Abstract
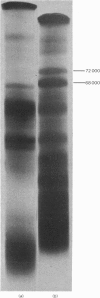
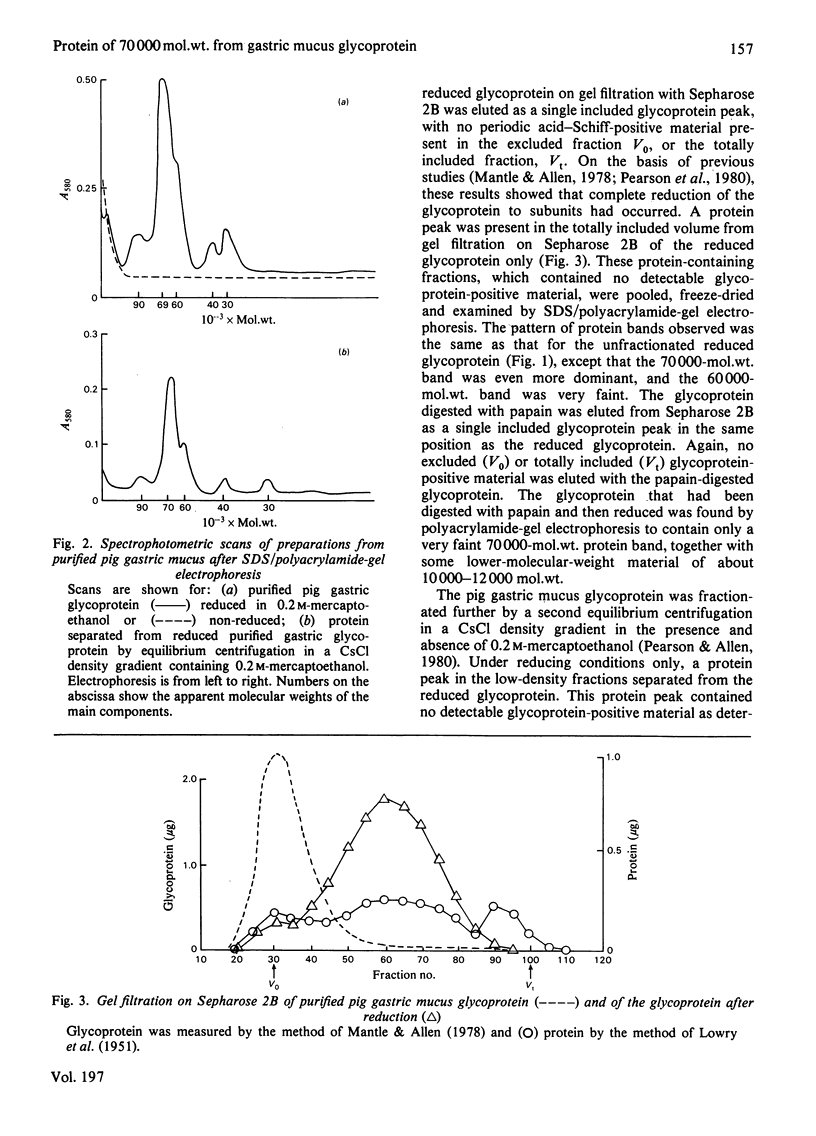
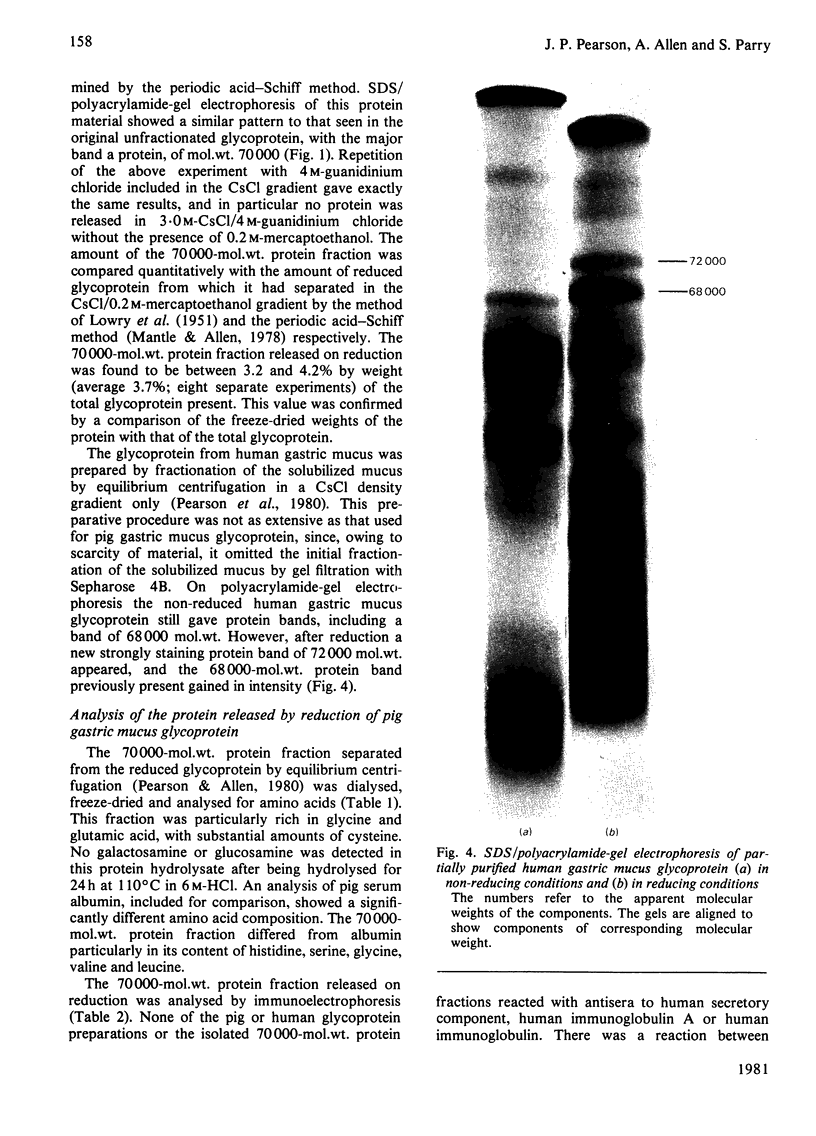
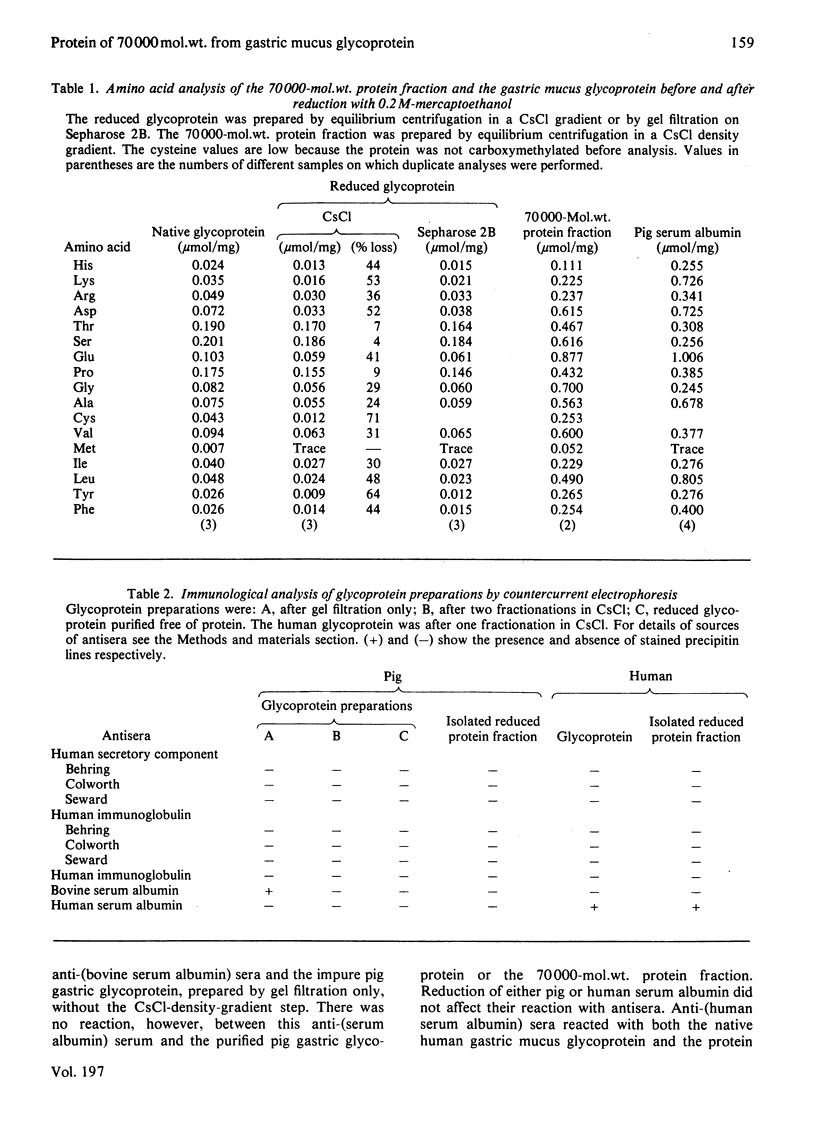
The glycoprotein of pig gastric mucus has been isolated free of non-covalently bound protein as judged by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation. After reduction with 0.2 M-mercaptoethanol, protein was released from the glycoprotein, which consisted of a major 70000-mol.wt. component and a minor 60000-mol.wt. component. The 70000-mol.wt. protein fraction was separated from the reduced glycoprotein by either density-gradient centrifugation in CsCl or by gel filtration. Analysis of the 70000-mol.wt. protein fraction showed that, within the limits of the analysis, it was non-glycosylated, and its amino acid analysis was quite different from that of the reduced glycoprotein, which is high in serine, threonine and proline. There was a ratio of one 70000-mol.wt. protein per native glycoprotein molecule of 2 X 10(6) mol.wt. Dissociation of the native glycoprotein into glycoprotein subunits (5 X 10(5) mol.wt.) by reduction or proteolysis results in the release or hydrolysis respectively of the 70000-mol.wt. protein. A similar 70000-mol.wt. protein is demonstrated in human gastric mucus glycoprotein. A structural role for the proteins in these mucus glycoproteins is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. Structure of gastrointestinal mucus glycoproteins and the viscous and gel-forming properties of mucus. Br Med Bull. 1978 Jan;34(1):28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R. The relationship between secretory