Abstract
Introduction:
Thymus is a primary lymphoid organ which has an important role in humoral and cellular immunity. It can be a site for various neoplasms including thymomas.
Case presentation:
The authors report a case of a 55-year-old patient presenting with weight loss, night sweats and sensation of heat. After thorough evaluation his histopathology analysis revealed the rare presence of Hodgkin lymphoma in a background of type B2 thymoma.
Discussion:
Thymoma is one of the well-known thymic tumors that is encountered in clinical practice. It has diverse associations with other autoimmune diseases and malignancies. The concurrent diagnosis of thymoma with thymic Hodgkin lymphoma is extremely rare.
Conclusion:
Although this association is very rare, it is crucial to distinguish between thymic Hodgkin lymphoma and thymoma and manage them appropriately.
Keywords: Hodgkin, lymphoma, nodes, thymoma, thymus
Introduction
Highlights
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ, responsible for T-cell production and B-cell maturation. Thus, playing a major role in immune function.
Thymoma is a relatively rare tumor arising from the thymic epithelial cells.
Thymoma can rarely be associated with classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
Distinguishing thymoma from thymic epithelial hyperplasia secondary to Hodgkin lymphoma is very challenging.
Histopathological analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing different thymic neoplasms.
The thymus is the primary lymphoid organ responsible for the production and maintenance of effector T lymphocytes throughout an individual’s lifetime. It also plays a role in the development and maturation of B cells1,2. A thymoma is a mass-producing neoplasm in the anterior mediastinum that arises from the epithelial cells of the thymus gland. Thymomas can be found incidentally or due to symptoms caused by compression of nearby organs, leading to coughing, difficulty breathing, and chest pain3.
The most prevalent thymic lymphoid neoplasms include Hodgkin’s lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL), and lymphoblastic lymphoma1. Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a malignancy characterized by the presence of specific monoclonal B-cell lymphocytes. It used to be categorized into two types: classical and nodular lymphocyte-predominant (NLP) subtypes. However, recently NLP was removed from the HL subtypes. The underlying mechanisms and clinical symptoms vary between these types. Approximately 95% of cases are classified as classical Hodgkin lymphoma, which can be further divided into four subtypes: lymphocyte-rich, lymphocyte-depleted, mixed cellularity, and nodular sclerosis3.
Thymomas have been reported rarely when associated with T-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. There have only been five reports of T-cell lymphoproliferative diseases coexisting with thymomas to date. Additionally, there have been rare occurrences of thymoma coexisting with Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)4. We report a new case of concurrent thymic Hodgkin lymphoma with thymoma. This case was written according to the SCARE (Surgical CAse REport) criteria 20205.
Case presentation
We report a case of a 55-year-old male patient, with no significant medical history, presenting with drenching night sweats, a sensation of heat and chills for the last 10 days. He experienced an unintentional weight loss of 5 Kg over the past 6 months. He also reported generalized itching for the previous 6 months, which did not resolve with antihistamine. The patient has a family history of cancers on the paternal side, specifically pancreatic cancer in his uncle and prostate cancer in another uncle. Physical examination revealed no muscle weakness or compressive symptoms.
Routine laboratory investigations showed normal hemoglobin and platelet count, with mild leukocytosis. His ESR was elevated. His cardiac echography showed a normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of greater than 60%. And His HIV serology and hepatitis profile were negative.
Abdominal and pelvic computed tomography (CT) was done; the lower cuts of the chest showed a predominant anterior mediastinal pre-pericardial mass measuring 5.1 cm in greatest dimension and showing cystic/necrotic center Fig. 1, along with multiple pathologically enlarged prevascular, bilateral hilar, subcarinal, epiphrenic and pericardial lymph nodes. Multiple pleural-based pulmonary nodules were observed in the right lower lobe, along with multiple enlarged intra-abdominal lymph nodes and evidence of distant lesions in the liver and soft tissue of the thigh.
Figure 1.
