Abstract
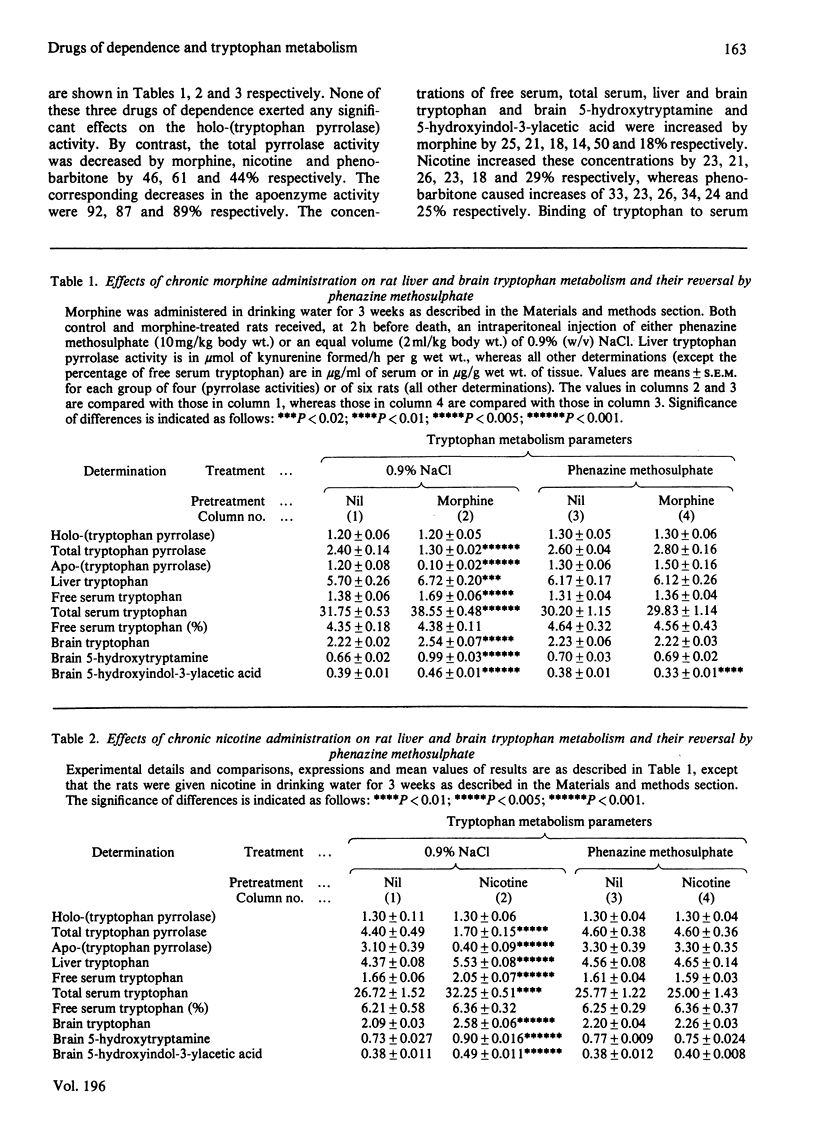
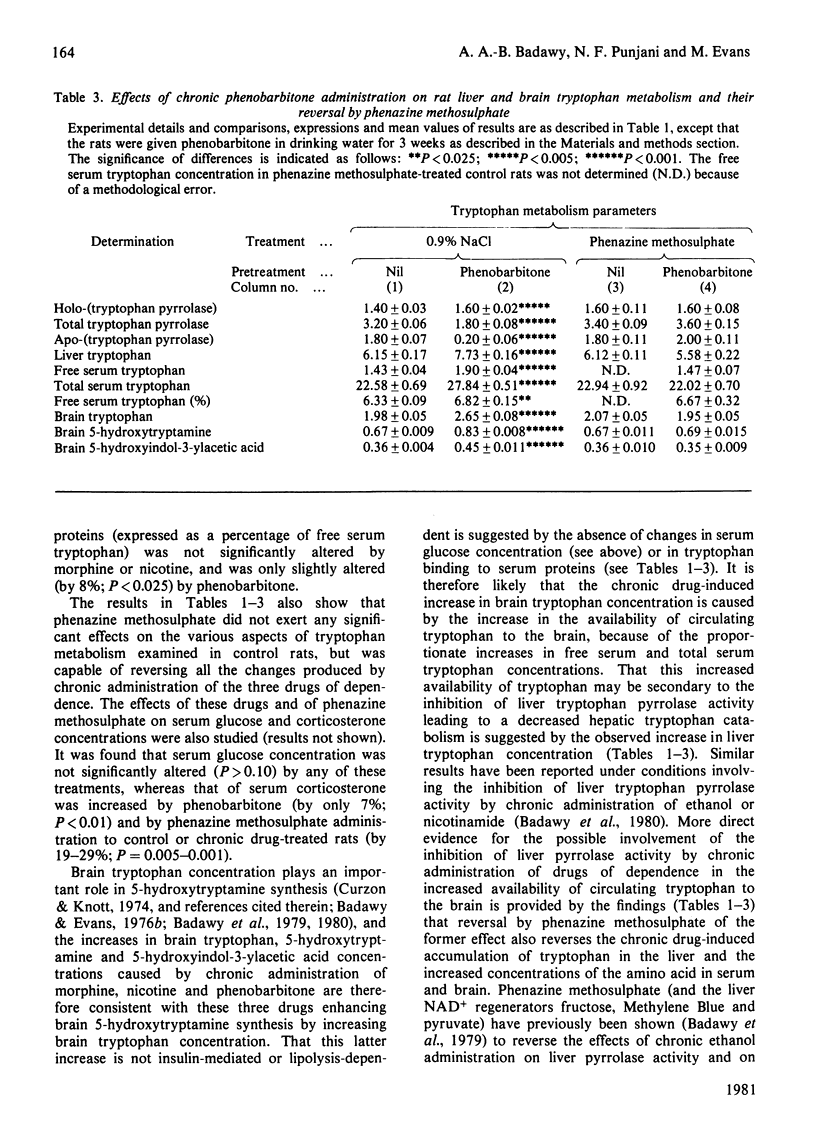
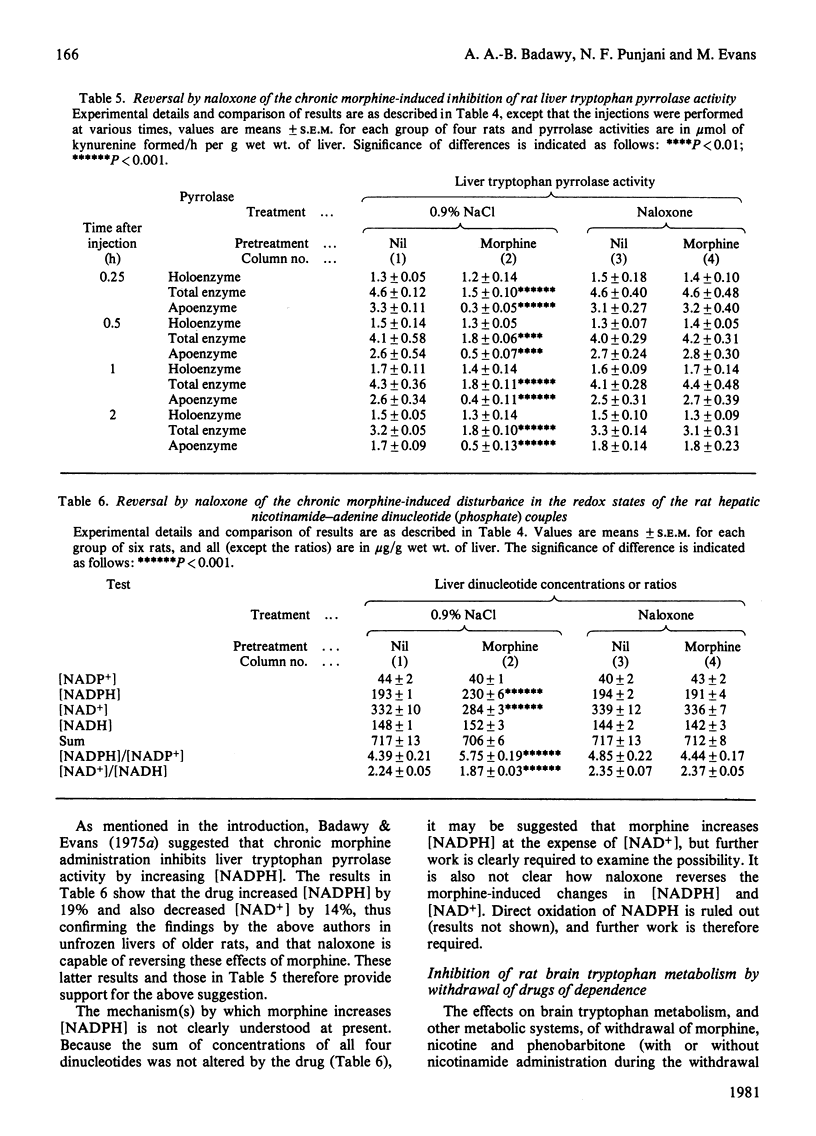
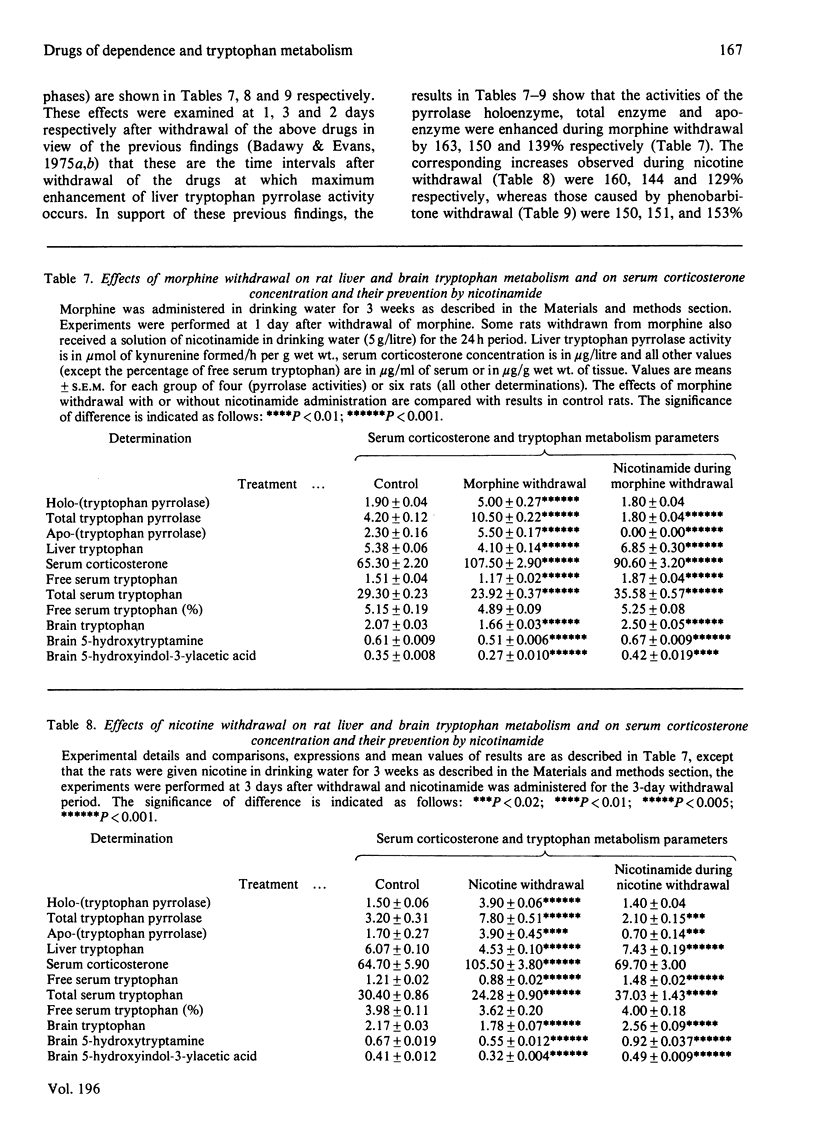
1. Chronic administration of morphine, nicotine or phenobarbitone has previously been shown to inhibit rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by increasing hepatic [NADPH], whereas subsequent withdrawal enhances pyrrolase activity by a hormonal-type mechanism. 2. It is now shown that this enhancement is associated with an increase in the concentration of serum corticosterone. 3. Chronic administration of the above drugs enhances, whereas subsequent withdrawal inhibits, brain 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis. Under both conditions, tryptophan availability to the brain is altered in the appropriate direction. 4. The chronic drug-induced enhancement of brain tryptophan metabolism is reversed by phenazine methosulphate, whereas the withdrawal-induced inhibition is prevented by nicotinamide. 5. The chronic morphine-induced changes in liver [NADPH], pyrrolase activity, tryptophan availability to the brain and brain 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis are all reversed by the opiate antagonist naloxone. 6. It is suggested that the opposite effects on brain tryptophan metabolism of chronic administration and subsequent withdrawal of the above drugs of dependence are mediated by the changes in liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity. 6. Similar conclusions based on similar findings have previously been made in relation to chronic administration and subsequent withdrawal of ethanol. These findings with all four drugs are briefly discussed in relation to previous work and the mechanism(s) of drug dependence.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Regulation of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase by its cofactor haem: Experiments with haematin and 5-aminolaevulinate and comparison with the substrate and hormonal mechanisms. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):511–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1500511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The effects of acute and chronic nicotine hydrogen (+)-tartrate administration and subsequent withdrawal on rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity and their comparison with those of morphine, phenobarbitone and ethanol. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):425–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1480425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The effects of chronic phenobarbitone administration and subsequent withdrawal on the activity of rat liver tryptohan pyrrolase and their resemblance to those of ethanol. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):555–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1350555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The effects of ethanol on tryptophan pyrrolase activity and their comparison with those of phenobarbitone and morphine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;59:229–251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0632-1_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The regulation of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (phosphate). Experiments with glucose and nicotinamide. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1560381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The role of free serum tryptophan in the biphasic effect of acute ethanol administration on the concentrations of rat brain tryptophan, 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindol-3-ylacetic acid. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):315–324. doi: 10.1042/bj1600315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Punjani N. F., Evans C. M., Evans M. Inhibition of rat brain tryptophan metabolism by ethanol withdrawal and possible involvement of the enhanced liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1920449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Punjani N. F., Evans M. Enhancement of rat brain tryptophan metabolism by chronic ethanol administration and possible involvement of decreased liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):575–580. doi: 10.1042/bj1780575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantutova I., Ovcharov R., Koburova K. Changes in the convulsion threshold and in the level of brain biogenic amines in rats chronically treated with phenobarbital or diazepam. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Bulg. 1978;4(2):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benwell M. E., Balfour D. J. Effects of nicotine administration and its withdrawal on plasma corticosterone and brain 5-hydroxyindoles. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 May 8;63(1):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00426913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava H. N., Matwyshyn G. A. Brain serotonin turnover and morphine tolerance-dependence induced by multiple injections in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 1;44(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava H. N. The synthesis rate and turnover time of 5-hydroxy-tryptamine in brains of rats treated chronically with morphine. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):311–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Francis D. L., Henderson G., Schneider C. Quasi morphine-abstinence syndrome. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):471–473. doi: 10.1038/249471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Knott P. J. Effects on plasma and brain tryptophan in the rat of drugs and hormones that influence the concentration of unesterified fatty acid in the plasma. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G. Tryptophan pyrrolase--a biochemical factor in depressive illness? Br J Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;115(529):1367–1374. doi: 10.1192/bjp.115.529.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLICK D., VONREDLICH D., LEVINE S. FLUOROMETRIC DETERMINATION OF CORTICOSTERONE AND CORTISOL IN 0.02-0.05 MILLILITERS OF PLASMA OR SUBMILLIGRAM SAMPLES OF ADRENAL TISSUE. Endocrinology. 1964 Apr;74:653–655. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-4-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Woods H. F., Knott P. G., Curzon G. Letter: Factors influencing effect of hydrocortisone on rat brain tryptophan metabolism. Nature. 