Abstract
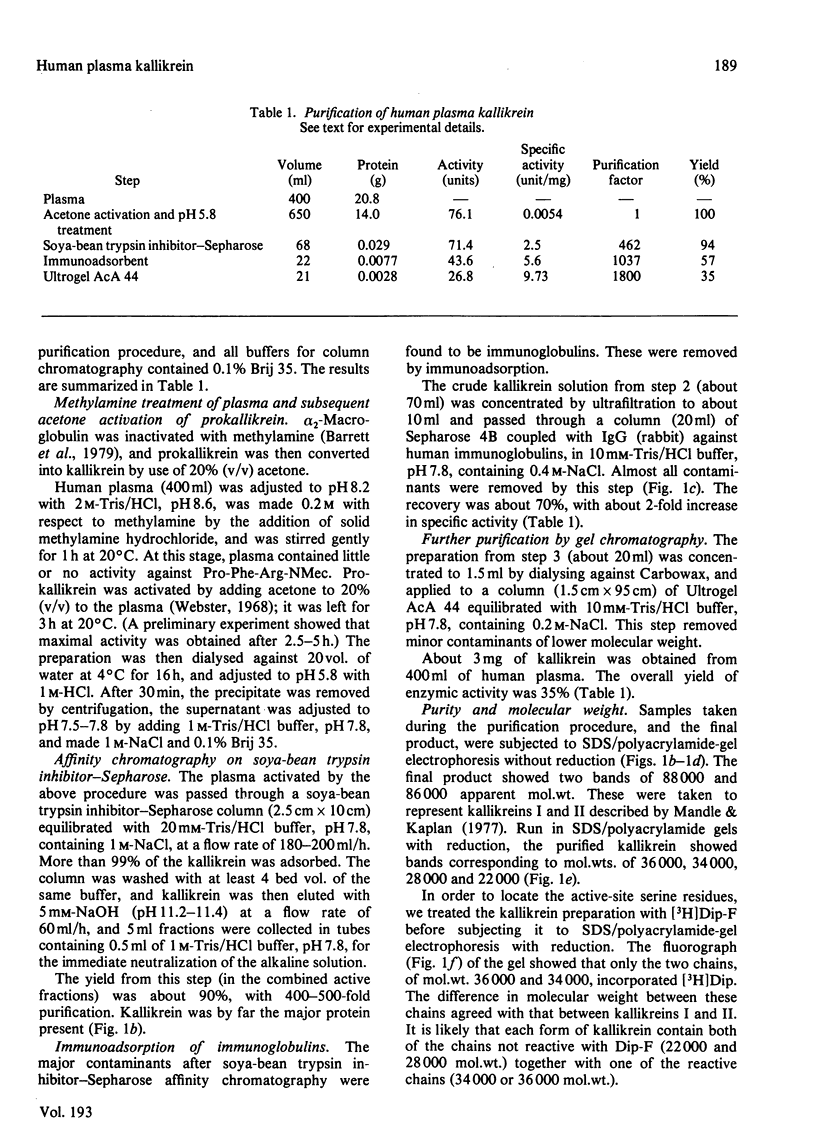
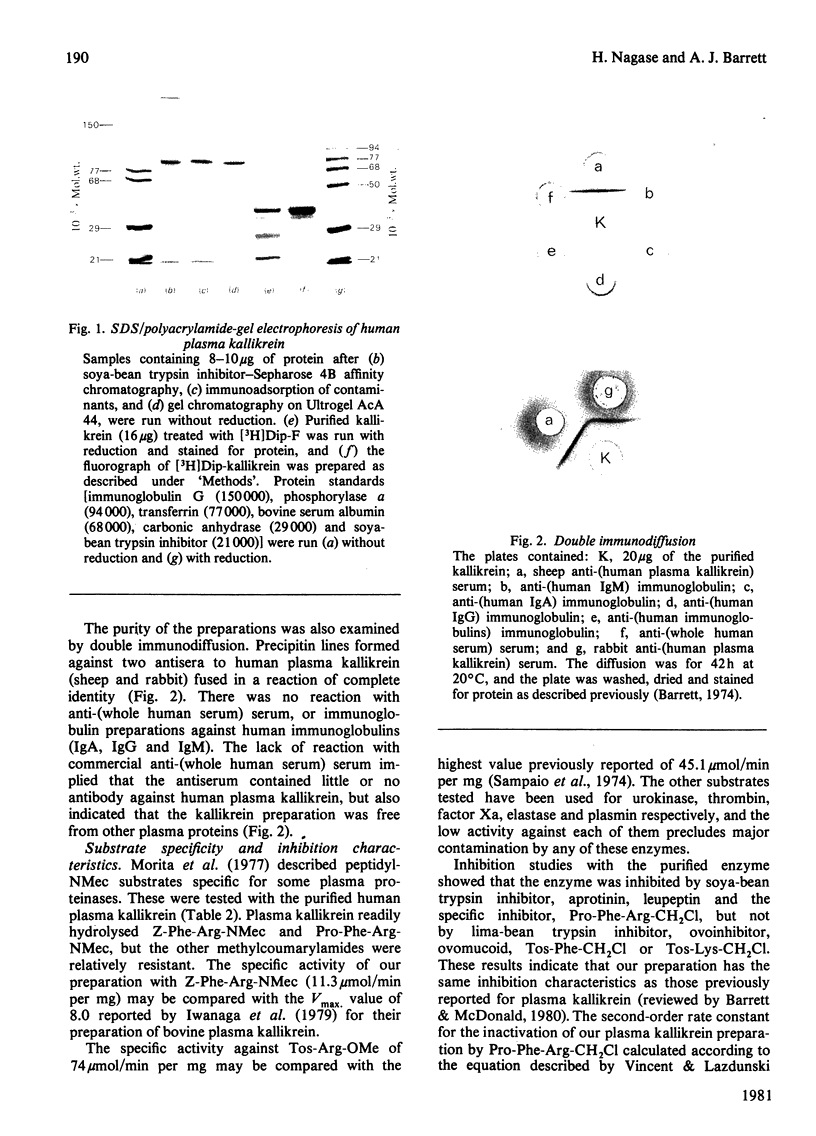
A simple method for isolation of kallikrein from human plasma is described. Before activation of the enzyme with acetone, the plasma was treated with 0.2 M-methylamine at pH 8.2 to inactivate alpha 2-macroglobulin and thus prevent the irreversible binding of the active enzyme to the inhibitor. The enzyme was adsorbed on soya-bean trypsin inhibitor-Sepharose 4B and eluted with 5 mM-NaOH, pH 11.3. It was further purified by immunoadsorption of contaminating proteins, and gel chromatography on Ultrogel AcA 44. About 3 mg of kallikrein was obtained from 400 ml of plasma (35% yield). The purified enzyme was shown to be homogeneous by electrophoretic and immunological criteria. The specific activities against benzyloxycarbonylphenylalanylarginine methylcoumarylamide, prolylphenylalanylarginine methylcoumarylamide and tosylarginine methyl ester were higher than any previously reported. The purified enzyme was resolved into two forms of mol.wts. 88 000 and 86 000 in sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis without reduction. Each consisted of three chains linked by disulphide bonds, one containing the reactive serine residue (mol.wt. 36 000 or 34 000), and two additional chains (mol.wt. 28 000 and 22 000).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian A., Lahiri B., Talamo R. C., Wong P., Colman R. W. Immunochemical studies of plasma kallikrein. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1444–1454. doi: 10.1172/JCI107892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Chicken alpha2-proteinase inhibitor: a serum protein homologous with ovoinhibitor of egg white. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Bagdasarian A., Talamo R. C., Scott C. F., Seavey M., Guimaraes J. A., Pierce J. V., Kaplan A. P. Williams trait. Human kininogen deficiency with diminished levels of plasminogen proactivator and prekallikrein associated with abnormalities of the Hageman factor-dependent pathways. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1650–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Mattler L., Sherry S. Studies on the prekallikrein (kallikreinogen)--kallikrein enzyme system of human plasma. I. Isolation and purification of plasma kallikreins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):11–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI105959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., Bouma B. N., Schalekamp M. P., Schalekamp M. A. An intrinsic factor XII- prekallikrein-dependent pathway activates the human plasma renin-angiotensin system. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):315–316. doi: 10.1038/280315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Wunderer G., Dittmann B. Zur Isolierung von Schweine- und Human-Serumkallikren durch Affinitätschromatographie. Spezifische Bindung an wasserunlösliche Kunitz-Sojabohnen-Inhibitor-Cellulosen und dissoziation mit kompetitiven Hemmstoffen (Benzamidin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jun;353(6):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J., Fareid E., Stormorken H. The purification of a human plasma kallikrein with weak plasminogen activator activity. Thromb Res. 1978 Mar;12(3):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms for the involvement of high molecular weight kininogen in surface-dependent reactions of Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Klett W. Reinigung und einige Eigenschaften eines Kallikreins aus Schweineserum. Biochem Z. 1966 Sep 8;346(2):133–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber H., Geiger R., Heimburger N. Human plasma kallikrein: purification, enzyme characterization and quantitative determination in plasma. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jun;359(6):659–669. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine plasma prekallikrein (Fletcher factor). Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 11;18(25):5743–5750. doi: 10.1021/bi00592a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Morita T., Kato H., Harada T., Adachi N., Sugo T., Maruyama I., Takada K., Kimura T., Sakakibara S. Fluorogenic peptide substrates for proteases in blood coagulation, kallikrein-kinin and fibrinolysis systems. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120A:147–163. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0926-1_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Synthesis of peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Selective inactivation of human plasma kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4778–4784. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laake K., Venneröd A. M. Factor XII-induced fibrinolysis: studies on the separation of prekallikrein, plasminogen proactivator, and factor XI in human plasma. Thromb Res. 1974 Feb;4(2):285–302. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Hageman factor substrates. Human plasma prekallikrein: mechanism of activation by Hageman factor and participation in hageman factor-dependent fibrinolysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6097–6104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGELMAN A. M., CARLSON A. S., ROBERTSON T. Investigation of serum trypsin and related substances. I. The quantitative demonstration of trypsinlike activity in human blood serum by a micromethod. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:159–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Donaldson V. H. Defective activation of clotting, fibrinolytic, and permeability-enhancing systems in human Fletcher trait plasma. Circ Res. 1974 May;34(5):641–651. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio C., Wong S. C., Shaw E. Human plasma kallikrein. Purification and preliminary characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Liu C. Y., Colman R. W. Human plasma prekallikrein: a rapid high-yield method for purification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Initiation of plasma prorenin activation by Hageman factor-dependent conversion of plasma prekallikrein to kallikrein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5914–5918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nagasawa S., Suzuki T. Studies on prekallikrein of bovine plasma. I. Purification and properties. J Biochem. 1972 Mar;71(3):471–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura Y., Fujii S. Purification of human plasma kallikrein and urokinase by affinity chromatography. J Biochem. 1976 Sep;80(3):507–511. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Trypsin-pancreatic trypsin inhibitor association. Dynamics of the interaction and role of disulfide bridges. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):2967–2977. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., PIERCE J. V. The nature of the kallidins released from human plasma by kallikreins and other enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:91–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E. Human plasma kallikrein, its activation and pathological role. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. S., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. Fletcher factor deficiency. A diminished rate of Hageman factor activation caused by absence of prekallikrein with abnormalities of coagulation, fibrinolysis, chemotactic activity, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):622–633. doi: 10.1172/JCI107597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Cochrane C. G. Plasma prekallikrein: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):1–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarovaya G. A., Dotsenko V. L., Orekhovich V. N., Kawiak J., Kawalec M. Preparation and some properties of highly purified human serum kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 May 2;93(3):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa N., Takahashi N., Inagami T., Page D. L. Isolation of completely inactive plasma prorenin and its activation by kallikreins. A possible new link between renin and kallikrein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