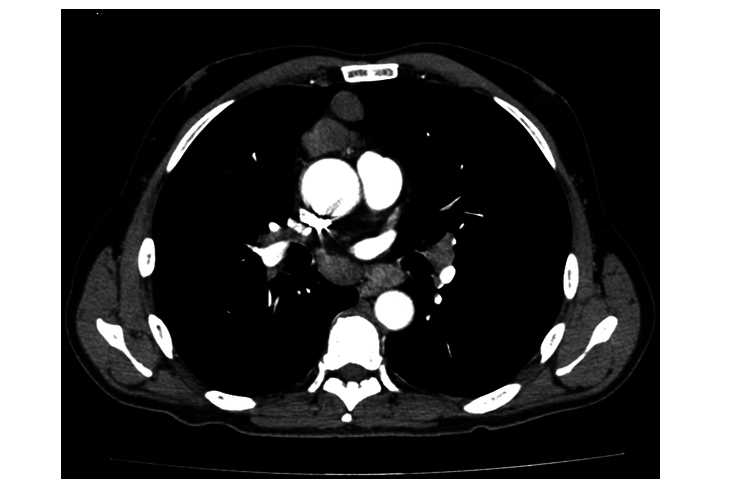
Shows a computed tomography scan of the chest.
Histopathological examination of tissue obtained through mediastinoscopy taken from pre-pericardial mass was consistent with classic Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular sclerosis type, involving pre-existing type B2 thymoma. The biopsy showed scattered large cells some binucleated and multilobulated, with prominent eosinophilic nucleoli, resembling typical Reed-Sternberg cells (Fig. 2). These cells were found in a background of small lymphocytes, with areas of scattered eosinophils and plasma cells and adjacent thymic tissue with multiple thymic cysts (Fig. 3). The thymoma showed broad fibrotic bands imparting a lobular architecture and a diffuse meshwork of epithelial cells.
Figure 2.
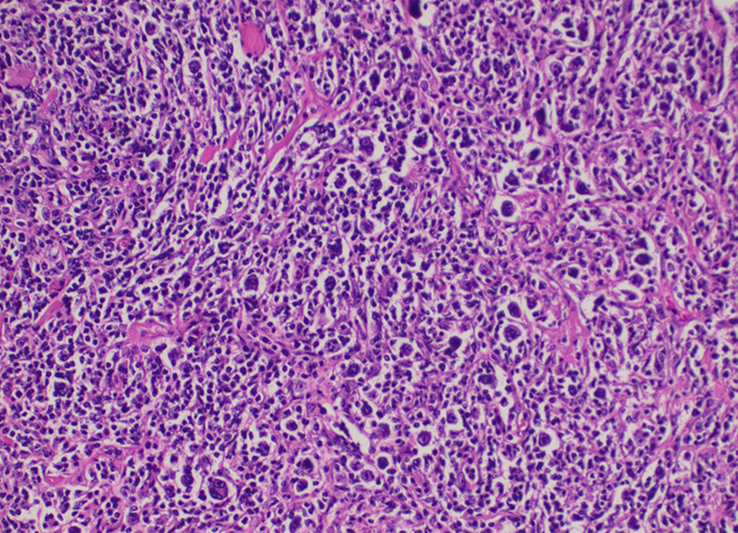
High power view at ×40 magnification shows typical Reed-Sternberg cells. (Binucleated and mononuclear).
Figure 3.
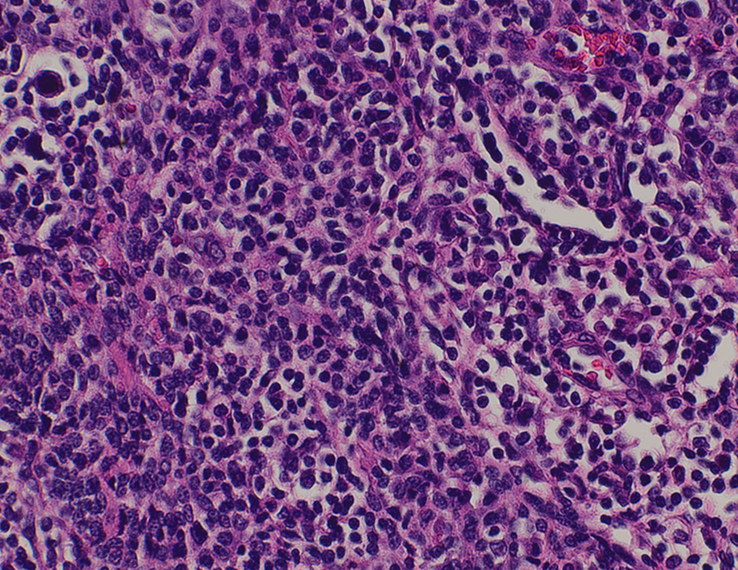
High power view at ×40 highlighting Epithelial strands of thymoma with adjacent Reed-Sternberg cells.
Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that the neoplastic cells (Reed-Sternberg cells) were positive for CD15, CD30 and PAX-5 (Figs. 4, 5, 6), respectively, and negative for CD45, CD3 and CD20. (Fig. 7)
Figure 4.
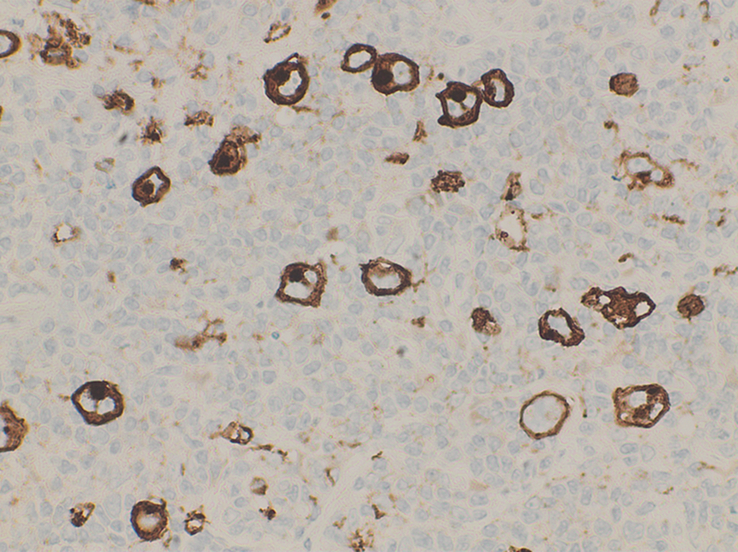
High power view at ×40 shows Reed-Sternberg cells positive for CD15.
Figure 5.
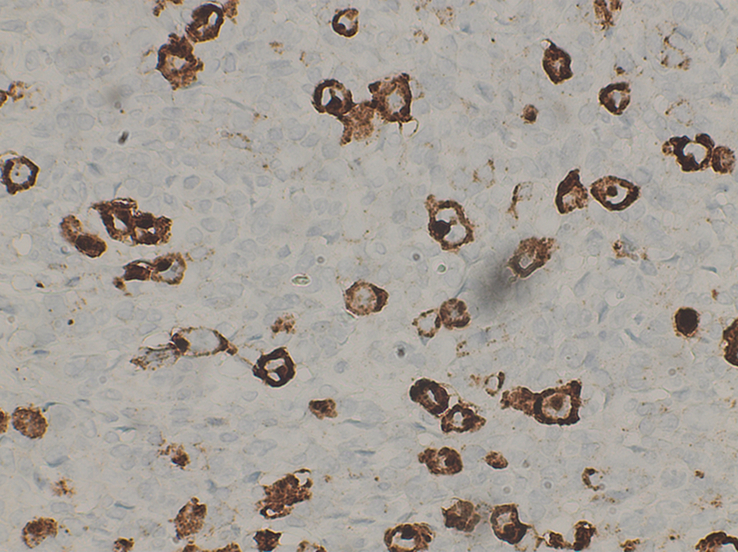
High power view at ×40 shows Reed-Sternberg cells positive for CD30.
Figure 6.
