Abstract
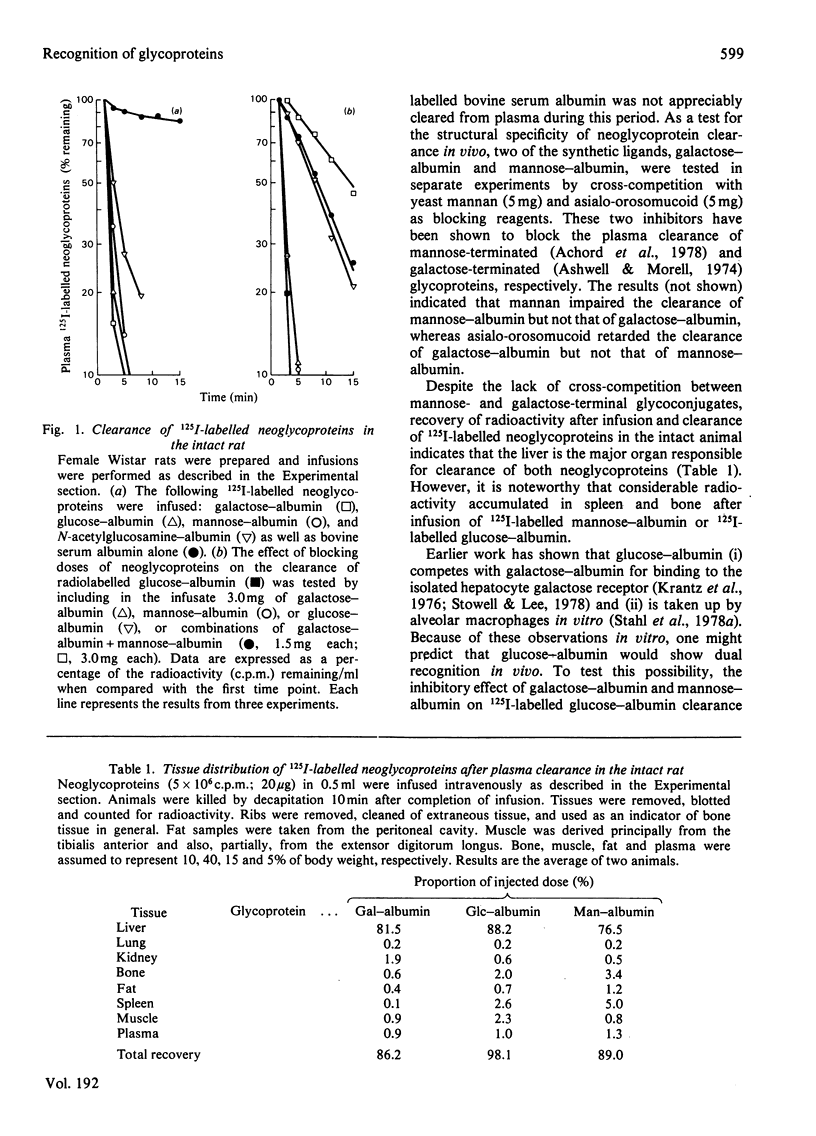
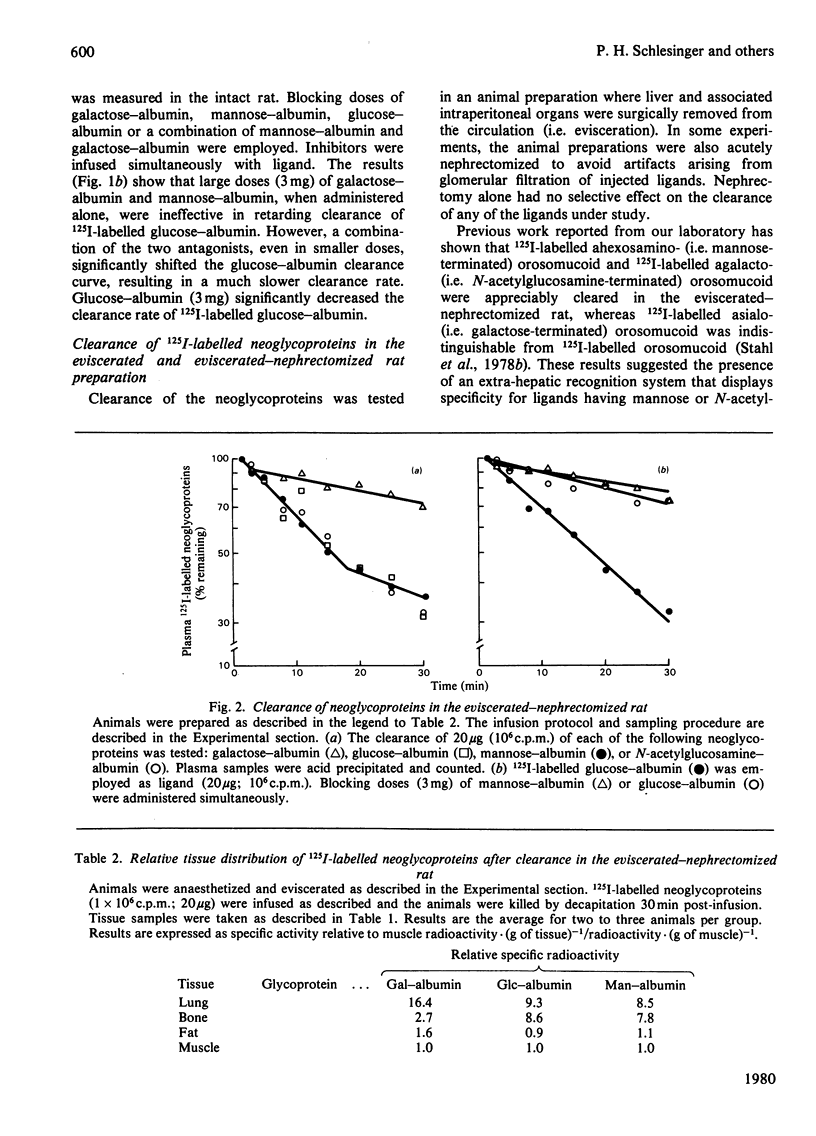
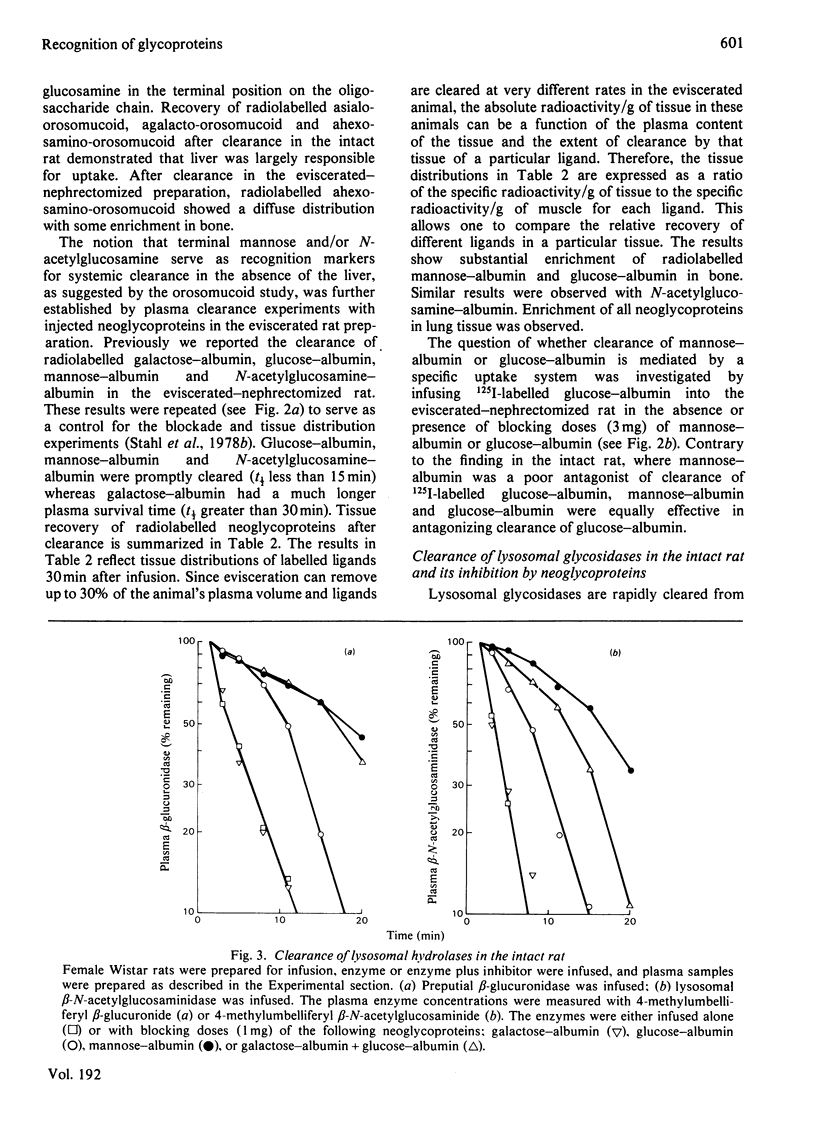
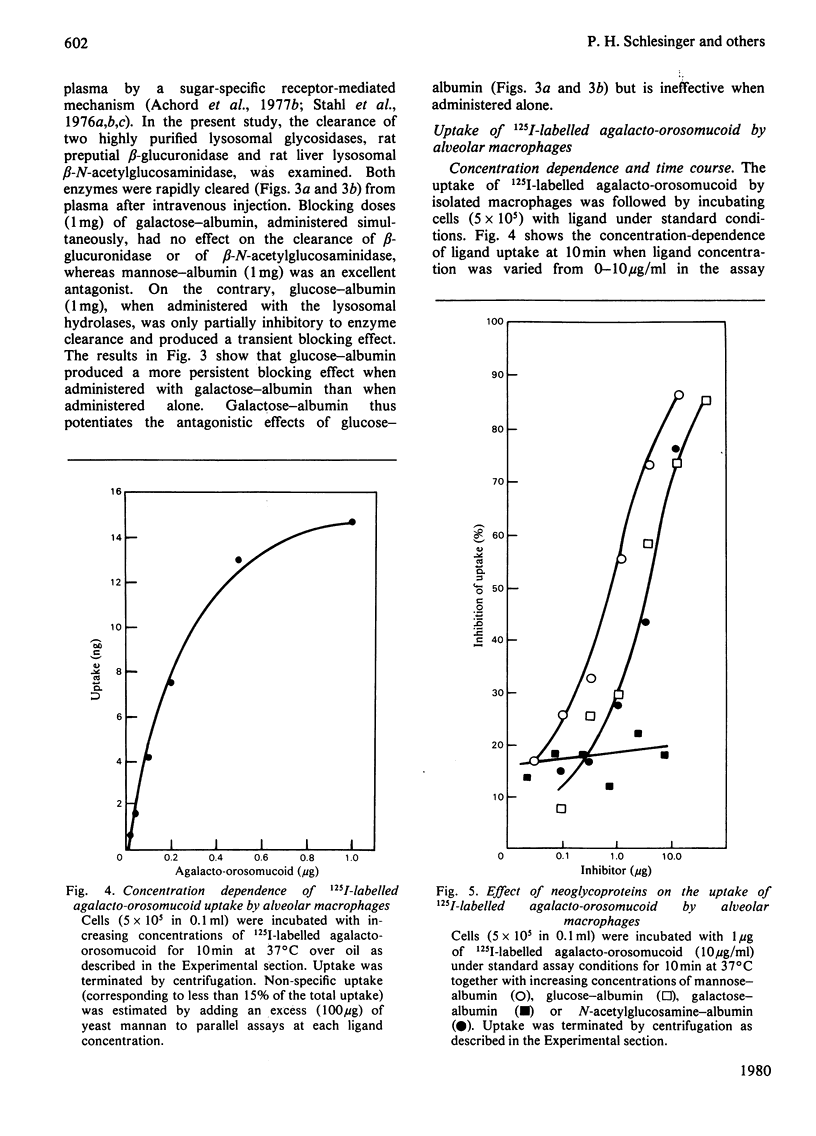
The mannose- and N-acetylglucosamine-specific pathway for the clearance of mammalian glycoproteins has been characterized by using 125I-labelled neoglycoproteins, glycosidase-treated orosomucoid and lysosomal glycosidases (beta-glucuronidase and beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase) as probes. There are two components to this pathway in vivo; one liver-dependent and the other extrahepatic or liver-independent. Cells that mediate clearance by the latter component of the pathway are present in spleen, bone and in elements of the reticuloendothelial system, but not in the kidney. Glycoproteins that possess terminal mannose, glucose or N-acetylglucosamine residues, including various lysosomal enzymes, are rapidly cleared from plasma via this pathway. Glucose-terminated glycoproteins are recognized by two pathways in the intact animal; the hepatic galactose-specific pathway and the mannose/N-acetylglycosamine-specific pathway, which is present in liver and in peripheral tissues. Following removal of the liver by surgical evisceration, glucose-terminated glycoproteins are cleared whereas glycoproteins bearing galactose are not cleared. Uptake of 125I-labelled neoglycoproteins and agalacto-orosomucoid by isolated alveolar macrophages closely mimics clearance in vivo by the mannose/N-acetylglucosamine pathway. Neoglycoproteins terminated by mannose, glucose or N-acetylglucosamine all compete with 125I-labelled agalacto-orosomucoid for uptake by receptor-mediated pinocytosis. The extent of substitution of the neoglycoproteins is a critical determinant of their inhibitory potency. It is proposed that mononuclear phagocytes are in important component of the clearance pathway in vivo. The mannose/N-acetylglucosamine pathway may be important in the regulation of extracellular levels of various glycosylated macromolecules, including lysosomal hydrolases.