immunoglobulin A and mucus [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1579–1581. doi: 10.1042/bst0051579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Bhaskar K. R., Horton J. R., Das I., Lopez-Vidriero M. T., Reid L. The separation and characterization of bronchial glycoproteins by density-gradient methods. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):557–569. doi: 10.1042/bj1670557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M. Constituents of mucus and their separation. Br Med Bull. 1978 Jan;34(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A. Mucus of the mammalian genital tract. Br Med Bull. 1978 Jan;34(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Greenberg J. Human secretory component. Comparison of the form occurring in exocrine immunoglobulin A to the free form. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2744–2750. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Allen A. A colorimetric assay for glycoproteins based on the periodic acid/Schiff stain [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):607–609. doi: 10.1042/bst0060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Mantle D., Allen A. Polymeric structure of pig small-intestinal mucus glycoprotein. Dissociation by proteolysis or by reduction of disulphide bridges. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):277–285. doi: 10.1042/bj1950277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. P., Allen A. A protein of 70 000 molecular weight is joined by disulphide bridges to pig gastric-mucus glycoprotein [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):388–389. doi: 10.1042/bst0080388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Allen A., Venables C. Gastric mucus: isolation and polymeric structure of the undegraded glycoprotein: its breakdown by pepsin. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):709–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P. The role of disulfide bonds in maintaining the gel structure of bronchial mucus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):528–537. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. C., Lynn W. S., Kaufman B. Resolution of the major components of human lung mucosal gel and their capabilities for reaggregation and gel formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):4030–4037. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scawen M., Allen A. The action of proteolytic enzymes on the glycoprotein from pig gastric mucus. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):363–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1630363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Allen A., Pain R. H. Structural studies on gastric mucoproteins: lowering of molecular weight after reduction with 2-mercaptoethanol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):844–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90980-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey B. J., Snary D., Allen A. Characterization of gastric mucoproteins isolated by equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation in caesium chloride. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):633–639. doi: 10.1042/bj1410633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]