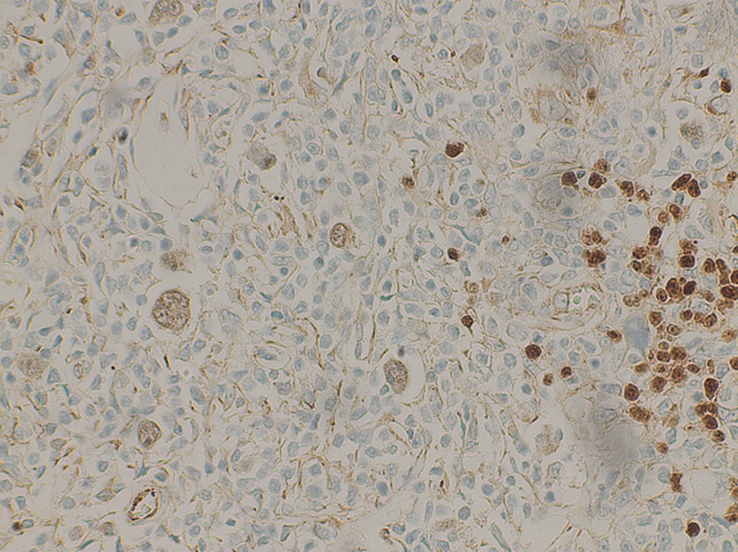
A High power view at ×40 shows neoplastic cells (R-S Cells) weakly positive for PAX-5.
Figure 7.
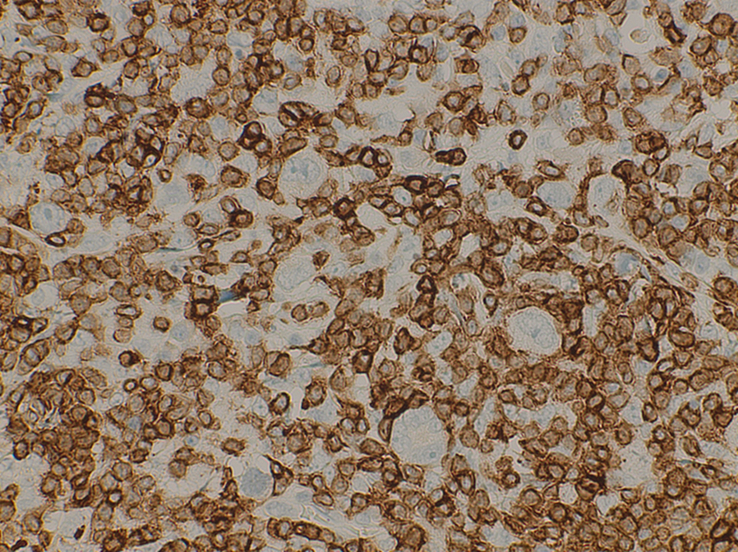
A high power view at ×40 shows neoplastic cells (R-S Cells) negative for CD3.
TdT was positive in scattered lymphocytes in the background of thymic tissue and Pan-CK highlighted a diffuse abnormal meshwork of thymic epithelial cells of the pre-existing thymoma (Fig. 8).
Figure 8.
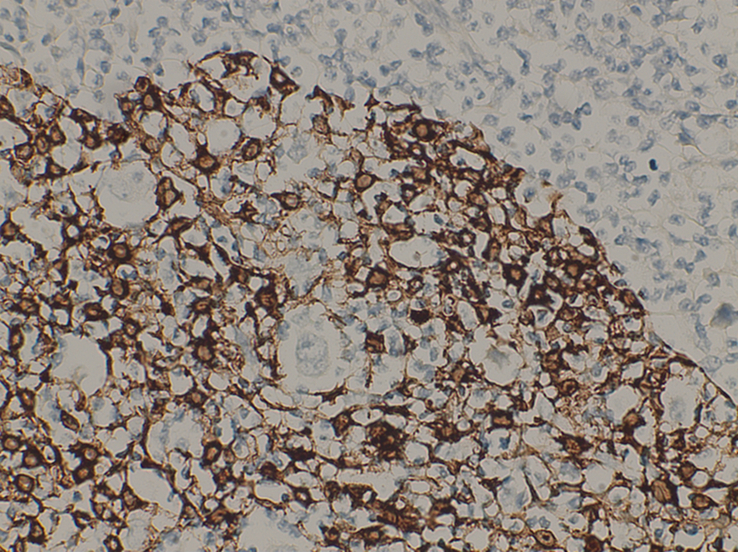
A High power view at ×40 shows Pan-CK highlights Epithelial strands with embedded R-S cells.
