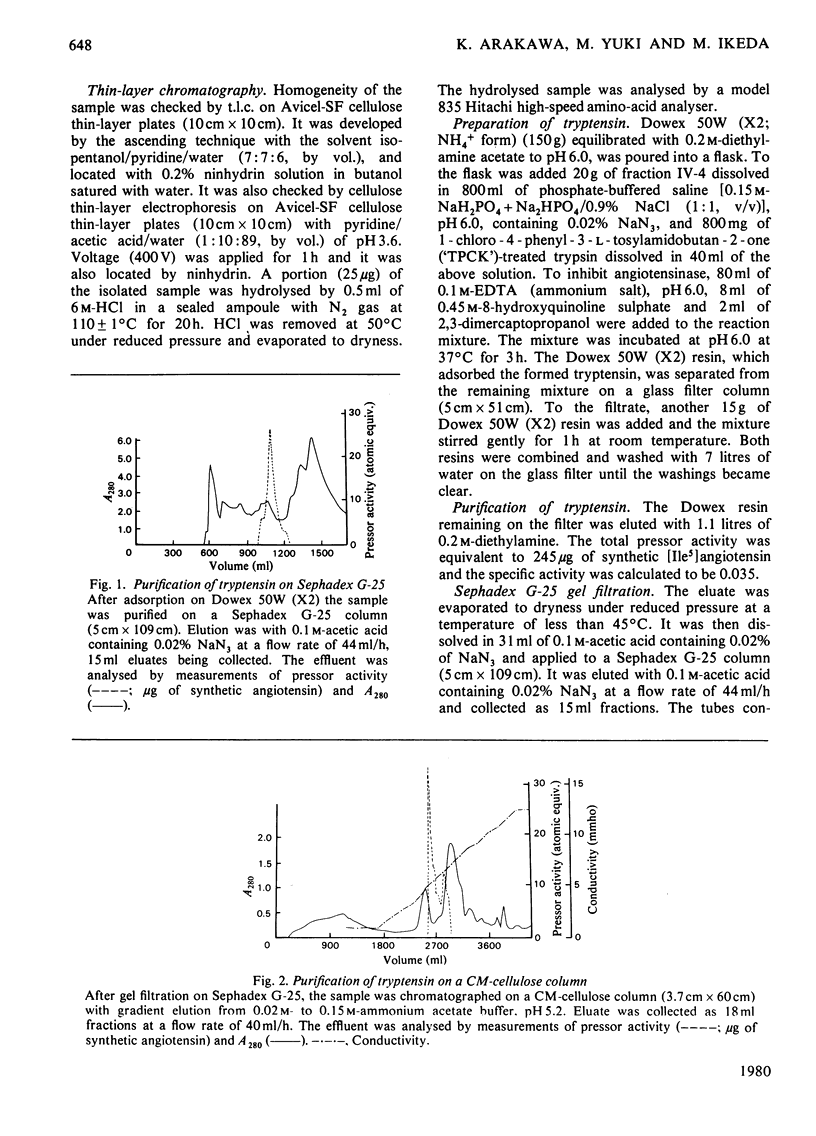
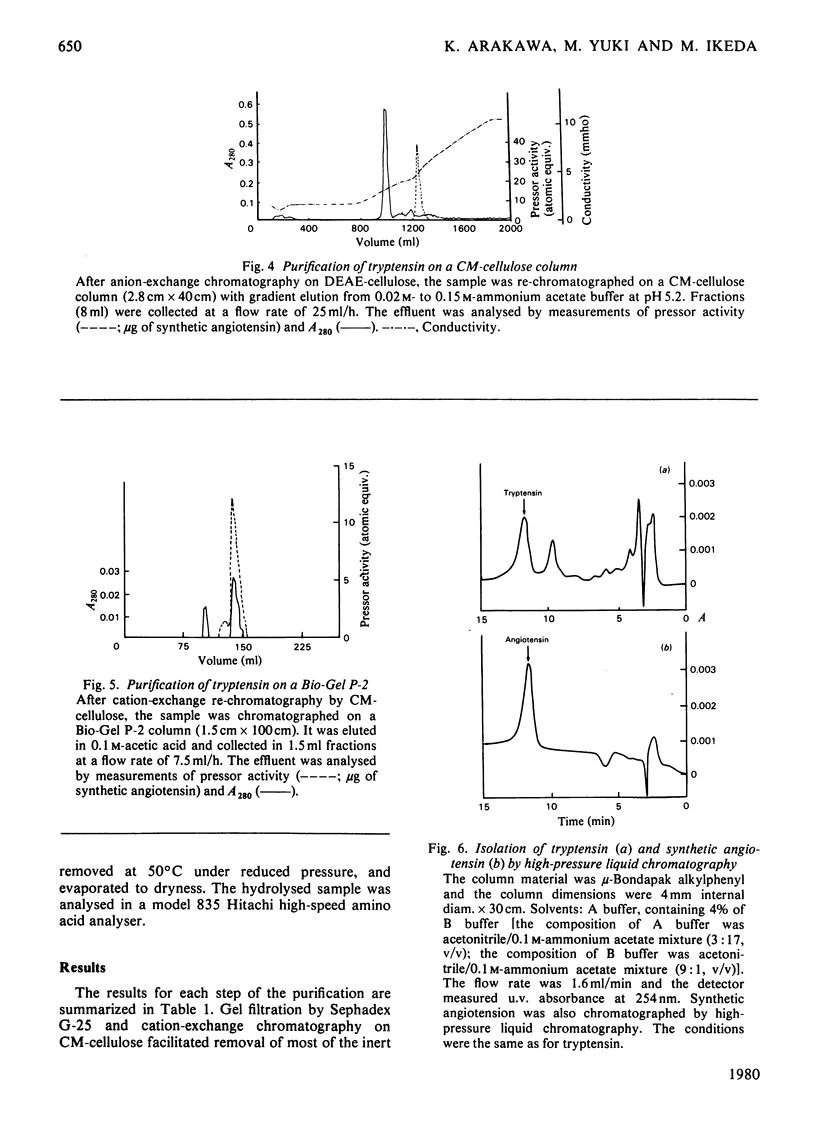
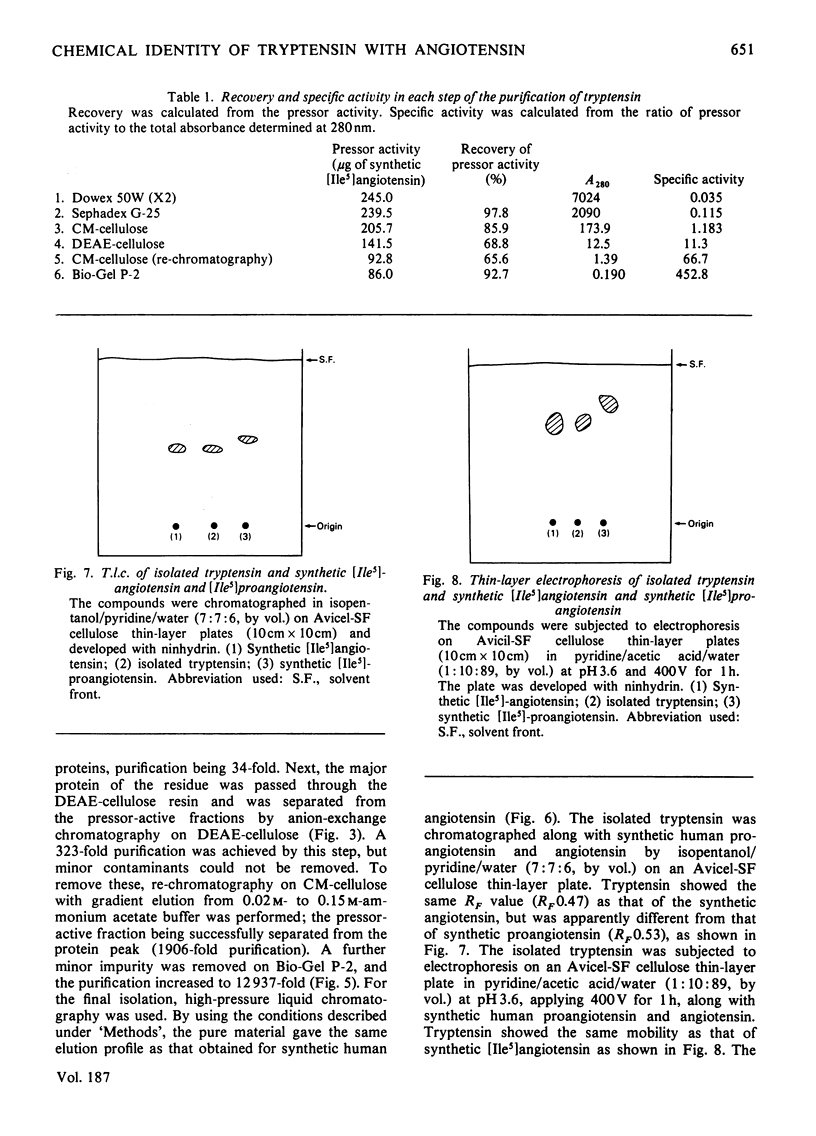
Abstract
Tryptensin, a vasopressor substance generated from human plasma protein fraction IV-4 by trypsin, has been isolated and the amino acid composition analysed. The procedures used for the isolation were: (a) adsorption of the formed tryptensin on Dowex 50W (X2; NH4+ form); (b) gel filtration through Sephadex G-25; (c) cation-exchange chromatography on CM-cellulose; (d) anion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose; (e) re-chromatography on CM-cellulose; (f) gel filtration on Bio-Gel P-2; (g) partition chromatography on high-pressure liquid chromatography. The homogeneity of the isolated tryptensin was confirmed by thin-layer chromatography and thin-layer electrophoresis. The amino acid analysis of the hydrolysate suggested the following proportional composition: Asp, 1; Val, 1; Ile, 1; Tyr, 1; Phe, 1; His, 1; Arg, 1; Pro, 1. This composition is identical with that of human angiotensin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa K., Ikeda M., Fukuyama J., Sakai T. A pressor formation by trypsin from renin-denatured human plasma protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):599–602. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Minohara A., Uemura N., Sakai T., Ikeda M. Characterization of renin-like activity in human plasma protein IV-4 fraction. Endocrinol Jpn. 1975 Oct;22(5):427–432. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.22.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Nakatani M., Minohara A., Nakamura M. Isolation and amino acid composition of human angiotensin I. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):900–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1040900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Nakatani M., Nakamura M. Purification of human angiotensin. Nature. 1967 Apr 15;214(5085):278–279. doi: 10.1038/214278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Nakatani M., Nakamura M. Species specificity in reaction between renin and angiotensinogen. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):636–636. doi: 10.1038/207636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arawaka K., Minohara A., Yamada J., Uemura N., Nakamura M. Micro-determination of human plasma renin activity with the addition of homologous substrate. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Nov;22(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT D. F., HORTON E. W., LEWIS G. P. The isolation of bradykinin, a plasma kinin from ox blood. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:60–65. doi: 10.1042/bj0780060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTKA V., CARPENTER F. H. INHIBITION OF CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTIVITY IN CRYSTALLINE TRYPSIN PREPARATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1799–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Lumbers E. R. The activation of renin in human amniotic fluid by proteolytic enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 7;289(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Oza N. B., Ryan J. W. Activation of a prorenin-like substance in human plasma by trypsin and by urinary kallikrein. Hypertension. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):179–189. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.3.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Wilchek M., Zamir A. Mapping of 23-S rRNA at the ribosomal peptidyl-transferase center by photo-affinity labeling. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


