Abstract
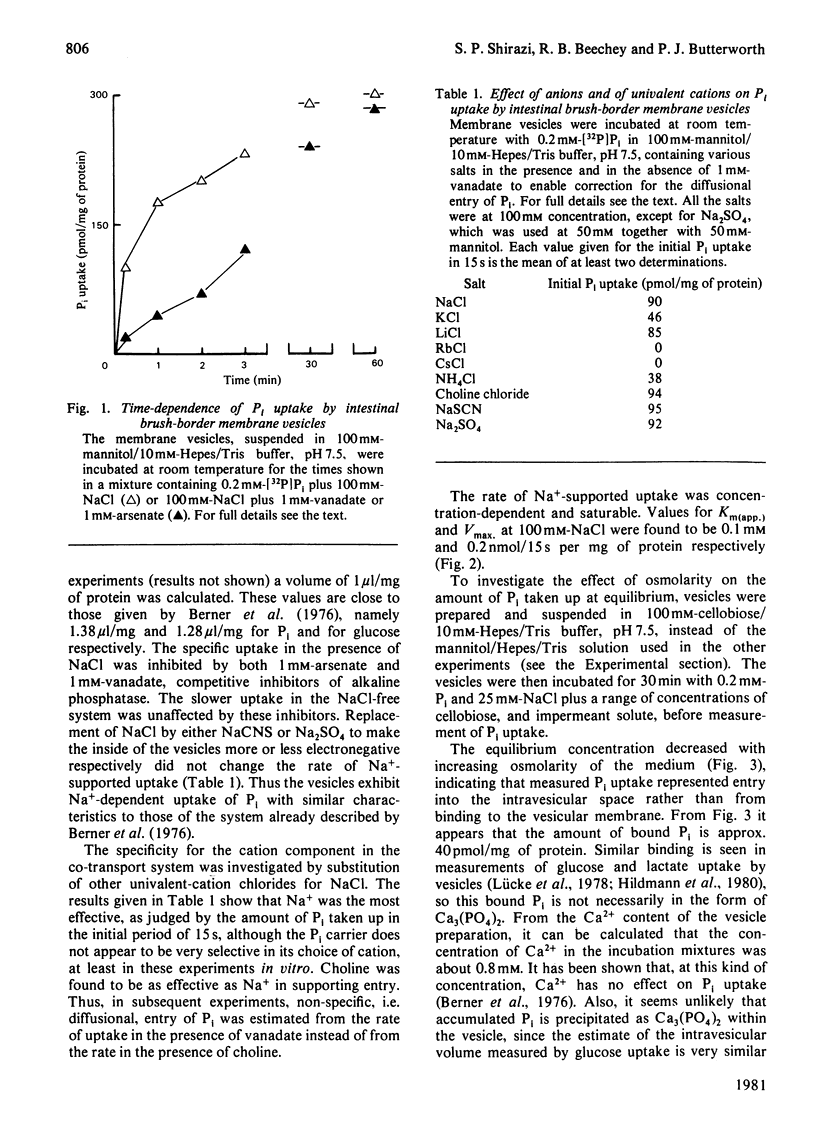
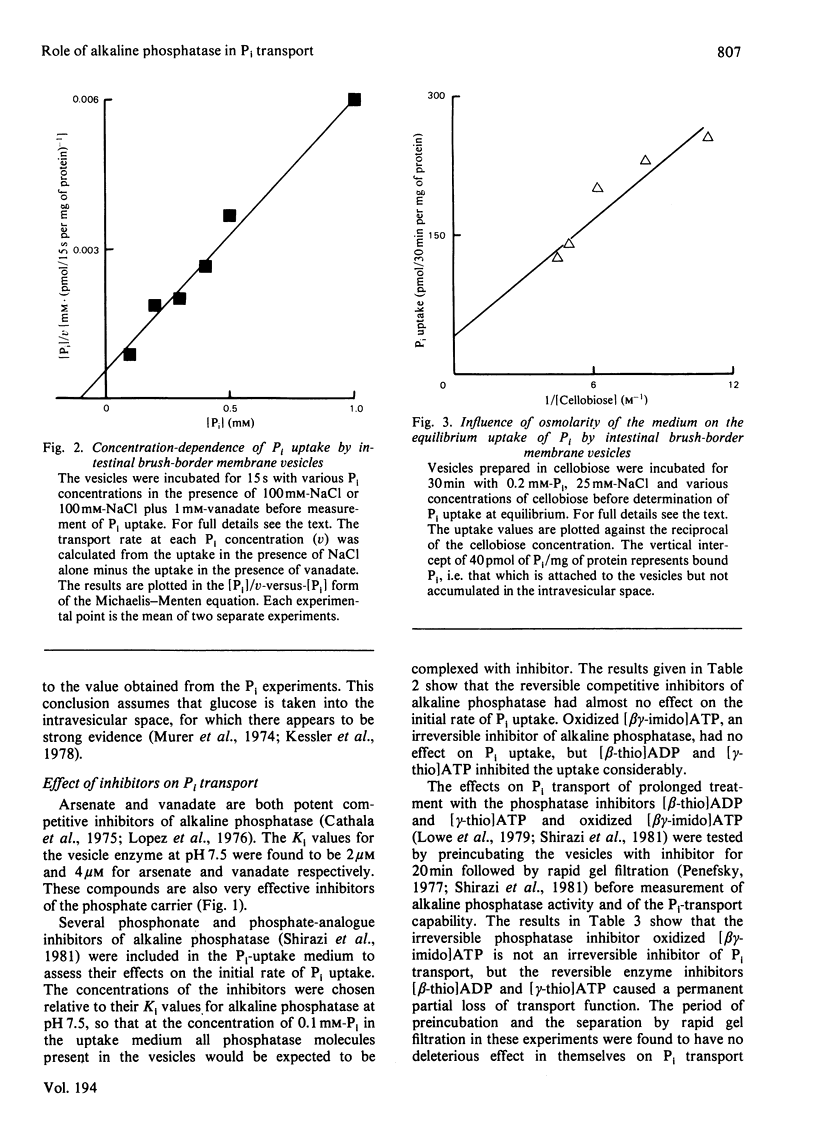
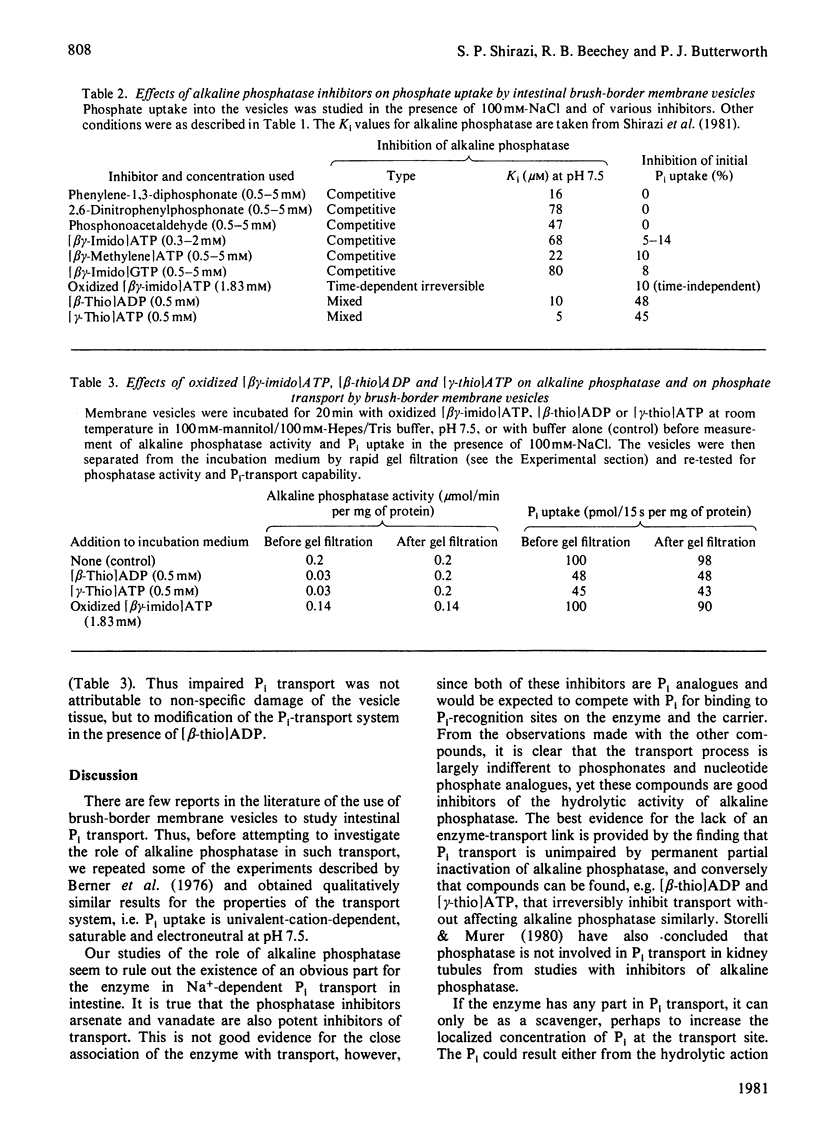
In an investigation of the link between Pi transport and alkaline phosphatase in mammalian small intestine, the characteristics of Pi uptake by brush-border membrane vesicles prepared from rat intestine were compared with the properties of the tissue alkaline phosphatase. The NaCl-dependent Pi uptake had a Km of 0.1 mM at pH 7.5 and was inhibited totally by 1 mM-arsenate and by 1 mM-vanadate. These compounds are also potent competitive inhibitors of the alkaline phosphatase activity of the vesicles, with Ki values less than 5 microM at pH 7.5. When the effect on Pi uptake of several other potent inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase, including phosphonates and phosphate analogues, was tested, however, it was found that there was little, if any, inhibition of transport under conditions in which the inhibition of phosphatase activity was total. Incubation of the vesicles for 20 min with oxidized adenosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate followed by rapid gel filtration to remove the inhibitor resulted in an irreversible loss of phosphatase activity, but left Pi transport unimpaired. Conversely, a similar prolonged incubation with adenosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate or adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate had no effect on alkaline phosphatase activity but resulted in a permanent partial loss of transport capability. The failure to demonstrate an inhibition of Pi transport resulting from inhibition of alkaline phosphatase and the different responses of enzymic activity and Pi transport to irreversible inhibition make it very unlikely that the enzyme is directly involved in the transport system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berner W., Kinne R., Murer H. Phosphate transport into brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):467–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1600467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge S. J., Miller R. The role of phosphate in the action of vitamin D on the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):980–988. doi: 10.1172/JCI108878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Brunel C. Bovine kidney alkaline phosphatase. Catalytic properties, subunit interactions in the catalytic process, and mechanism of Mg2+ stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6046–6053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Peterlik M. Pathways of phosphate transport in chick jejunum: influence of vitamin D and extracellular sodium. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Sep;381(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00583252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J. The uptake and release of calcium by heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):447–456. doi: 10.1042/bj1680447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M., Nagode L. A., Rasmussen H. Induction of intestinal brush border alkaline phosphatase by vitamin D and identity with ca-ATPase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1199–1201. doi: 10.1038/2281199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildmann B., Storelli C., Haase W., Barac-Nieto M., Murer H. Sodium ion/L-lactate co-transport in rabbit small-intestinal brush-border-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):169–176. doi: 10.1042/bj1860169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson S. A., Dousa T. P. Phosphate transport across renal cortical brush border membrane vesicles from rats stabilized on a normal, high or low phosphate diet. Life Sci. 1979 Mar 5;24(10):881–887. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Acuto O., Storelli C., Murer H., Müller M., Semenza G. A modified procedure for the rapid preparation of efficiently transporting vesicles from small intestinal brush border membranes. Their use in investigating some properties of D-glucose and choline transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 4;506(1):136–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Coggins J. R., Dixon H. B. Aldolase-like imine formation in the mechanism of action of phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):409–411. doi: 10.1042/bj1650409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez V., Stevens T., Lindquist R. N. Vanadium ion inhibition of alkaline phosphatase-catalyzed phosphate ester hydrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Baum H., Beechey R. B. Preparation and chemical properties of periodate-oxidized adenosine triphosphate and some related compounds [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):1131–1133. doi: 10.1042/bst0071131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lúcke H., Berner W., Menge H., Murer H. Sugar transport by brush border membrane vesicles isolated from human small intestine. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Mar 20;373(3):243–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00580831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik N., Butterworth P. J. Catalytic and ligand-binding properties of rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Feb;179(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moog F., Glazier H. S. Phosphate absorption and alkaline phosphatase activity in the small intestine of the adult mouse and of the chick embryo and hatched chick. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):321–336. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U., Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Glucose transport in isolated brush-border and lateral-basal plasma-membrane vesicles from intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Mircheff A. K., Adams T. H., Spielvogel A. Studies on the mechanism of action of calciferol. 3. Vitamin D-mediated increase of intestinal brush order alkaline phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):348–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi S. P., Beechey R. B., Butterworth P. J. Potent inhibition of membrane-bound rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase by a new series of phosphate analogues. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):797–802. doi: 10.1042/bj1940797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi S. P., Colston K. W., Butterworth P. J. Alkaline phosphatase: a possible transport protein for inorganic phosphate. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):933–935. doi: 10.1042/bst0060933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R., Kinne R., Murer H. Effect of dietary phosphate intake on phosphate transport by isolated rat renal brush-border vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):465–470. doi: 10.1042/bj1800465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storelli C., Murer H. On the correlation between alkaline phosphatase and phosphate transport in rat renal brush border membrane vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Mar;384(2):149–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00584431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Taylor A. N. Intestinal absorption of phosphate in the chick: effect of vitamin D and other parameters. J Nutr. 1973 Apr;103(4):586–599. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