A diagnosis of an existing myasthenia gravis was excluded.
FDG-18 Whole-Body Pet Scan, conducted for lymphoma staging, revealed hypermetabolic nodal and extra-nodal lymphomatous disease involving multiple groups of both sides of the diaphragm, in addition to a single muscular deposit, hypermetabolic suspicious focus visualized adjacent to the left lateral rectus muscle, multiple hepatic and bony lesions and massively enlarged prostate and seminal vesicles. These findings suggest stage IV Classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
The patient completed six cycles of ABVD Therapy (Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Dacarbazine) for his Classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Table 1. He showed a positive response to chemotherapy for his Hodgkin lymphoma. Then he will be referred to thoracic surgery for the evaluation of his thymoma.
Table 1.
Demonstrates each cycle of ABVD therapy.
| Cycle day | Treatment | Drugs and dosages |
|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Chemotherapy administration | Doxorubicin 47 mg Vincristine 1 mg Bleomycin 20 mg Dacarbazine 720 mg |
| Days 2–14 | No treatment | |
| Day 15 | Chemotherapy administration (same as day 1) | Doxorubicin 47 mg Vincristine 1 mg Bleomycin 20 mg Dacarbazine 720 mg |
| Days 16–28 | No treatment |
ABVD, Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Dacarbazine.
Discussion
Thymus is a well-known primary lymphoid organ located in the anterior superior mediastinum. It has an essential role in maintaining the cellular and humoral immunity. Despite that the thymus undergoes involution in early adulthood, awareness of the variety of masses that could arise in the thymus should not be overlooked6. As the thymus functions to create and preserve the pool for effector T cells7 consequently, it is not unexpected that T-cell neoplasms, namely T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma, account for a large number of lymphoid malignant neoplasms that emerge within the thymus. Conversely, B cells make up around one-third of all medullary cells in the medulla, mostly near Hassall corpuscles, and they may be involved in thymic negative selection. Thus, Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma are two examples of B-cell lineage malignant neoplasms that are not rare to be found in the thymus2. In general, thymic epithelial tumors (mostly thymomas) are the most common primary neoplasms found in the thymus. These are followed in frequency by lymphomas, germ cell tumors, and neuroendocrine tumors8.
Thymoma is a tumor that develops in the thymic epithelial cells, which are typically responsible for controlling T-cell maturation. Thymomas often have a robust infiltration of T cells. These erroneously conditioned T cells, when released into the bloodstream, are probably the cause of autoimmune diseases such myasthenia gravis, blood disorders, and connective tissue diseases that frequently coexist with thymomas9.
Thymic epithelial tumors mostly thymoma often manifest with a range of differentiation that is composed of lobules like jigsaw puzzles, divided by acellular fibrous bands, when viewed histologically. Neoplastic epithelial cells (either epithelioid or spindle cells) make up the cellular components8, which stain positive for broad-spectrum cytokeratins and cytokeratin 5/610. These cellular components are intermingled with wildly varying proportions of reactive polymorphous lymphoid cells (i.e. thymocytes) exhibiting both mature and immature T-cell characteristics8. This T-cell component is highlighted with CD45 and TDT immunostainings10.
Thymomas are well-known to be associated with concurrent or secondary neoplasms occurring in the same patients, such as thyroid carcinoma and colorectal adenocarcinoma, with an incidence rate as high as 31%11.
