Abstract
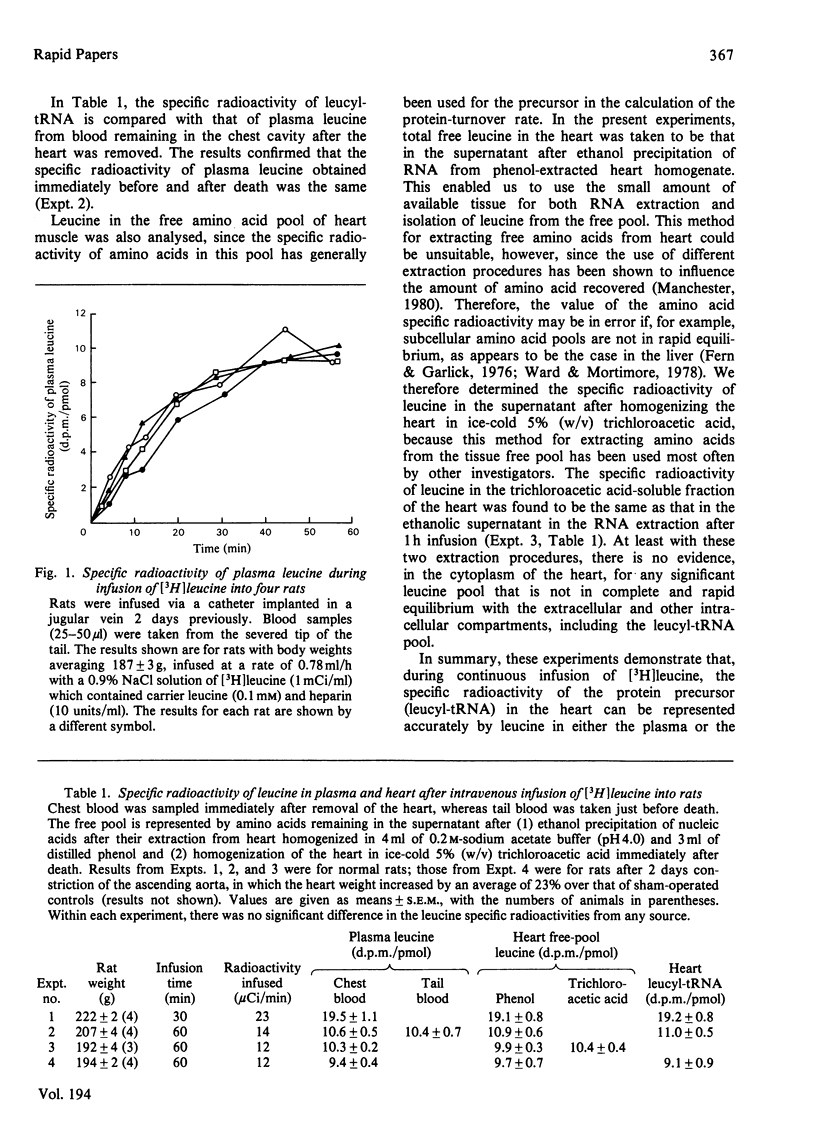
By 30min continuous infusion of [3H]leucine into rats, the specific radioactivities of plasma leucine and tissue-free and tRNA-bound leucine in heart were equal. The specific radioactivity of leucyl-tRNA in heart therefore follows a time course identical with that of plasma leucine soon after the start of infusion. The half-life of cardiac myosin heavy chain (5.5 days) was the same as that reported by other investigators who used the pulse-labelling protocol.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airhart J., Kelley J., Brayden J. E., Low R. B., Stirewalt W. S. An ultramicro method of amino acid analysis: application to studies of protein metabolism in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. E., Raines P. L., Regen D. M. Regulatory significance of transfer RNA charging levels. I. Measurements of charging levels in livers of chow-fed rats, fasting rats, and rats fed balanced or imbalanced mixtures of amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):323–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briel G., Neuhoff V. Microanalysis of amino acids and their determination in biological material using dansyl chloride. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Apr;353(4):540–553. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett A. W., Sparrow M. P., Taylor R. R. Early changes in myocardial protein synthesis in vivo in response to right ventricular pressure overload in the dog. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Dec;11(12):1253–1263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fern E. B., Garlick P. J. Compartmentation of albumin and ferritin synthesis in rat liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1560189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Burk T. L., Swick R. W. Protein synthesis and RNA in tissues of the pig. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., Sparrow M. P., Bates P. C., Millward D. J. Turnover of muscle protein in the fowl (Gallus domesticus). Rates of protein synthesis in fast and slow skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle of the adult fowl. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):393–401. doi: 10.1042/bj1760393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester K. L. Influence of extraction procedure on size of free amino acid pool of heart muscle. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):300–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. F., Rabinowitz M., Blough R., Prior G., Zak R. Measurements of half-life of rat cardiac myosin heavy chain with leucyl-tRNA used as precursor pool. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3422–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee E. E., Cheung J. Y., Rannels D. E., Morgan H. E. Measurement of the rate of protein synthesis and compartmentation of heart phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1030–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair K. G., Cutilletta A. F., Zak R., Koide T., Rabinowitz M. Biochemical correlates of cardiac hypertrophy. I. Experimental model; changes in heart weight, RNA content, and nuclear RNA polymerase activity. Circ Res. 1968 Sep;23(3):451–462. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas G. A., Lobley G. E., Harris C. I. Use of the constant infusion technique for measuring rates of protein synthesis in the New Zealand White rabbit. Br J Nutr. 1977 Jul;38(1):1–17. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidrich A., Airhart J., Bruno M. K., Khairallah E. A. Compartmentation of free amino acids for protein biosynthesis. Influence of diurnal changes in hepatic amino acid concentrations of the composition of the precursor pool charging aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):257–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1620257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEEKS J. R., DAVIS J. D. CHRONIC INTRAVENOUS CANNULAS FOR RATS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 May;19:540–541. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.3.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. F., Mortimore G. E. Compartmentation of intracellular amino acids in rat liver. Evidence for an intralysosomal pool derived from protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3581–3587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyborny L. E., Kritcher E. M., Luchi R. J. Synthesis of guinea-pig cardiac myosin as measured by constant infusion. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1700189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Martin A. F., Blough R. Assessment of protein turnover by use of radioisotopic tracers. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):407–447. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Prior G., Rabinowitz M. Assessment of protein synthesis by the use of aminoacyl-tRNA as precursor. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:310–321. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


