Abstract
Intact pig aortic strips were incubated in medium containing [32P]P1 and various Ca2+ concentrations. The 32P content of the myosin P-light chain was determined by radioautography after electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Although treatment of the strips with noradrenaline always caused a rise in tension, this was not necessarily accompanied by increased phosphorylation of the P-light chain. These results indicate that, in aortic smooth muscle, phosphorylation of the P-light chain is not obligatory for contraction.
Full text
PDF
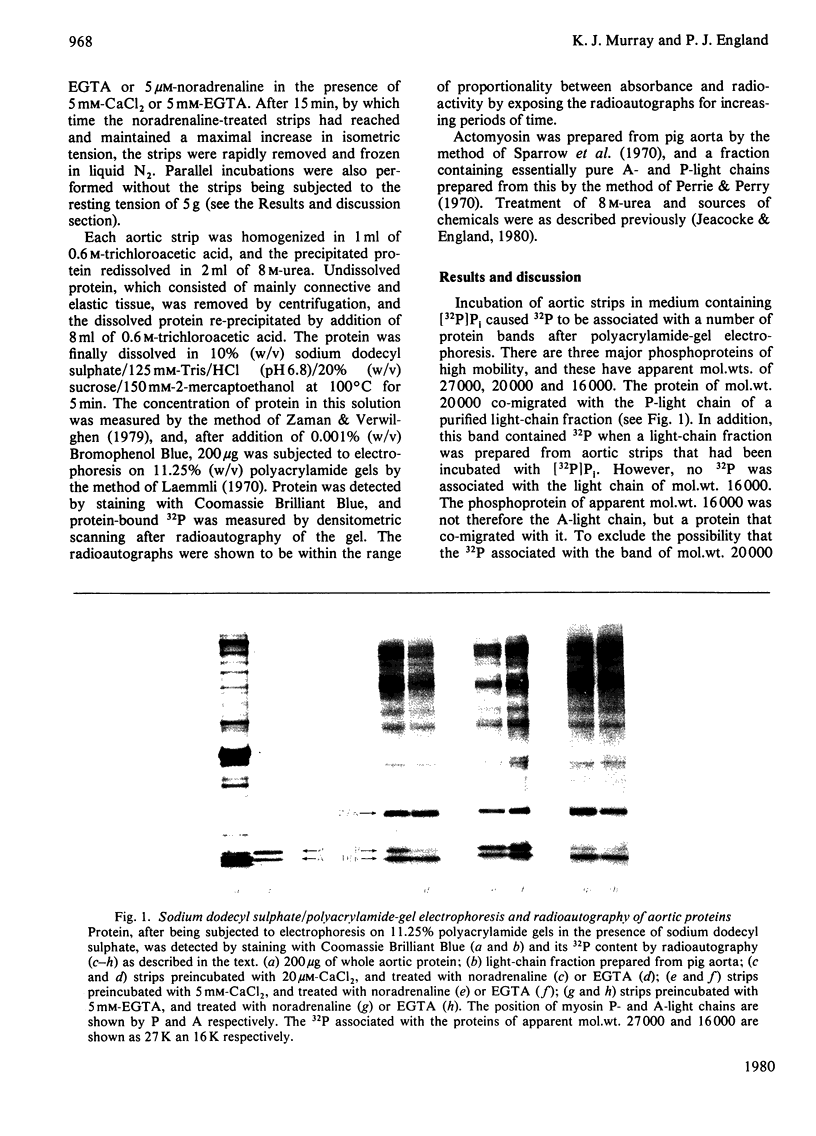


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy M. O., Williams D., Sharkey E. M., Hartshorne D. J. A relationship between Ca2+ sensitivity and phosphorylation of gizzard actomyosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson R. Role of cyclic AMP and Ca ++ in mechanical and metabolic events in isometrically contracting vascular smooth muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jan;87(1):84–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron J. T., Bárány M., Bárány K. Phosphorylation of the 20,000-dalton light chain of myosin of intact arterial smooth muscle in rest and in contraction. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4954–4956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M., Bárány K. Phosphorylation of the myofibrillar proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R., van Breemen C. Relative contributions of Ca2+ influx and cellular Ca2+ release during drug induced activation of the rabbit aorta. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 4;348(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00587735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo J., Gruenstein E., Silver P. Ca2+ dependent phosphorylation of bovine aortic actomyosin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jul;158(3):410–414. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J., Walsh D. A. A rapid method for the measurement of [gamma-32P]ATP specific radioactivity in tissue extracts and its application to the study of 32Pi uptake in perfused rat heart. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson N., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of the light-chain components of myosin from cardiac and red skeletal muscles. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):99–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1510099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeacocke S. A., England P. J. Phosphorylation of myosin light chains in perfused rat heart. Effect of adrenaline and increased cytoplasmic calcium ions. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):763–768. doi: 10.1042/bj1880763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Osa T., Ito Y., Suzuki H. Excitation-contraction coupling mechanism in visceral smooth muscle. Adv Biophys. 1976;8:115–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Trevett R. M., Walters M. Calcium ion-regulated thin filaments from vascular smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):355–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1850355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikawa T., Nonomura Y., Ebashi S. Does phosphorylation of myosin light chain have direct relation to regulation in smooth muscle? J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1789–1791. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M., Perry S. V., Ottaway J. Myosin light-chain phosphatase. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):687–697. doi: 10.1042/bj1570687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrwa U., Troschka M., Gross C., Katzinski L. Calcium-sensitivity of pig-carotid-actomyosin ATPase in relation to phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):415–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., England P. J. Phosphorylation of myosin light chains and other low molecular weight proteins in aorta during contraction [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):365–366. doi: 10.1042/bst0080365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A. Ca-linked phosphorylation of a light chain of vertebrate smooth-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow M. P., Maxwell L. C., Ruegg J. C., Bohr D. F. Preparation and properties of a calcium ion-sensitive actomyosin from arteries. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1366–1372. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman Z., Verwilghen R. L. Quantitation of proteins solubilized in sodium dodecyl sulfate-mercaptoethanol-Tris electrophoresis buffer. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):64–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]