Abstract
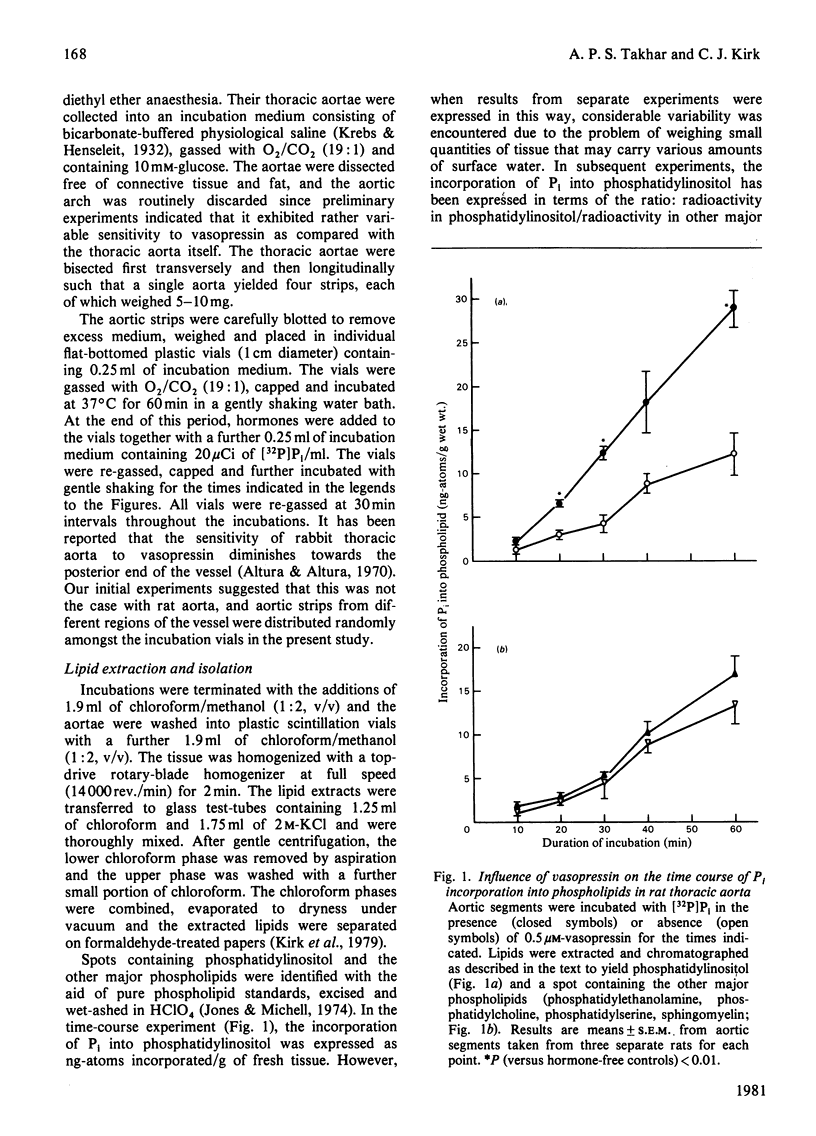
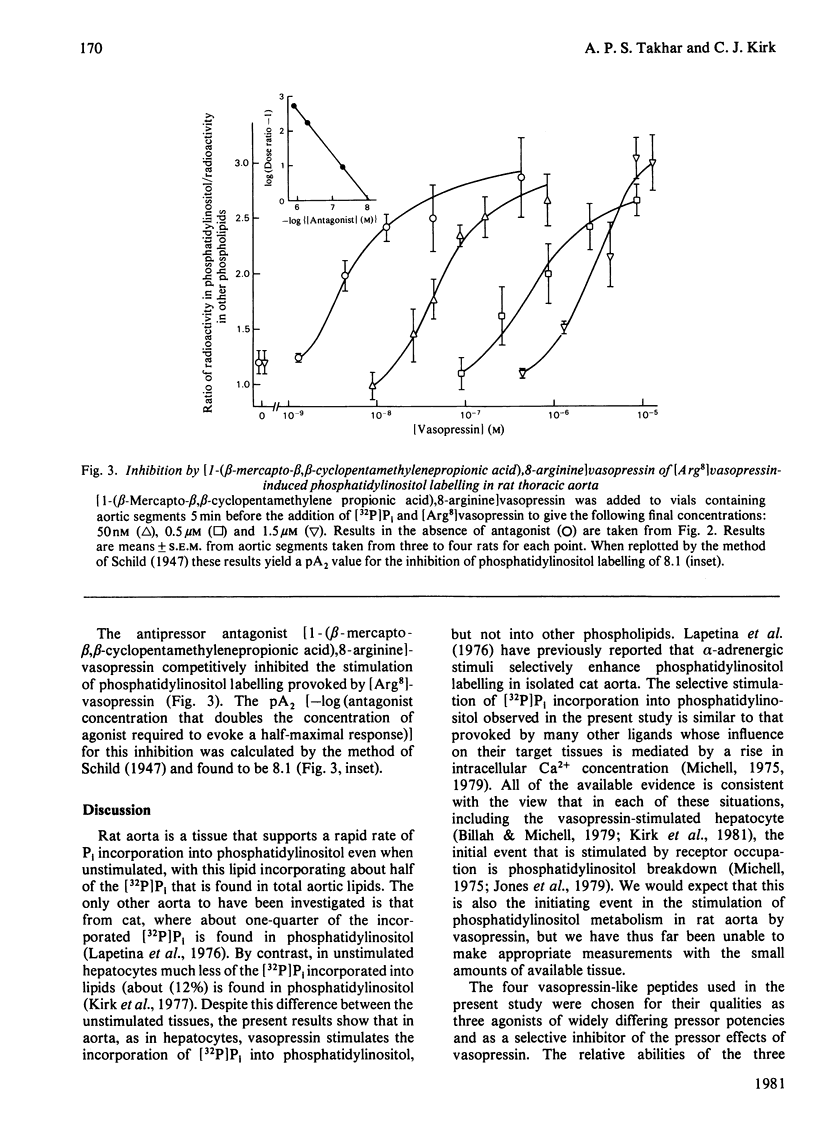
Vasopressin stimulates the incorporation of [32P]Pi into phosphatidylinositol but not into other phospholipids in rat thoracic aorta strips. The relative abilities of three vasopressin analogues to stimulate phosphatidylinositol labelling in rat aorta are similar to their relative pressor potencies in vivo and to their relative potencies in stimulating the metabolism of rat hepatocytes, but very different from their relative antidiuretic potencies. The vasopressor antagonist [1-(beta-mercapto-beta, beta-cyclopentamethylenepropionic acid),8-arginine]vasopressin competitively inhibits [Arg8]vasopressin-stimulated phosphatidylinositol labelling in rat aorta with a pA2 of 8.1. It is concluded that the Ca2+-mobilizing vasopressin receptors (V1-receptors) of the rat aorta stimulate phosphatidylinositol metabolism, probably by enhancing phosphatidylinositol breakdown.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Heterogeneity of drug receptors in different segments of rabbit thoracic aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Sep 1;12(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Magnesium withdrawal and contraction of arterial smooth muscle: effects of EDTA, EGTA, and divalent cations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Apr;151(4):752–755. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Vascular smooth muscle and neurohypophyseal hormones. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1853–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M. Dose-response relationships for arginine vasopressin and synthetic analogs on three types of rat blood vessels: possible evidence for regional differences in vasopressin receptor sites within a mammal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 May;193(2):413–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M. Neurohypophyseal hormones and analogues: rat pressor potency versus contractile potency on rat arterioles and arteries. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Sep;146(4):1054–1060. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by glycogenolytic hormones. Effects of angiotensin, vasopressin, adrenaline, ionophore A23187 and calcium-ion deprivation. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):661–668. doi: 10.1042/bj1820661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Michell R. H. Stimulation of the breakdown and resynthesis of of phosphatidylinositol in rat hepatocytes by angiotensin, vasopressin and adrenaline. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):1033–1035. doi: 10.1042/bst0061033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Borland M. K., Florio V. A., Twible D. A. The role of calcium ion as a mediator of the effects of angiotensin II, catecholamines, and vasopressin on the phosphorylation and activity of enzymes in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7147–7156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Rodrigues L. M., Whitton P. D. Glycogen phosphorylase, glucose output and vasoconstriction in the perfused rat liver. Concentration-dependence of actions of adrenaline, vasopressin and angiotensin II. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):367–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1600367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D. Stimulation by vasopressin of glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):705–709. doi: 10.1042/bj1360705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Cockcroft S., Michell R. H. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover in various tissues by cholinergic and adrenergic agonists, by histamine and by caerulein. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):669–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1820669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol provoked by muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1420583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandenheede J. R., De Wulf H. On the role of calcium as second messenger in liver for the hormonally induced activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 28;496(2):448–457. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., de Wulf H. The nature of the hepatic receptors involved in vasopressin-induced glycogenolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 15;588(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Hems D. A. Hepatic action of vasopressin: lack of a role for adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80441-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Michell R. H., Hems D. A. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):155–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1940155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Rodrigues L. M., Hems D. A. The influence of vasopressin and related peptides on glycogen phosphorylase activity and phosphatidylinositol metabolism in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):493–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1780493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Verrinder T. R., Hems D. A. Rapid stimulation, by vasopressin and adrenaline, of inorganic phosphate incorporation into phosphatidyl inositol in isolated hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 15;83(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Verrinder T. R., Hems D. A. The influence of extracellular calcium concentration on the vasopressin-stimulated incorporation of inorganic phosphate into phosphatidylinositol in hepatocyte suspensions. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):1031–1033. doi: 10.1042/bst0061031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynski M., Lammek B., Manning M., Seto J., Haldar J., Sawyer W. H. [1-beta-Mercapto-beta,beta-cyclopentamethylenepropionic acid),2-(O-methyl)tyrosine ]argine-vasopressin and [1-beta-mercapto-beta,beta-cyclopentamethylenepropionic acid)]argine-vasopressine, two highly potent antagonists of the vasopressor response to arginine-vasopressin. J Med Chem. 1980 Apr;23(4):364–368. doi: 10.1021/jm00178a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Briley P. A., De Robertis E. Effect of adrenergic agonists on phosphatidylinositol labelling in heart and aorta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):624–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Billah M. M. Hormonal stimulation of phosphatidylinositol breakdown with particular reference to the hepatic effects of vasopressin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):861–865. doi: 10.1042/bst0070861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara T., Terada S., Pincus J., Flouret G., Hechter O. Neurohypophyseal hormone-responsive renal adenylate cyclase. I. General characteristics of the neurohypophyseal hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase in bovine renal medullary membranes prepared using a double phase polymer system. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3211–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer W. H., Acosta M., Balaspiri L., Judd J., Manning M. Structural changes in the arginine vasopressin molecule that enhance antidiuretic activity and specificity. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1106–1115. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M., Kirk C. J., Hems D. A. Role of extracellular calcium in the action of vasopressin on hepatic glycogenolysis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80686-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


