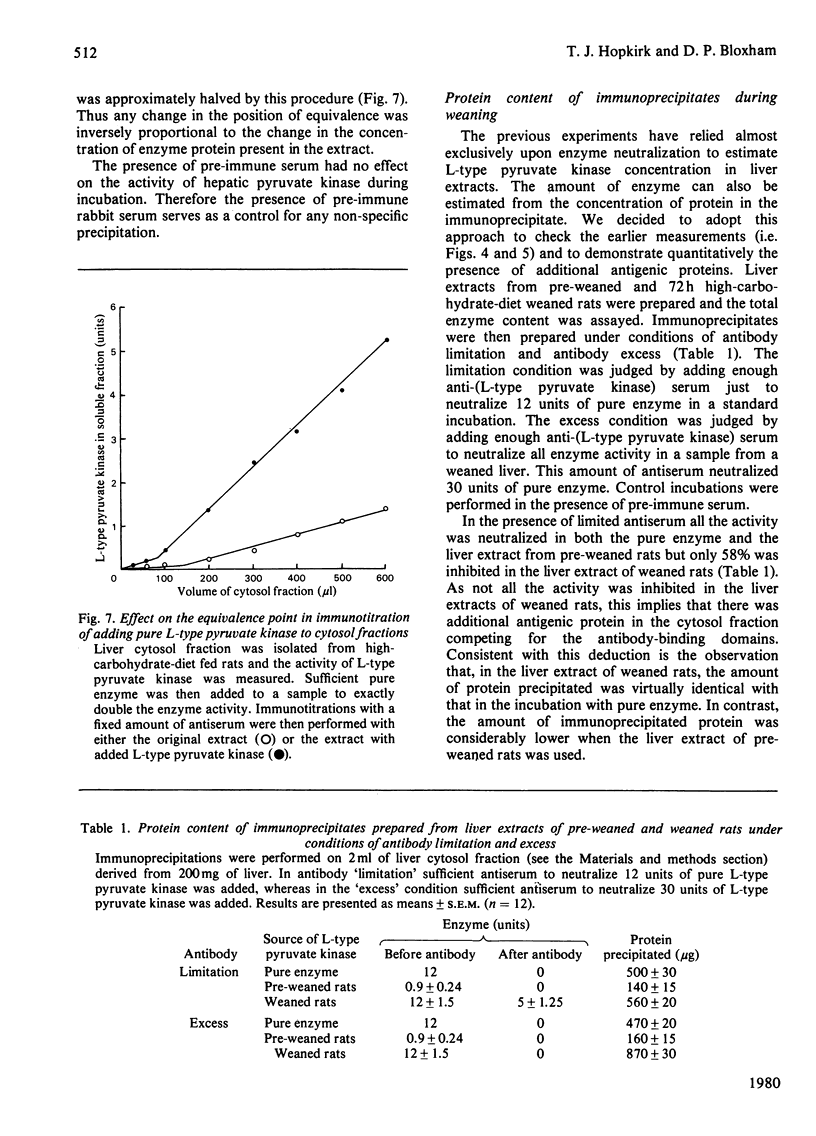
- Hopkirk T. J., Bloxham D. P. Studies on the biosynthesis of hepatic pyruvate kinase and its correlation with enhanced hepatic lipogenesis in meal-trained rats. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):383–397. doi: 10.1042/bj1820383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip M. M., Ip C., Tepperman H. M., Tepperman J. Effect of adaptation to meal-feeding on insulin, glucagon and the cyclic nucleotide-protein kinase system in rats. J Nutr. 1977 May;107(5):746–757. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.5.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl E. A., Cottam G. L. Alteration in liver pyruvate kinase protein and catalytic acitivity upon starvation and refeeding. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):671–682. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl E. A., Cottam G. L. Kinetic studies with L-type pyruvate kinase from rats either fed a high carbohydrate, low protein diet or starved. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 15;484(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laube H., Wojcikowski C., Schatz H., Pfeiffer E. F. The effect of high maltose and sucrose feeding on glucose tolerance. Horm Metab Res. 1978 May;10(3):192–195. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. S., Harris R. A. Studies on the relationship between glycolysis, lipogenesis, gluconeogenesis, and pyruvate kinase activity of rat and chicken hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Goodman M. N., Toews C. J. Effect of glucagon: insulin ratios on hepatic metabolism. Diabetes. 1974 Sep;23(9):725–731. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.9.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. P., Claus T. H., Pilkis S. J. Stimulation of glucagon of in vivo phosphorylation of rat hepatic pyruvate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):656–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Jiménez de Asúa L., Carminatti H. Some kinetic properties of liver pyruvate kinase (type L). II. Effect of pH on its allosteric behavior. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3142–3147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert W., Henning H. V., Schoner W., L'age M. Effects of cortisol on the levels of metabolites and enzymes controlling glucose production from pyruvate. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1968;6:153–187. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(68)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Abraham S. Fatty acid synthesis in developing mouse liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawa-Katayama Y., Morita N. Effect of a high fructose diet on lipogenic enzyme activities of meal-fed rats. J Nutr. 1977 Apr;107(4):534–538. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick R. W., Ip M. M. Measurement of protein turnover in rat liver with (14C)carbonate. Protein turnover during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6836–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taunton O. D., Stifel F. B., Greene H. L., Herman R. H. Rapid reciprocal changes in rat hepatic glycolytic enzyme and fructose diphosphatase activities following insulin and glucagon injection. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7228–7239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. B., Bailey E., Bartley W. Changes in hepatic lipigenesis during development of the rat. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):717–722. doi: 10.1042/bj1050717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses. Diabetes. 1971 Dec;20(12):834–838. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.12.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel T. J., Kruijt J. K., Van den Berg G. B., Koster J. F. Difference in the effect of glucagon and starvation upon L-type pyruvate kinase from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):553–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Walker D. G. Adaptive behaviour of some enzymes involved in glucose utilization and formation in rat liver during the weaning period. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):331–338. doi: 10.1042/bj1060331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Walker D. G. Changes in activity of some enzymes involved in glucose utilization and formation in developing rat liver. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1060321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Singhal R. L., Stamm N. B., Lea M. A., Fisher E. A. Synchronous behavior pattern of key glycolytic enzymes: glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:59–81. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalitis J. G., Pitot H. C. The synthesis and degradation of rat liver and kidney fructose bisphosphatase in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 May;194(2):620–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berkel T. J., Kruijt J. K., Koster J. F. Hormone-induced changes in pyruvate kinase. Effects of glucagon and starvation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]