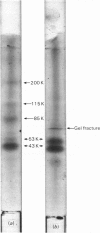
Abstract
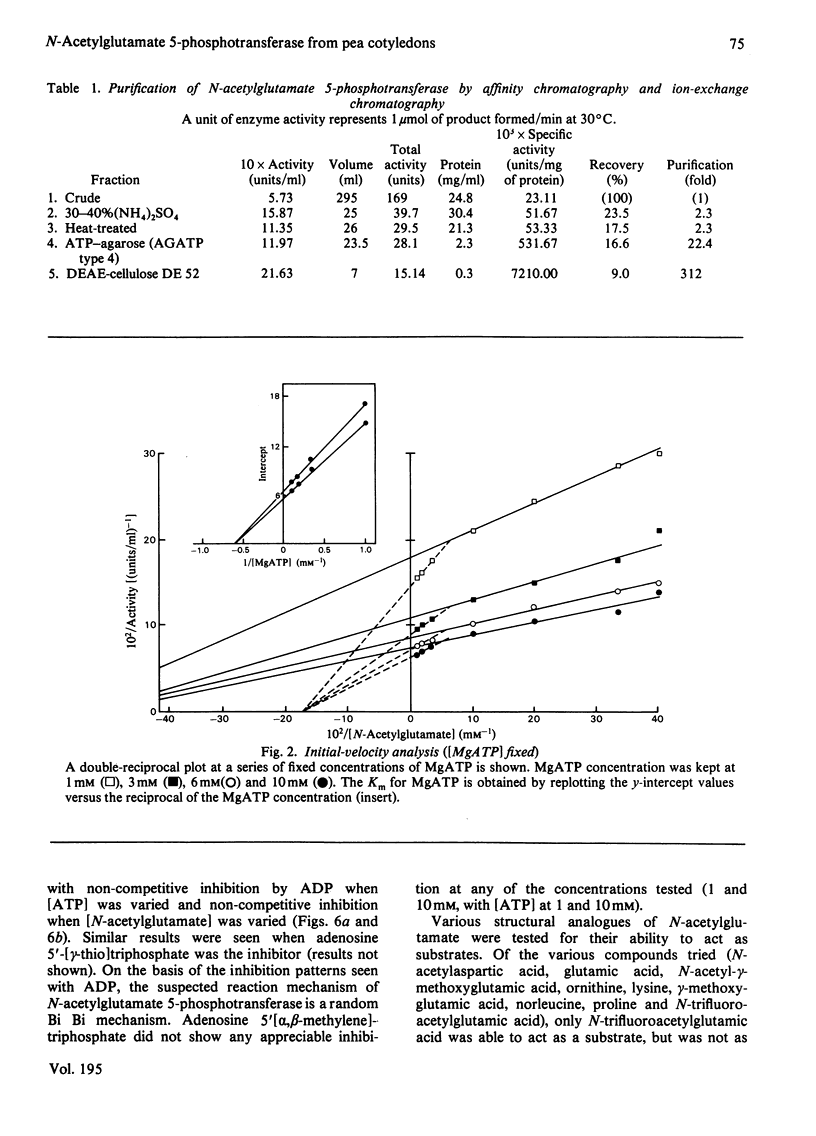
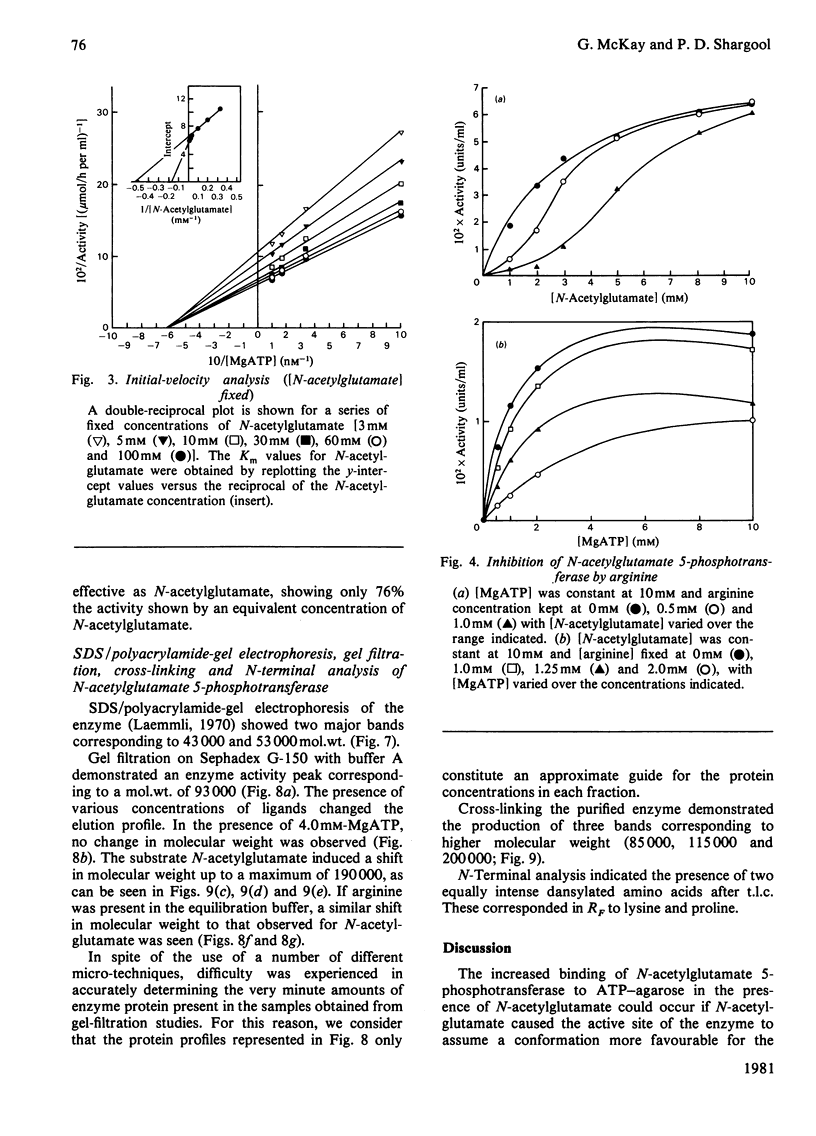
N-Acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase (acetylglutamate kinase, EC 2.7.2.8) has been isolated from pea (Pisum sativum) cotyledons and purified 312-fold by using heat treatment, (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, affinity chromatography on ATP--Sepharose and ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. This preparation was shown on polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis to yield one band staining with Coomassie Blue. The enzyme was shown by a variety of techniques to be composed of two different kinds of subunits, of mol.wts. 43000 and 53000 respectively. These subunits are arranged to give either a dimeric or tetrameric enzyme composed of equal numbers of each type of subunit. The dimeric and tetrameric enzyme forms are thought to be interconvertible, the equilibrium between these forms being influenced by the type of ligand bound to the subunits. Kinetic studies performed on the purified enzyme, indicated a random Bi Bi type of mechanism. The enzyme displayed apparent negative co-operativity with respect to one of its substrates, N-acetylglutamate; as a result, two Km values were found for this substrate, one at 1.9 X 10(-3) M and the other at 6.2 X 10(-3) M. A single Km value for ATP was found to be 1.7 X 10(-3) M. Allosteric regulation by arginine was also shown. A model, based on the Koshland, Némethy & Filmer [(1966) Biochemistry 5, 365-385] Sequential model, which adequately describes the kinetic and structural properties of N-acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase, is presented.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen C. M., Jr, Jones M. E. Studies on the function of N-acyl glutamates in the carbamyl phosphate synthetase reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybis J. J., Davis R. H. Acetylglutamate kinase: a feedback-sensitive enzyme of arginine biosynthesis in Neurospora. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faragó A., Dénes G. Mechanism of arginine biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardti. II. Purification and properties of N-acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase, the allosteric enzyme of the pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 7;136(1):6–18. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Labouesse B. Study of the dansylation reaction of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Leisinger T. N-acetylglutamate 5-phosphotransferase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Purification and ligand-directed association-dissociation. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):365–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G., Wu C. W. Kinetics of allosteric enzymes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):1–33. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHEDOURI E., MEISTER A. SYNTHESIS OF D-BETA-GLUTAMINE FROM BETA-GLUTAMIC ACID BY GLUTAMINE SYNTHETASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3357–3360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. J., Thompson J. F. Formation of N-acetylglutamate by extracts of higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):684–687. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGINO Y., MIYOSHI Y. THE SPECIFIC PRECIPITATION OF ORTHOPHOSPHATE AND SOME BIOCHEMICAL APPLICATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. J. Path of Ornithine Synthesis in Escherichia Coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Jul;39(7):578–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.7.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]