Abstract
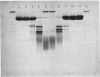
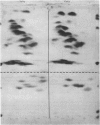
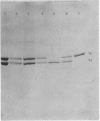
The two dimeric lithocholic acid-binding proteins previously identified as ligandin (YaYa) and glutathione S-transferase B (YaYc) were isolated from rat liver cytosol. These proteins have molecular weights of 44000 and 47000 respectively. The recovery of these two proteins from liver was not affected by the addition of the proteinase inhibitor Trasylol. No spontaneous interconversion between these two proteins was observed on storage. YaYa and YaYc proteins yielded peptides of identical molecular weight after limited digestion with Staphylococcus aureus V8 proteinase. Analytical and preparative tryptic-digest peptide 'maps' showed that all the soluble peptides obtained from YaYa protein were also recovered from YaYc protein. Approximately six extra soluble peptides, which were not recovered from YaYa protein, were obtained from the tryptic digest of YaYc protein. Subdigests of the insoluble tryptic-digest 'cores' also resulted in the recovery of identical peptides from both proteins. Evidence is presented that the Ya subunit possessed by both proteins is identical; glutathione S transferase B is a hybrid of ligandin and glutathione S-transferase AA. The Ya monomer is responsible for lithocholate binding.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Brown L. H. The amino acid sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens azurin. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):784–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1040784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. M., Kirsch R. E., Tuff S. A., Marks I., Saunders S. J. Ligandin heterogeneity : evidence that the two non-identical subunits are the monomers of two distinct proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava M. M., Listowsky I., Arias I. M. Studies on subunit structure and evidence that ligandin is a heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4116–4119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carne T., Tipping E., Ketterer B. The binding and catalytic activities of forms of ligandin after modification of its thiol groups. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):433–439. doi: 10.1042/bj1770433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Smith G. J., Litwack G. Translation in vitro of rat liver messenger RNA coding for ligandin (glutathione S-transferase B). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1899–1902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Fleischner G., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M., Jakoby W. B. The identity of glutathione S-transferase B with ligandin, a major binding protein of liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Neims A. H. A sex difference in hepatic glutathione S-transferase B and the effect of hypophysectomy. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/bj1600223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Strange R. C., Percy-Robb I. W. Cholic acid binding by glutathione S-transferases from rat liver cytosol. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):83–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1850083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Strange R. C., Percy-Robb I. W. Identification of two lithocholic acid-binding proteins. Separation of ligandin from glutathione S-transferase B. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):699–708. doi: 10.1042/bj1810699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Ketterer B., Arias I. M. Ligandin: a hepatic protein which binds steroids, bilirubin, carcinogens and a number of exogenous organic anions. Nature. 1971 Dec 24;234(5330):466–467. doi: 10.1038/234466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully N. C., Mantle T. J. Tissue distribution and subunit structures of the multiple forms of glutathione S-transferase in the rat. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):367–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1930367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R. C., Cramb R., Hayes J. D., Percy-Robb I. W. Partial purification of two lithocholic acid-binding proteins from rat liver 100 000g supernatants. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):425–429. doi: 10.1042/bj1650425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange R. C., Nimmo I. A., Percy-Robb I. W. Equilibrium-dialysis studies of the interaction between cholic acid and 100000g-supernatant preparations from the rat liver. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1560427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher D. R. The partial amino acid sequence of the extracellular beta-lactamase I of Bacillus cereus 569/H. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):313–326. doi: 10.1042/bj1470313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]