Abstract
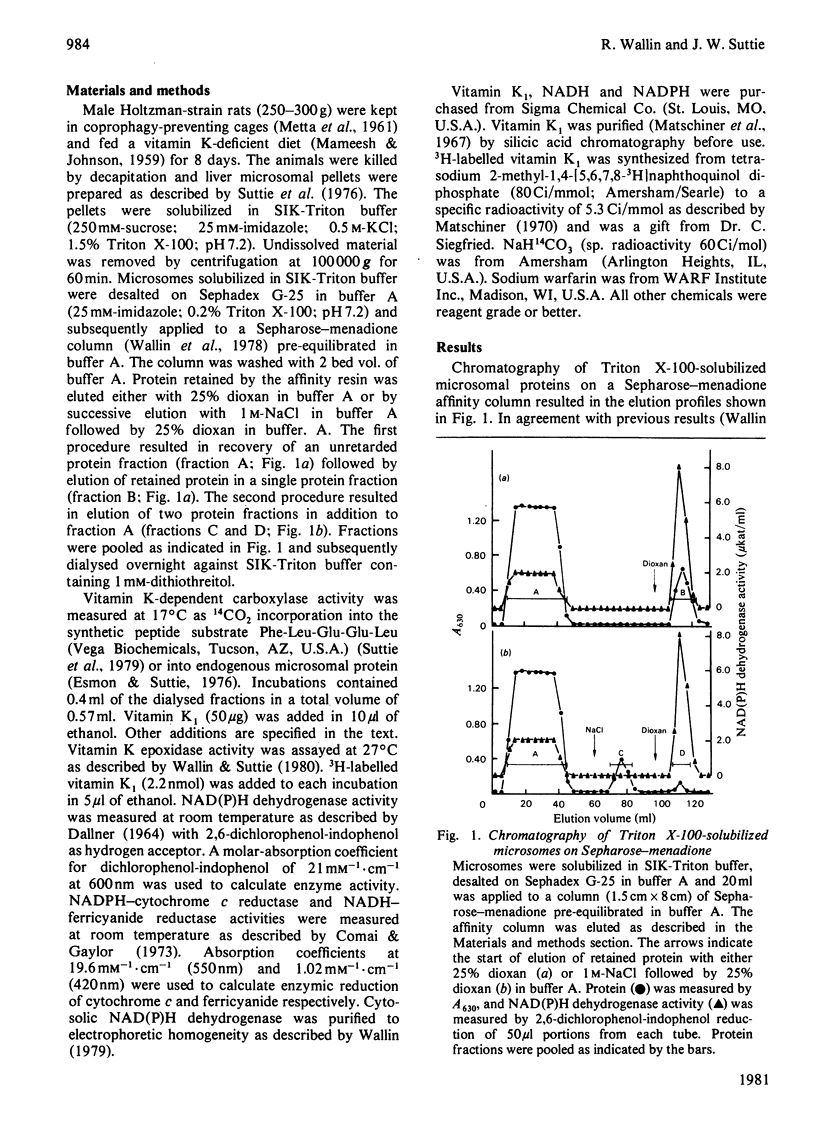
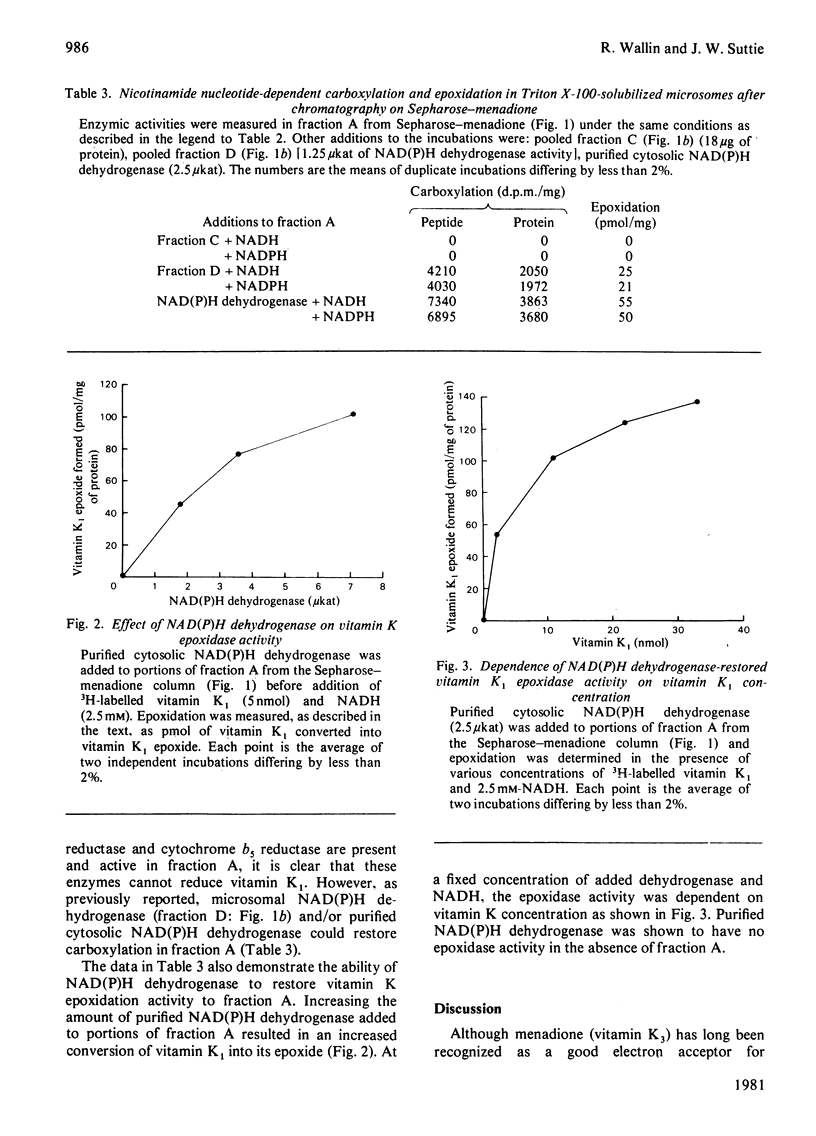
Passage of a Triton X-100-solubilized microsomal systems in vitro that are used to study these reactions is the warfarin-sensitive NAD(P)H dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlisle T. L., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K dependent carboxylase: subcellular location of the carboxylase and enzymes involved in vitamin K metabolism in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1161–1167. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai K., Gaylor J. L. Existence and separation of three forms of cytochrome P-450 from rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4947–4955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Solubilization and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Smith M. W. Epoxidation of several vitamins K by rat liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 15;28(6):937–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koli A. K., Yearby C., Scott W., Donaldson K. O. Purification and properties of three separate menadione reductases from hog liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):621–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAMEESH M. S., JOHNSON B. C. Production of dietary vit. K deficiency in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jul;101(3):467–468. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martius C., Ganser R., Viviani A. The enzymatic reduction of K-vitamins incorporated in the membrane of liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):13–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschiner J. T., Taggart W. V., Amelotti J. M. The vitamin K content of beef liver. Detection of a new form of vitamin K. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1243–1248. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Sato R. Detergent-solubilized NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:102–108. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson R. E., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K and gamma-carboxyglutamate biosynthesis. Vitam Horm. 1977;35:59–108. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftell M., Blomberg K. Immunochemical studies on two DT diaphorase active antigens isolated from rat liver cytosol by affinity chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jan;199(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel H. W., Dignam J. D. Purification and properties of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:89–96. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Geweke L. O., Martin S. L., Willingham A. K. Vitamin K epoxidase: dependence of epoxidase activity on substrates of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation reaction. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 14;109(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hageman J. M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Development of a peptide substrate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5827–5830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Jackson C. M. Prothrombin structure, activation, and biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):1–70. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Larson A. E., Canfield L. M., Carlisle T. L. Relationship between vitamin K-dependent carboxylation and vitamin K epoxidation. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2605–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Lehrman S. R., Geweke L. O., Hageman J. M., Rich D. H. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: requirements for carboxylation of soluble peptide and substrate specificity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91742-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Mechanism of action of vitamin K: synthesis of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):191–223. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER M. M., BRODIE A. F., MERSELIS J. E. Possible role for vitamin K in electron transport. Science. 1958 Oct 17;128(3329):896–898. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3329.896-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Gebhardt O., Prydz H. NAD(P)H dehydrogenase and its role in the vitamin K (2-methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthaquinone)-dependent carboxylation reaction. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):95–101. doi: 10.1042/bj1690095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R. Some molecular properties of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):127–135. doi: 10.1042/bj1810127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: possible artifact of analysis due to a pyridine nucleotide-dependent carboxylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1374–1380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90571-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlon D. S., Sadowski J. A., Suttie J. W. Mechanism of coumarin action: significance of vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibition. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1371–1377. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