Many previous cases have been reported of thymoma associated with hematopoietic malignancies. While B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases have been reported as the most common association, isolated cases with chronic myelogenous leukemia and classic Hodgkin lymphoma have also been reported. These associations were supposed to be due to abnormal stimulation or failed suppression of B cells by abnormal T cells, which arise in a dysfunctional thymoma environment. Strong evidence linking T-cell immunodeficiency to B-cell malignant neoplasms supports this theory4. Diagnosis of concurrent thymoma with thymic Hodgkin lymphoma is very rare with only 2 reported cases in the literature. Ridell et al. 12 reported the first case of coexistence of thymoma with thymic Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular sclerosis type. The second reported case was conducted by Almuqbil and colleagues. They reported typical features of HL and thymoma supported by immunohistochemical stains that revealed expression of CD15 and CD30 by the Hodgkin cells, with negative expression for CD45 and occasional weak membranous positivity for CD20. On the other hand, mixed reactivity of CD3 and CD5 was revealed as background T cells. In addition, a meshwork of thymic epithelial cells that showed membranous positivity for cytokeratin 19 (CK19) and focal membranous positivity for pan-cytokeratin (pan-CK) was seen. They also showed nuclear positivity for tumor protein 63 (P63). These results confirm the presence of Hodgkin lymphoma in a background of thymoma3. Distinguishing these two types of tumor is very challenging as the classic Hodgkin lymphoma that could arise in the thymus stimulate the proliferation of reactive epithelial cells and/ or cystic changes, which simulates thymoma formation. The differentiation points include the broad fibotic bands seen in thymoma versus the normal architecture of thymic hyperplasia. It is recommended to sample every mediastinal cystic mass to rule out the presence of Hodgkin lymphoma6. Moreover, the cytologic picture may be complicated when a lymphoma only partially replaces the thymus and leaves behind thymic parenchymal cells. The cytoplasm of obscured thymic epithelial cells is hazy, and they frequently resemble the hallmark cells in Hodgkin lymphoma—the large Reed-Sternberg cells or the mononuclear variants—by appearing as scattered, “naked” nuclei with vesicular chromatin. It is crucial to accurately differentiate between a thymic epithelial tumor and lymphoma by using appropriate immunostaining. This is due to the major differences in their treatment regimens as some patients had thymectomy as a result of primary thymic Hodgkin lymphoma being misdiagnosed as thymoma, according to reports in the literature8.
Formerly, thymic Hodgkin’s lymphoma was thought to be a unique morphologic variation of thymoma. Castelman (1955) articulated the alternative theory that this illness is a manifestation of Hodgkin’s disease involving the thymus. Unlike systemic Hodgkin’s disease, which is more common in women and appears with two peaks in the second and third decades and after the fifth decade of age. Hodgkin’s lymphoma of thymic origin typically presents in the second or third decade of life and affects men more frequently. While Hodgkin lymphoma’s involvement of intrathoracic structures like mediastinal lymph nodes is well described, the exact prevalence of thymic gland involvement is unknown. However, patients with thymic gland involvement are frequently found to have lymphadenopathy. Before extrathymic illness manifests, patients with thymic Hodgkin lymphoma frequently have no symptoms.
A third of patients typically have fever, night sweats, weight loss, and other constitutional symptoms when they are first diagnosed. If compression or invasion of the mediastinal structure occur, symptoms like chest pain, dyspnea or cough may be present13. Diagnosis of thymic Hodgkin lymphoma depends mainly on classic CD30 positivity of the large atypical cells. As the most frequent subtype of thymic Hodgkin lymphoma is nodular sclerosis, differentiating this subtype from primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, which is also associated to sclerosis is challenging. These two tumors have the same origin with B cell, present with the same morphology and may have similarities with a clinical presentation which necessitates the need for other immunophenotypes like CD45, CD79a, BOB1 and MAL6.
The Ann Arbor system has been used for anatomical staging for Hodgkin lymphoma. This system has been replaced with the Cotswold Ann Arbor modified staging system13. Modalities of treatment depend on this updated system as radiotherapy is sufficient in stages I or II. Chemotherapy is sometimes used in conjunction with radiation therapy for patients in stages Ill or IV14. Positron emission tomography and gammagraphy with gallium 67 are the most useful tool for follow-up for any residual mass that remains after lymphoma treatment to determine if this mass is fibrosis or a viable tumor.
Wang and colleagues performed a retrospective study with 233 patients diagnosed with thymic lymphoma, 58 patients diagnosed with nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma. They found that the pathologic type and age were independent predictors of prognosis in cases of thymic lymphoma. While chemotherapy and radiation therapy could both greatly increase the chance of survival, surgical treatment had no influence on overall survival15.
