Abstract
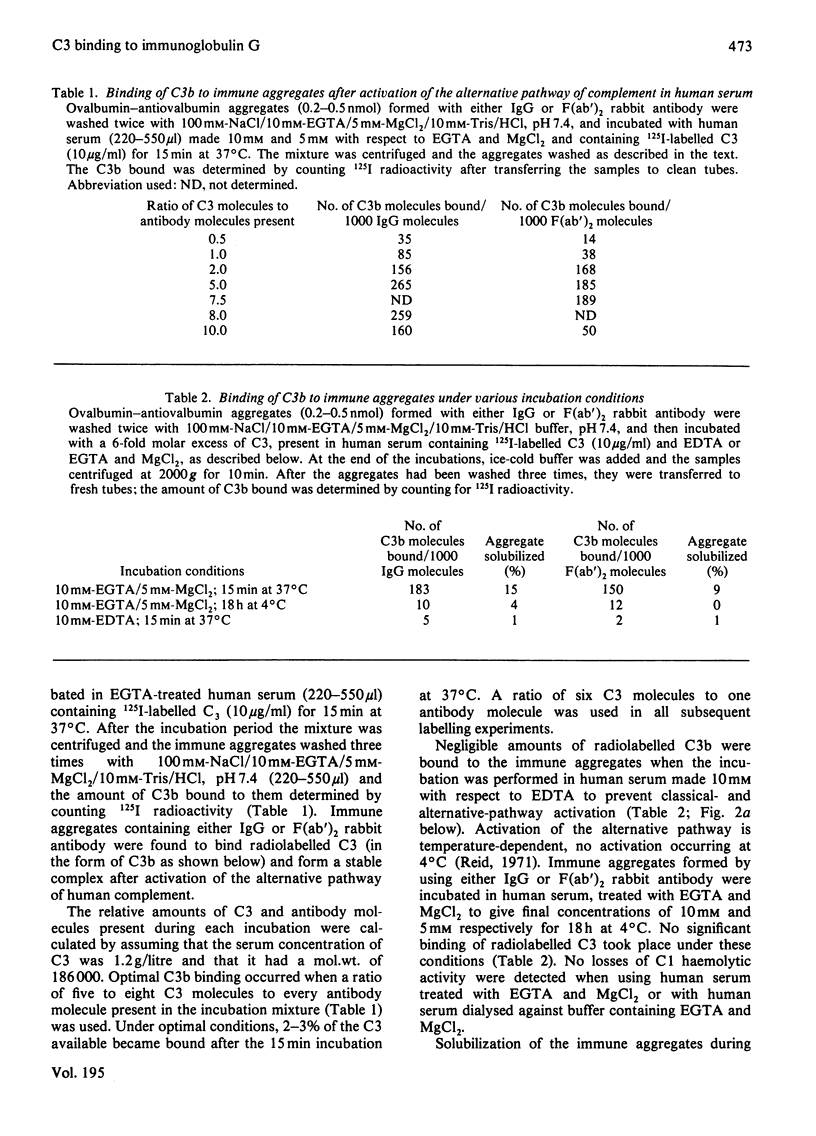
Preformed immune aggregates, containing antigen and either IgG (immunoglobulin G) or F(ab')2 rabbit antibody, were incubated with normal human serum under conditions allowing activation of only the alternative pathway of complement. Both the IgG and F(ab')2 immune aggregates bound C3b, the activated form of the complement component C3, in a similar manner, 2-3% of the C3 available in the serum being bound to the aggregates as C3b, and the rest remaining in the fluid phase as inactive C3b or uncleaved C3. It was found that the C3b was probably covalently bound to the IgG in the aggregates, since C3b-IgG complexes could be demonstrated on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, after repeated washing with buffers containing high salt or boiling under denaturing conditions. Incubation of the C3b-antibody-antigen aggregates in buffers known to destroy ester linkages had little effect on the C3b-IgG complexes, which suggested that C3b and IgG might be linked by an amide bond. Two main types of C3b-IgG complexes were found that had apparent mol.wts. of 360000 and 580000, corresponding to either one to two C3b molecules respectively bound to one molecule of antibody. On reduction of the C3b-IgG complexes it was found that the beta-chain, but not the alpha'-chain, of C3b was released along with all the light chain of IgG but only about half or less of the heavy chain of IgG. These results indicate that, during activation of the alternative pathway of complement by immune aggregates containing IgG antibody, the alpha'-chain of C3b may become covalently bound at one or two sites in the Fd portion of the heavy chain of IgG.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Duplaa A. M., Colomb M. G. Differential elution of Clq, Clr and Cls from human Cl bound to immune aggregates. Use in the rapid purification of Cl subcomponents. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jul;16(7):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis: a simplified method for the preparation of EAC'4 with guinea pig or with human complement. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Boyd J., Brampton A. D., Easterbrook-Smith S. B., Emanuel E. J., Novotny J., Rademacher T. W., van Schravendijk M. R., Sternberg M. J., Dwek R. A. The Clq receptor site on immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):338–344. doi: 10.1038/288338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Dodds A. W., Porter R. R. The binding of human complement component C4 to antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):67–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1890067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel P. J., Groeneboer O., Grosveld G., Pondman K. W. The binding of activated C3 to polysaccharides and immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2566–2572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. C., Cebra J. J. Structural studies of products of antigen-antibody-complement interaction. Immunochemistry. 1968 Jan;5(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Lewis M. S., Folk J. E. Relationships of the catalytic properties of human plasma and platelet transglutaminases (activated blood coagulation factor XIII) to their subunit structures. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):940–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A comparison of methods for the molecular quantitation of the fourth component of human complement. Immunochemistry. 1968 Mar;5(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALMASSO A. P., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. INTERACTION OF AUTOLOGOUS COMPLEMENT WITH RED CELLS IN THE ABSENCE OF ANTIBODY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:643–650. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmasso A. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Physico-chemical characteristics of the third and fourth component of complement after dissociation from complement-cell complexes. Immunology. 1967 Sep;13(3):293–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Kerr M. A. Activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1750383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Takiuchi M., Iida K., Nagaki K., Inai S. The activation mechanism of the alternative pathway of the human complement system by the immune precipitate formed with F(ab')2 of rabbit IgG antibody: the generation of C3- and C5-cleaving enzymes on the immune precipitate. Immunochemistry. 