Abstract
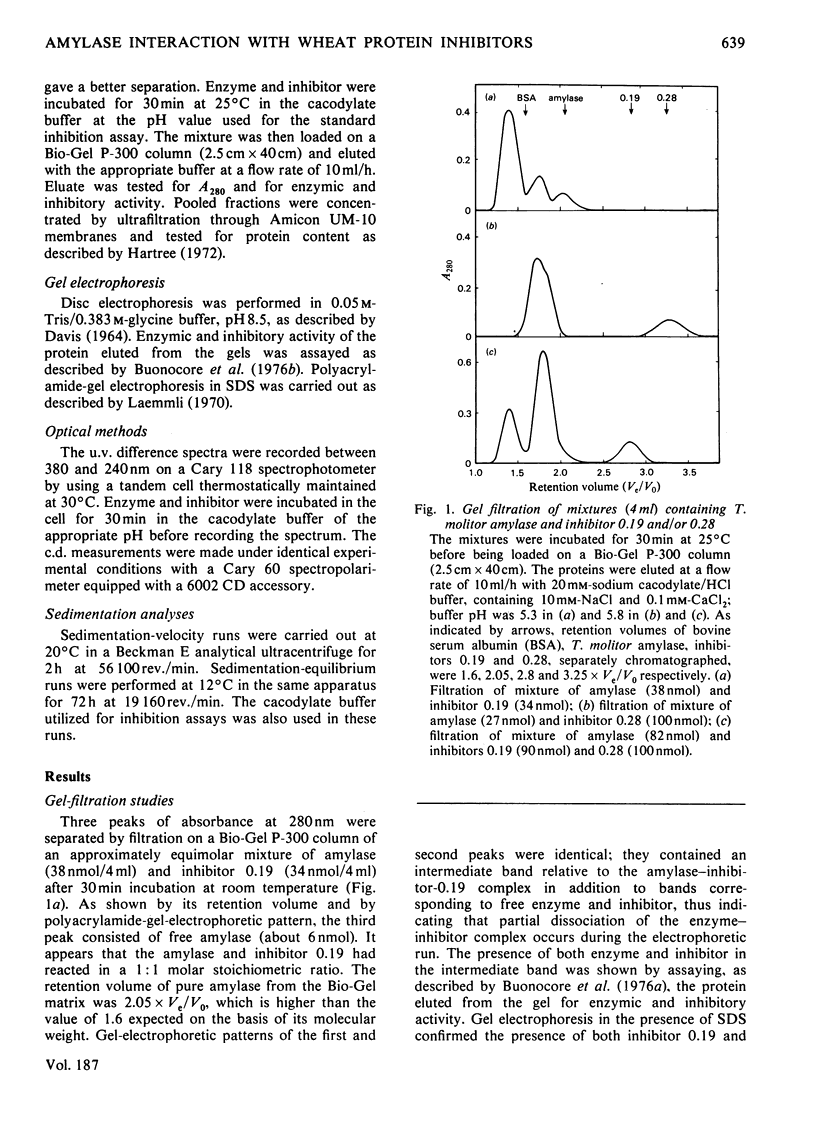
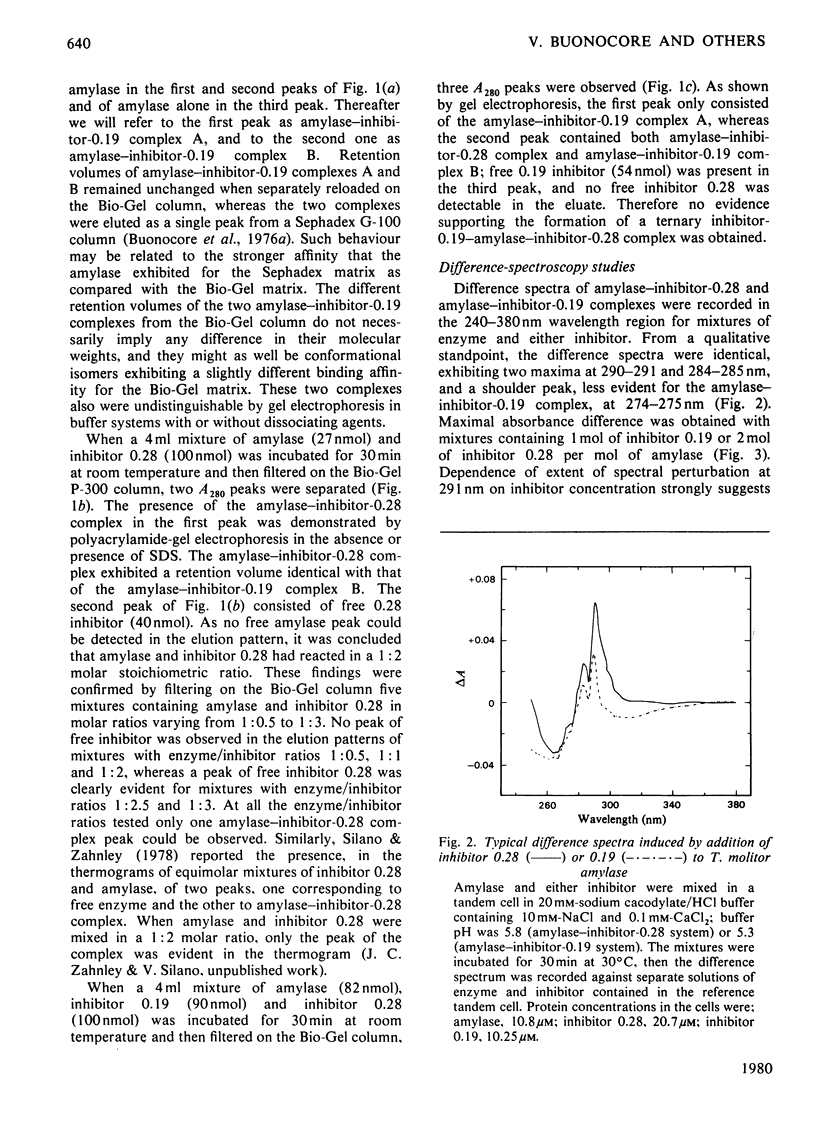
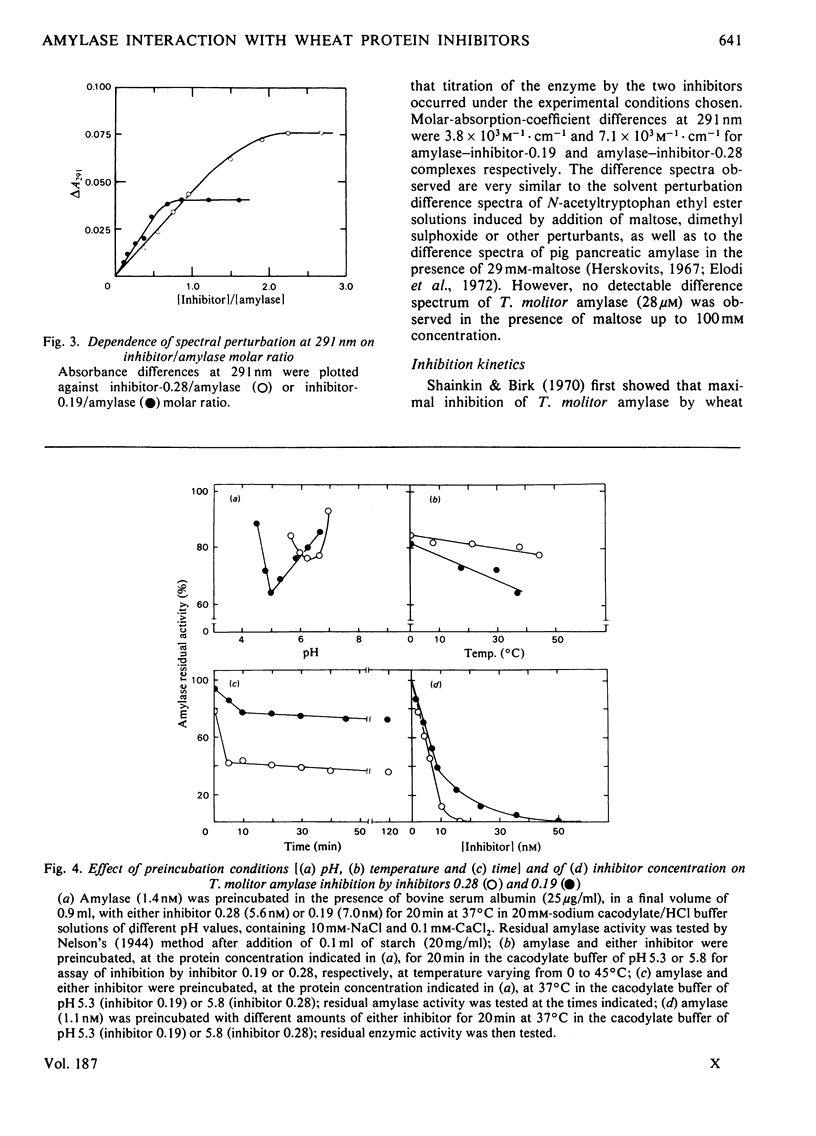
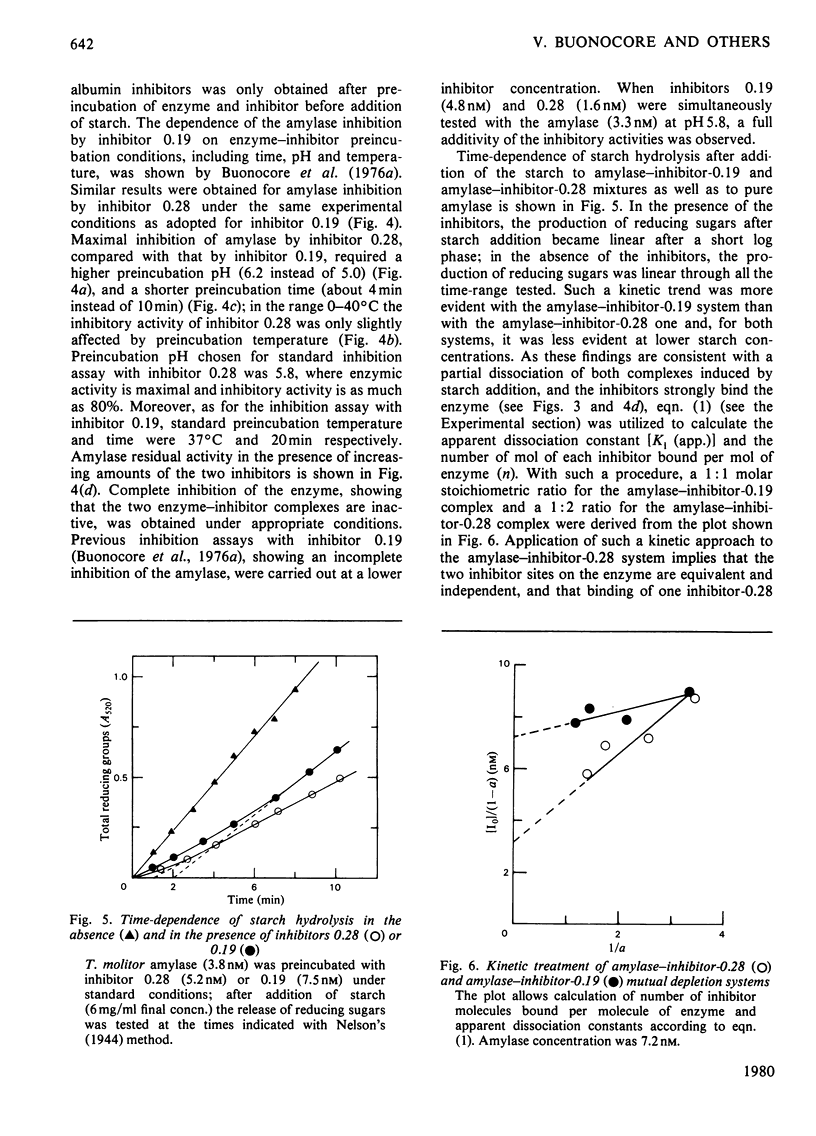
The highly purified alpha-amylase from Tenebrio molitor L. larva (yellow mealworm) reversibly combines with two closely related homogeneous glycoprotein inhibitors, one dimeric (termed 'inhibitor 0.19') and one monomeric (termed 'inhibitor 0.28'), from wheat flour. As established by means of difference spectroscopy and kinetic studies, molar combining ratios for the amylase--inhibitor-0.19 and amylase-inhibitor-0.28 complexes were 1:1 and 1:2 respectively. Two amylase--inhibitor-0.19 complexes with slightly different retention volumes on Bio-Gel P-300 and only one amylase--inhibitor-0.28 complex were observed. Dissociation constants of the amylase--inhibitor-0.19 and amylase--inhibitor-0.28 complexes were 0.85 nM and 0.13 nM respectively. A strong tendency of both complexes to precipitate under an ultracentrifugal field was observed; the minimum molecular weight calculated for the two complexes under such conditions was approx. 