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achord D. T., Brot F. E., Bell C. E., Sly W. S. Human beta-glucuronidase: in vivo clearance and in vitro uptake by a glycoprotein recognition system on reticuloendothelial cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achord D. T., Brot F. E., Sly W. S. Inhibition of the rat clearance system for agalacto-orosomucoid by yeast mannans and by mannose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):409–415. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achord D., Brot F., Gonzalez-Noriega A., Sly W., Stahl P. Human beta-glucuronidase. II. Fate of infused human placental beta-glucuronidase in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1977 Jul;11(7):816–822. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197707000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baynes J. W., Wold F. Effect of glycosylation on the in vivo circulating half-life of ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6016–6024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Gregory W., Fletcher P., Kornfeld S. Vertebrate lectins, Comparison of properties of beta-galactoside-binding lectins from tissues of calf and chicken. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):528–537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. L., Henderson L. A., Thorpe S. R., Baynes J. W. The effect of alpha-mannose-terminal oligosaccharides on the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. Rapid uptake and catabolism of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease B by nonparenchymal cells of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):418–428. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno M., Ohara H., Arakawa Y. Beta-glucuronidase of rat preputial gland. Crystallization, properties, carbohydrate composition, and subunits. J Biochem. 1975 Feb;77(2):427–438. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz M. J., Holtzman N. A., Stowell C. P., Lee Y. C. Attachment of thioglycosides to proteins: enhancement of liver membrane binding. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3963–3968. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. C., Stowell C. P., Krantz M. J. 2-Imino-2-methoxyethyl 1-thioglycosides: new reagents for attaching sugars to proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3956–3963. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P., Rodman J. S., Frey M., Lang S., Stahl P. Clearance of lysosomal hydrolases following intravenous infusion. The role of liver in the clearance of beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P., Rodman J. S., Frey M., Lang S., Stahl P. Clearance of lysosomal hydrolases following intravenous infusion. The role of liver in the clearance of beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Schlesinger P. H. Evidence for receptor-mediated binding of glycoproteins, glycoconjugates, and lysosomal glycosidases by alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1399–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Mandell B., Rodman J. S., Schlesinger P., Lang S. Different forms of rat beta-glucuronidase with rapid and slow clearance following intravenous injection: selective serum enhancement of slow clearance forms by organophosphate compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):536–540. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Schlesinger P. H., Rodman J. S., Doebber T. Recognition of lysosomal glycosidases in vivo inhibited by modified glycoproteins. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):86–88. doi: 10.1038/264086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Six H., Rodman J. S., Schlesinger P., Tulsiani D. R., Touster O. Evidence for specific recognition sites mediating clearance of lysosomal enzymes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Kusiak J. W., Brady R. O., Jones E. A. Selective hepatic uptake of human beta-hexosaminidase A by a specific glycoprotein recognition system on sinusoidal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2774–2778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H. The existence of a second route for the transfer of certain glycoproteins from the circulation into the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):988–993. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowell C. P., Lee Y. C. The binding of d-glucosyl-neoglycoproteins to the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6107–6110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Silman I., Beitsch D. D., Resheff G. A beta-D-galactoside binding protein from electric organ tissue of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhake J. L., Nicolson G. L. Aglycosylantibody. Effects of exoglycosidase treatments on autochthonous antibody survival time in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1074–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waard A., Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Isolation and properties of beta-galactoside binding lectins of calf heart and lung. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7581–7587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