1977 Jan;14(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadd K. J., Reid K. B. Importance of the integrity of the inter-heavy-chain disulphide bond of rabbit IgG in the activation of the alternative pathway of human complement by the F(ab')2 region of rabbit IgG antibody in immune aggregates. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goers J. W., Porter R. R. The assembly of early components of complement on antibody-antigen aggregates and on antibody-coated erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):675–684. doi: 10.1042/bj1750675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B. Methylamine reaction and denaturation-dependent fragmentation of complement component 3. Comparison with alpha2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7082–7084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J., Lorenz P. E., Schechter A. N., Prahl J. W., Tack B. F. Third component of human complement: appearance of a sulfhydryl group following chemical or enzymatic inactivation. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4471–4478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J., Tack B. F., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: structural requirements for its function. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4479–4485. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A. Limited proteolysis of complement components C2 and factor B. Structural analogy and limited sequence homology. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1830615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A. The human complement system: assembly of the classical pathway C3 convertase. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):173–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1890173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., BIRO C. E. ISOLATION AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1963 Sep 1;118:447–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., LEPOW I. H. C'1 ESTERASE EFFECT ON ACTIVITY AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:819–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllerèberhard H. J., Dalmasso A. P., Calcott M. A. The reaction mechanism of beta-1C-globulin (C'3) in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):33–54. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The fractionation of rabbit gamma-globulin by partition chromatography. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):405–410. doi: 10.1042/bj0590405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Ishizaka K. Activation of the alternate pathway of human complements by rabbit cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Oliveira B., Osler A. G. Two complement interaction sites in guinea pig immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Twose T. M., Paterson D. S., Sim E. The covalent-binding reaction of complement component C3. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1930115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Harrison R. A., Janatova J., Thomas M. L., Prahl J. W. Evidence for presence of an internal thiolester bond in third component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5764–5768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tack B. F., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement: assembly of a factor B-dependent C3-convertase on the immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):86–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Hirose S. Solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes: a new function of complement as a regulator of immune reactions. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:134–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Schmidt G., Von Buttlar B., Dieminger L. A new function of the activated third component of complement: binding to C5, an essential step for C5 activation. Immunology. 1978 Jan;34(1):29–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. Variation in the N-terminal sequence of heavy chains of immunoglobulin G from rabbits of different allotype. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):173–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1120173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]