1975 May 8;255(5504):170–170. doi: 10.1038/255170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokka N., Garcia J. F., Elliott H. W. Effects of acute and chronic adminstration of narcotic analgesics on growth hormone and corticotrophin (ACTH) secretion in rats. Prog Brain Res. 1973;39:347–360. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapin I. P., Oxenkrug G. F. Intensification of the central serotoninergic processes as a possible determinant of the thymoleptic effect. Lancet. 1969 Jan 18;1(7586):132–136. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing R. B., Flinchbaugh C., Waymire J. C. Changes in brain tryptophan and tyrosine following acute and chronic morphine administration. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Jun;17(6):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punjani N. F., Badawy A. A., Evans M. Prevention by pyrazole of the effects of chronic ethanol administration on the redox states of the hepatic nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) couples and on liver and brain tryptophan metabolism in the rat. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):165–168. doi: 10.1042/bj1840165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen F. H., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Brain serotonin turnover in morphine tolerant and dependent mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Nov;175(2):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F., Sawyer B., Sträuli U. An assay procedure for nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides in rat liver and other tissues. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1964 Jun;72(3):427–447. doi: 10.3109/13813456409065351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way E. L., Ho I. K., Loh H. H. Brain 5-hydroxytryptamine and cyclic AMP in morphine tolerance and dependence. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;10:219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way E. L. Role of serotonin in morphine effects. Fed Proc. 1972 Jan-Feb;31(1):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


