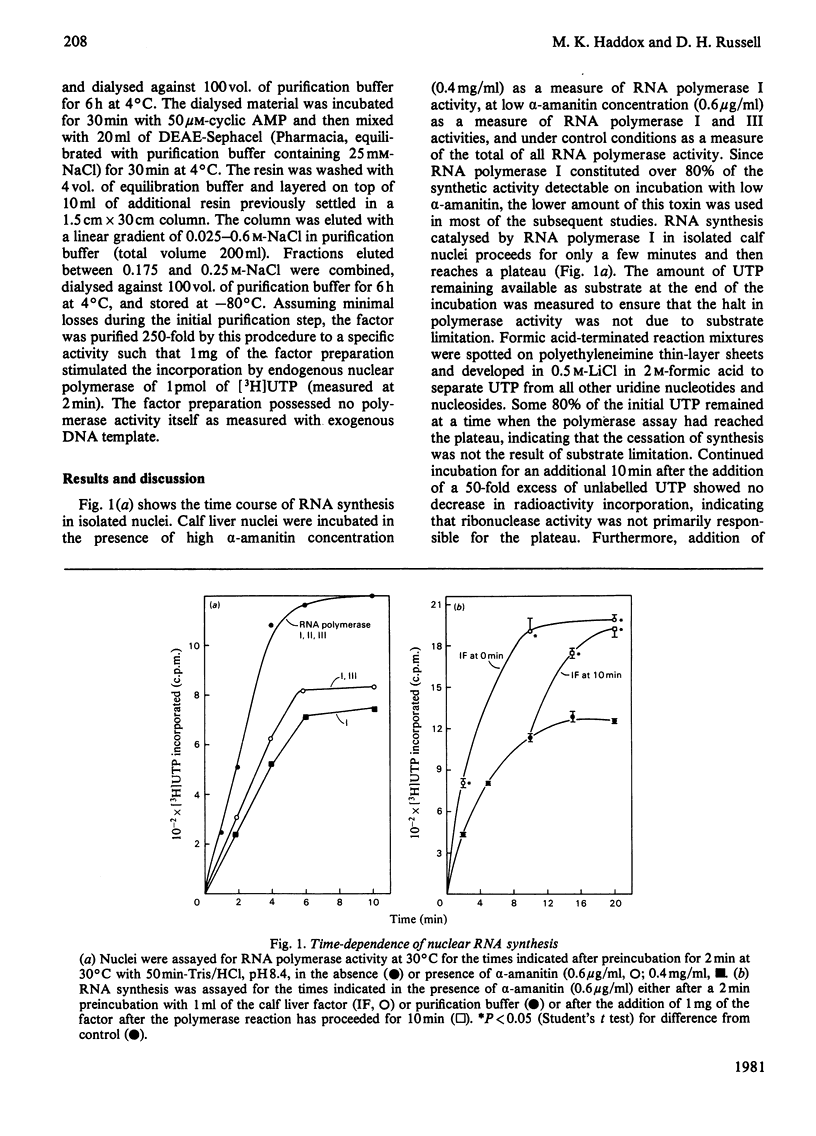
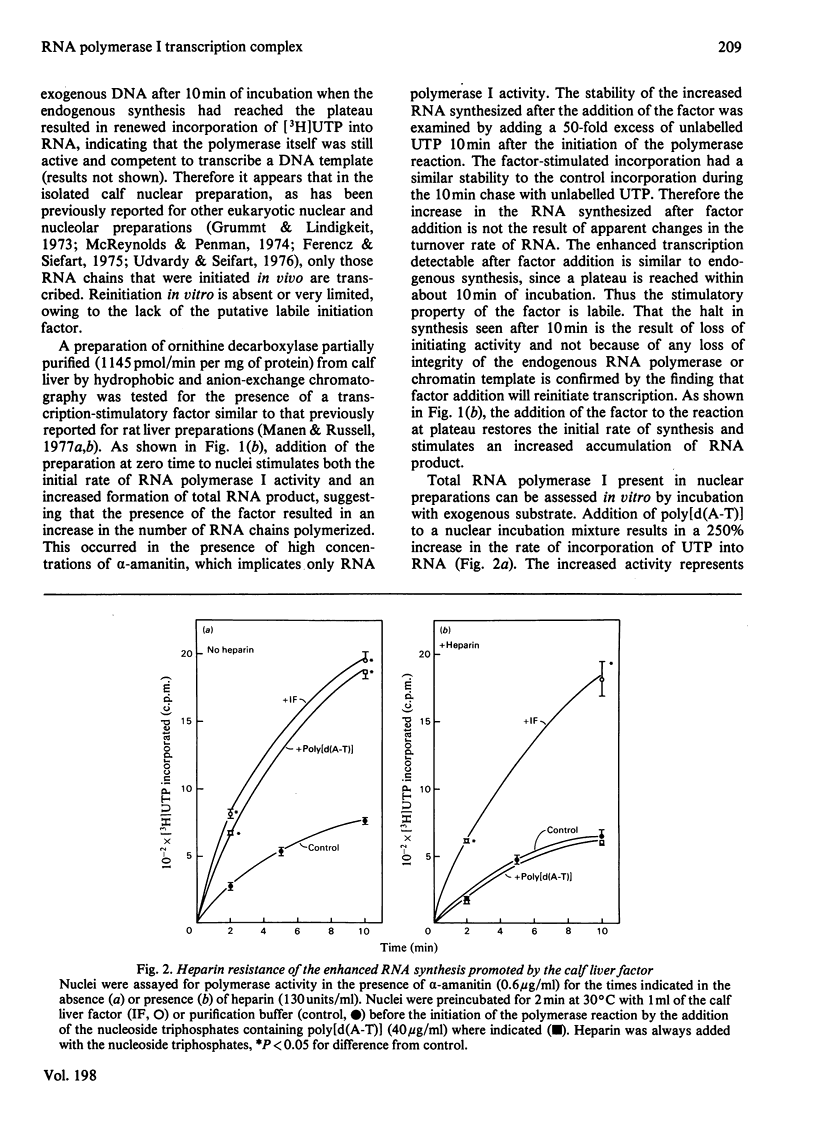
Abstract
A soluble factor partially purified from calf liver increases transcription by RNA polymerase I in isolated nuclei. Addition of the factor to reactions which have reached a plateau owing to the inability to reinitiate on the endogenous chromatin template restores the initial rate of synthesis and stimulates an increased accumulation of RNA product. The RNA synthesis stimulated by factor addition is identical with that initiated in vivo in that it is resistant to heparin disruption.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of chromatin in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):237–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Coupar B. E., Butterworth P. H., Green M. H. Studies on the control of ribosomal RNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):79–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Transcription of high-molecular-weight RNA from hen-oviduct chromatin by bacterial and endogenous form-B RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. C., Perry R. P. Aberrant intranucleolar maturation of ribosomal precursors in the absence of protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):554–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferencz A., Seifart K. H. Comparative effect of heparin on RNA synthesis of isolated rat-liver nucleoli and purified RNA polymerase A. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernańdez M. T., Fontanive-Sengüesa A. V. Effect of amino acids on the alpha-amanitin-insensitive RNA polymerase activity in the isolated nuclei of Ehrlich ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 26;331(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90420-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. I., Perriard J. C., Rutter W. J. Purification of rat liver and mouse ascites DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1655–1665. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K. J., Pogo A. O. Control mechanism of ribonucleic acid synthesis in eukaryotes. The effect of amino acid and glucose starvation and cycloheximide on yeast deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):568–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Lindigkeit R. Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated rat-liver nucleoli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):244–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Smith V. A., Grummt F. Amino acid starvation affects the initiation frequency of nucleolar RNA polymerase. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Muramatsu M., Sugano H. Isolation of nucleoli from rat liver in the presence of magnesium ions. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert A., Feigelson P. A short lived polypeptide component of one of two discrete functional pools of hepatic nuclear alpha-amanitin resistant RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):1030–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen C. A., Russell D. H. Regulation of RNA polymerase I activity by ornithine decarboxylase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 15;26(24):2379–2384. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen C., Russel D. H. Ornithine decarboxylase may function as an initiation factor for RNA polymerase I. Science. 1977 Feb 4;195(4277):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.835013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., Penman S. Pre-4S RNA made in isolated HeLa cell nuclei terminates with U. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Seifart K. H. Transcription of specific genes in isolated nuclei from HeLa cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):353–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems M., Penman M., Penman S. The regulation of RNA synthesis and processing in the nucleolus during inhibition of protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):177–187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. Cortisone stimulation of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2177–2180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


