Abstract
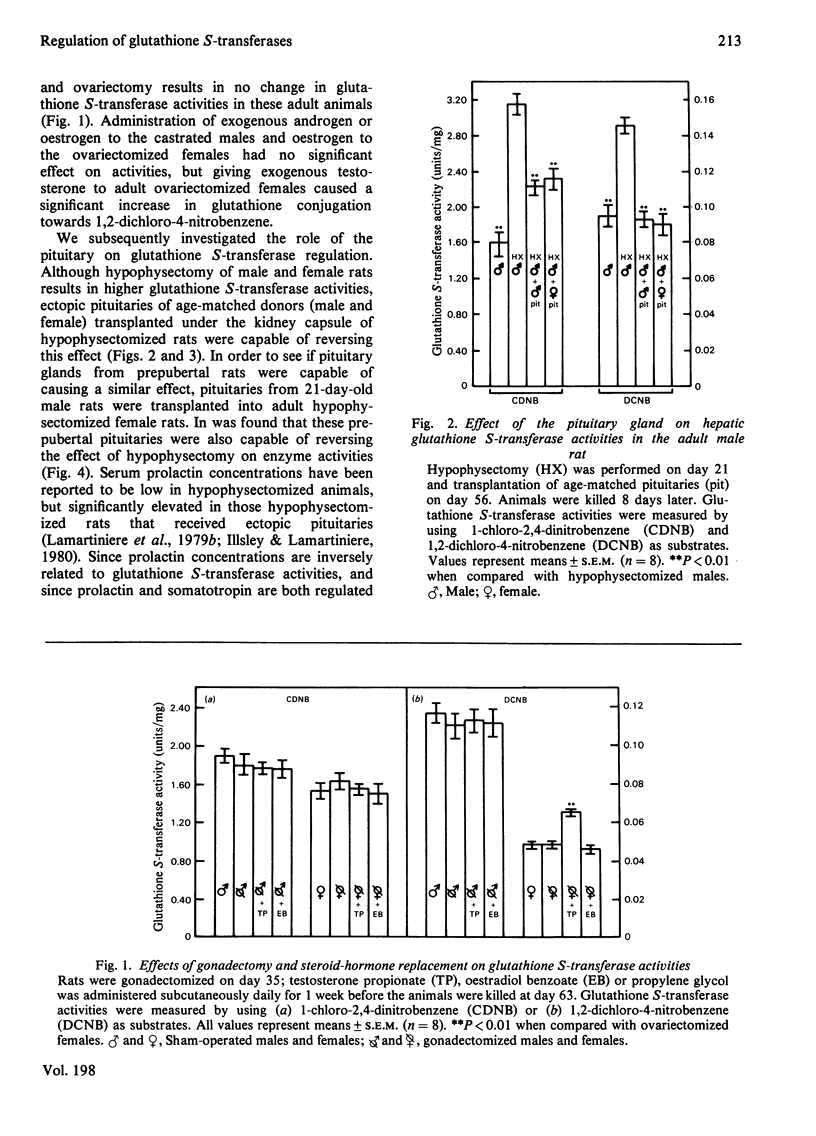
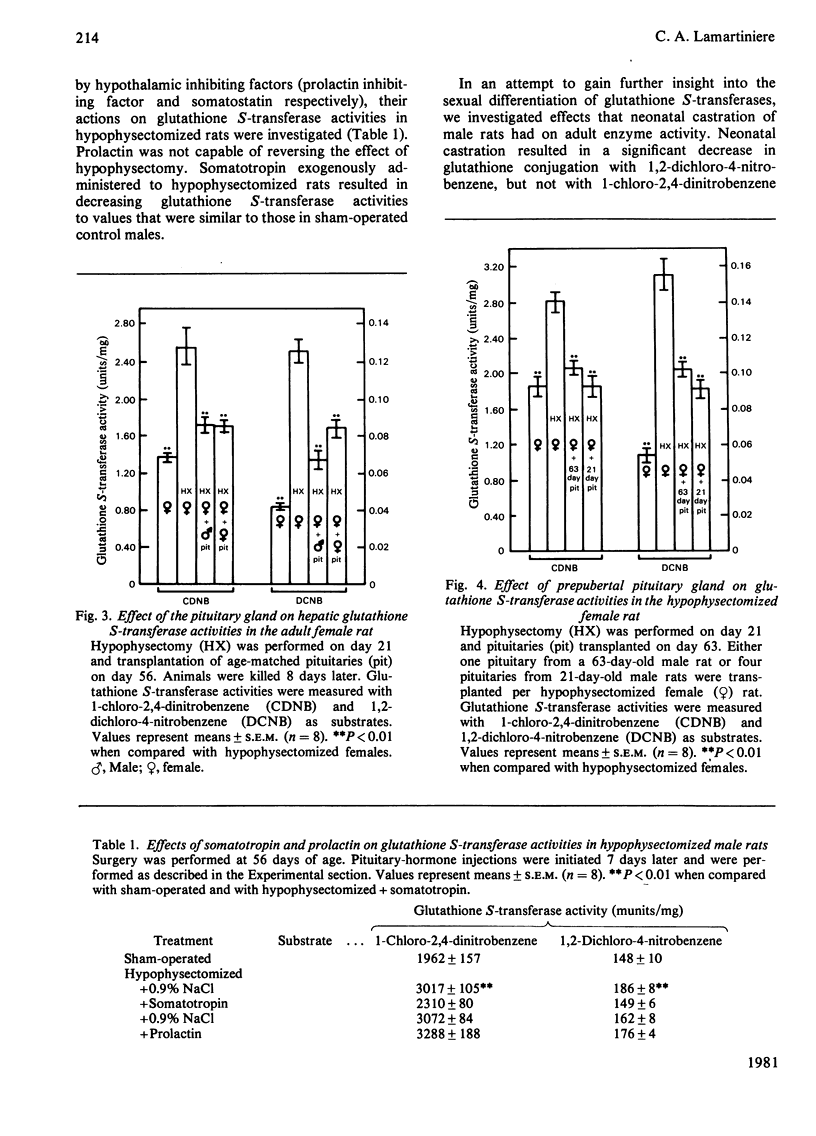
Hepatic glutathione S-transferase activities were determined with the substrates 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Sexual differentiation of glutathione S-transferase activities is not evident during the prepubertal period, but glutathione conjugation with 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene is 2–3-fold greater in adult males than in females. Glutathione conjugation with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene is slightly higher in adult males than adult females. No change in activity was observed after postpubertal gonadectomy of males or females. Neonatal castration of males results in a significant decrease in glutathione conjugation with 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene. Hypophysectomy, or hypophysectomy followed by gonadectomy did result in significantly higher glutathione S-transferase activities in both sexes. These increases can be reversed by implanting an adult male or female pituitary or four prepubertal pituitaries under the kidney capsule. Postpubertal sexual differentiation of glutathione S-transferase activities is neither dependent on pituitary sexual differentiation nor pituitary maturation. Prolactin concentrations are inversely related to glutathione S-transferase activities in hypophysectomized rats with or without ectopic pituitaries. Somatotropin exogenously administered to hypophysectomized rats results in decreased glutathione S-transferase activities, whereas prolactin has no effect. Adult male rats treated neonatally with monosodium l-glutamate to induce arcuate nucleus lesions of the hypothalamus have decreased glutathione S-transferase activities towards 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene and decreased somatotropin concentrations. Our experiments suggests that sexual differentiation of hepatic glutathione S-transferase is a result of a hypothalamic inhibiting factor in the male (absent in the female). This postpubertally expressed inhibiting factor acts on the pituitary to prevent secretion of a pituitary inhibiting factor (autonomously secreted by the female), resulting in higher glutathione S-transferase activities in the adult male than the adult female.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darby F. J., Grundy R. K. Glutathione S-aryltransferase: the effect of treating male and female rats with phenobarbitone on the apparent kinetic parameters for the conjugation of 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with glutathione. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):175–177. doi: 10.1042/bj1280175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieringer C. S., Lamartiniere C. A., Lucier G. W. Sex differences in pituitary-gonadal regulation of hepatic 5 alpha-reductase and 16 alpha-hydroxylase. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Nov-Dec;11(5-6):1519–1525. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Gustafsson J. A., Stenberg A. Neonatal imprinting of liver microsomal hydroxylation and reduction of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4987–4997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J. A., Stenberg A. On the obligatory role of the hypophysis in sexual differentiation hepatic metabolism in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1462–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Neims A. H. A sex difference in hepatic glutathione S-transferase B and the effect of hypophysectomy. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/bj1600223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Neims A. H. Developmental aspects of glutathione S-transferase B (ligandin) in rat liver. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):231–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1600231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Neims A. H. Induction of rat hepatic glutathione S-transferase B by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 15;26(6):555–556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illsley N. P., Lamartiniere C. A. The imprinting of adult hepatic monoamine oxidase levels and androgen responsiveness by neonatal androgen. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):551–556. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione transferases. Catalysis of nucleophilic reactions of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5654–5657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamartiniere C. A., Dieringer C. S., Kita E., Lucier G. W. Altered sexual differentiation of hepatic uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase by neonatal hormone treatment in rats. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):313–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1800313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamartiniere C. A., Dieringer C. S., Lucier G. W. Altered ontogeny of glutathione S-transferases by 2,4,5-2',4',5'-hexachlorobiphenyl. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;51(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. S. Interactions between hormones and nerve tissue. Sci Am. 1976 Jul;235(1):48–58. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0776-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff C. B., Lipton M. A., Kizer J. S. Models of neuroendocrine regulation: use of monosodium glutamate as an investigational tool. Dev Neurosci. 1978;1(2):102–109. doi: 10.1159/000112561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Studies of Y and Z, two hepatic cytoplasmic organic anion-binding proteins: effect of drugs, chemicals, hormones, and cholestasis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2242–2252. doi: 10.1172/JCI106721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumbaugh R. C., Colby H. D. Is growth hormone the pituitary feminizing factor mediating the actions of estradiol on hepatic drug and steroid metabolism? Endocrinology. 1980 Sep;107(3):719–724. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-3-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg A., Eneroth P., Gustafsson J. A., Skett P. In vitro techniques for studies on pituitary regulation of rat liver enzymes. J Steroid Biochem. 1977 May;8(5):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(77)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