95 000. The two complexes showed difference spectra indicating involvement of structurally related or identical tryptophyl side chains in the binding of inhibitors 0.28 and 0.19 to the amylase. A model summarizing the main features of the inhibition of the insect amylase by the two wheat protein inhibitors is proposed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buonocore V., Poerio E., Gramenzi F., Silano V. Affinity column purification of amylases on protein inhibitors from wheat kernel. J Chromatogr. 1975 Nov 12;114(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)85247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonocore V., Poerio E. Interaction of Tenebrio molitor L. alpha-amylase with a wheat flour protein inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 15;67(2):202–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80366-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonocore V., Poerio E., Silano V., Tomasi M. Physical and catalytic properties of alpha-amylase from Tenebrio molitor L. larvae. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):621–625. doi: 10.1042/bj1530621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elödi P., Móra S., Krysteva M. Investigation of the active center of porcine-pancreatic amylase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 21;24(3):577–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb19720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci T., Rab A., Tomasi M., Silano V. Further characterization studies of the alpha-amylase protein inhibitor of gel electrophoretic mobility 0.19 from the wheat kernel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 20;420(2):288–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci T., Sannia G., Parlamenti R., Silano V. Structural studies of wheat monomeric and dimeric protein inhibitors of alpha-amylase. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj1730229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman D. G. Structural studies on wheat (Triticum aestivum) proteins lacking phenylalanine and histidine residues. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):725–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1490725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainkin R., Birk Y. Alpha-amylase inhibitors from wheat. Isolation and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):502–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silano V., Furia M., Gianfreda L., Macri A., Palescandolo R., Rab A., Scardi V., Stella E., Valfre F. Inhibition of amylases from different origins by albumins from the wheat kernel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 23;391(1):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silano V., Pocchiari F., Kasarda D. D. Physical characterization of alpha-amylase inhibitors from wheat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silano V., Poerio E., Buonocore V. A model for the interaction of wheat monomeric and dimeric protein inhibitors with alpha-amylase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1977 Dec 29;18(2-3):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00280273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silano V., Zahnley J. C. Association of Tenebrio molitor L. alpha-amylase with two protein inhibitors--one monomeric, one dimeric--from wheat flour. Differential scanning calorimetric comparison of heat stabilities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 28;533(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon I., Móra S., Elödi P. Studies on the active center of pancreatic amylase. II. Small angle x-ray scattering investigations. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 Oct 30;4(3):211–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01731483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