Conclusion
This case highlights the possibility of having a rare association between thymoma with thymic Hodgkin lymphoma. In addition, it emphasizes the crucial role of histopathology analysis in the diagnosis such rare associations which affect how these patients will be treated. Finally, reporting such rare associations adds to the existing literature which helps other doctors to be familiar with upcoming similar cases.
Ethical approval
This study is exempt from ethical approval in our intuition.
Consent
We obtained verbal and written informed consent from the patient for this case report. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal on request.
Source of funding
The study did not receive any financial help.
Author contribution
Data collection: M.A.S. Study concept or design: R.A., Z.M.M.Z., Z.A.H., N.K., Y.A., M.S. Writing the manuscript: R.A., Z.M.M.Z., Z.A.H., N.K., Y.A., M.S. Review and editing the manuscript: R.A., Z.M.M.Z., Z.A.H., N.K., Y.A., M.S.
Conflicts of interest disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research registration unique identifying number (UIN)
Not applicable.
Guarantor
Maher A. Sughayer.
Data availability statement
Dataset is available upon reasonable request.
Provenance and peer review
Not commissioned, externally peer-reviewed.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful for the patient and his family for their great cooperation.
Footnotes
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Contributor Information
Rahaf M. AbuKhalaf, Email: Rahafak52@gmail.com.
Zahraa M. M. Zeer, Email: Zahraamaher998@gmail.com.
Zahra Hosam Abu Harb, Email: zahrahb.201@gmail.com.
Nazmi Kamal, Email: nkamal@khcc.jo.
Yasmin Alseedat, Email: yasminsaidat92@gmail.com.
Maher A. Sughayer, Email: msughayer@khcc.jo.
References
- 1. Marak AF, Singh RB, Bipin T, et al. A rare case of primary B cell lymphoma of the thymus. J Med Soc 2018;32:61–65. [Google Scholar]
- 2. Xu J, Wu X, Reddy V. T cell/histiocyte-rich large B cell lymphoma of the thymus: a diagnostic pitfall. Case Rep Hematol 2016;2016:2942594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Almuqbil S, Alharbi A, Alzouri FS, et al. Primary thymic hodgkin lymphoma coexisting with thymoma and myasthenia gravis: a case report. Am J Case Rep 2023;24:e941792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Fraser CR, Rios C, Kaya B. Composite lymphocyte-rich thymoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified: case report and literature review. Lab Med 2012;43:4–8. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Sohrabi C, Mathew G, Maria N, et al. The SCARE 2023 guideline: updating consensus Surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int J Surg Lond Engl 2023;109:1136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Marino M, Ascani S. An overview on the differential diagnostics of tumors of the anterior-superior mediastinum: the pathologist’s perspective. Mediastinum 2019;3:6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Marak AF, Singh RB, Bipin T, et al. A rare case of primary B cell lymphoma of the thymus. J Med Soc 2018;32:61–65. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Wang M, Kundu U, Gong Y. Pitfalls of FNA diagnosis of thymic tumors. Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:57–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Engels EA. Epidemiology of thymoma and associated malignancies. J Thorac Oncol 2010;5:260–265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Alqaidy D. Thymoma: an overview. Diagnostics 2023;13. 10.3390/diagnostics13182982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mizrahi N, Kugler E, Hayman L, et al. T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and thymoma: a case report and review of the literature of a rare association. Acta Haematol 2022;145:106–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ridell B, Larsson S. Coexistence of a thymoma and hodgkin’s disease of the thymus: a case report. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Sec A Pathol 1980;88 A:1–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ayadi-Kaddour A, Mlika M, Djilani H, et al. Primary thymic Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a rare mediastinal mass. Respir Med CME 2008;1:48–50. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Zambudio AR, Lanzas JT, Fernández PJG, et al. Hodgkin disease of thymic origin. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002;123:1208–1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Wang L, Wang Z, Huo L, et al. Incidence, mortality, and survival analyses of patients with thymic lymphoma. Front Oncol 2022;12:933672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset is available upon reasonable request.


