Abstract
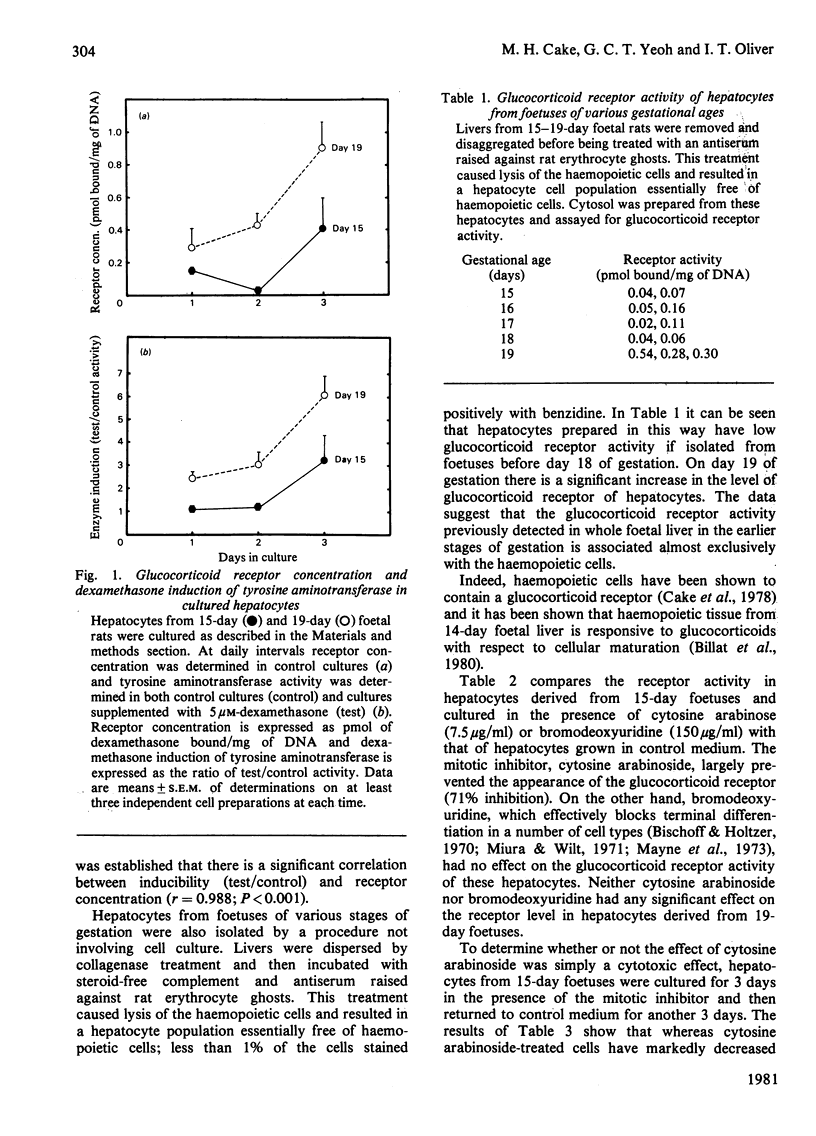
The glucocorticoid receptor activity that can be detected in the liver from 15-day foetal rats would appear to be associated with the haemopoietic cells. In hepatocytes, purified by culture for 1-2 days from 15-day foetal rats, the glucocorticoid receptor activity is low and dexamethasone does not induce the enzyme tyrosine aminotransferase. If culture is continued both receptor activity and steroid responsiveness are acquired. Cultured hepatocytes from 19-day foetal liver contain receptor from the first day of culture and, furthermore, the subsequent level of response to glucocorticoids is directly correlated with the actual receptor concentration. It would appear that the glucocorticoid receptor is not acquired by hepatocytes until after 18 days of gestation. Nevertheless, the fact that bromodeoxyuridine has no effect on the rate of accumulation of receptor in hepatocytes suggests that the differentiative event leading to the subsequent appearance of the receptor has already occurred before day 15 of gestation. However, the acquisition of the receptor would appear to be dependent on mitosis as cytosine arabinoside can inhibit the process.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M., Feigelson P. Glucocorticoid-binding proteins of rat liver cytosol. I. Separation and identification of the binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7890–7896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Inhibition of myoblast fusion after one round of DNA synthesis in 5-bromodeoxyuridine. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jan;44(1):134–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cake M. H., Ghisalberti A. V., Oliver I. T. Cytoplasmic binding of dexamethasone and induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in neonatal rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90791-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croizat B., Granelli-Piperno A., Gros F. Induction de la tyrosine amino transférase en cultures primaires de foie foetal de rat. Effets inducteurs des stéroïdes et du dibutyryl AMP cyclique. Biochimie. 1974;56(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D. Ontogeny of rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptors. Endocrinology. 1974 Nov;95(5):1219–1227. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-5-1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz J. M., Knox W. E. The effect of development and hydrocortisone on tryptophan oxygenase, formamidase, and tyrosine aminotransferase in the livers of young rats. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3464–3471. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G. Ontogeny of glucocorticoid receptors in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5847–5851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Bersch N., Cline M. J. Potentiation of erythropoiesis in vitro by dexamethasone. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):57–62. doi: 10.1172/JCI108269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Dewey H. K. The premature deposition or lysis of glycogen in livers of fetal rats injected with hydrocortisone or glucagon. Dev Biol. 1970 Mar;21(3):452–461. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Federman M., Knox W. E. Cytomorphometry of developing rat liver and its application to enzymic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):261–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O. The hormonal regulation of enzymes in penatal and postnatal rat liver. Effects of adenosine 3',5'-(cyclic)-monophosphate. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):19–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1150019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost A. Problems of fetal endocrinology: the adrenal glands. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1966;22:541–574. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9825-5.50017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallos J., Fasy T. M., Hollander V. P., Bick M. D. Estrogen receptor has enhanced affinity for bromodeoxyuridine-substituted DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4896–4900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees G. J., Weiner N. An examination of the catalytic properties of several aminotransferases in brain and liver by means of an improved radiometric assay with dinitrophenylhydrazine. J Neurochem. 1975 Sep;25(3):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb06973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Dorfman A. The irreversible inhibition of differentiation of limb-bud mesenchyme by bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1253–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Abbott J., Holtzer H. Requirement for cell proliferation for the effects of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine on cultures of chick chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 15;77(1):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90575-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. V., Jr, Thompson E. B. Radioactive assay for tyrosine aminotransferase. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura Y., Wilt F. H. The effects of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on yolk sac erythropoiesis in the chick embryo. J Cell Biol. 1971 Mar;48(3):523–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER I. T., BLUMER W. F., WITHAM I. J. FREE RIBOSOMES DURING MATURATION OF RAT LIVER. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1963 Sep;10:33–38. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(63)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parchman L. G., Cake M. H., Litwack G. Functionality of the liver glucocorticoid receptor during the life cycle and development of a low-affinity membrane binding site. Mech Ageing Dev. 1978 Mar;7(3):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Chapeville F., Jacquot R. Development of glycogen storage ability under cortisol control in primary cultures of rat fetal hepatocytes. Dev Biol. 1973 May;32(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Higgins S. J., Tomkins G. M. Steroid-induced nuclear binding of glucocorticoid receptors in intact hepatoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):539–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENI F., KENNEY F. T., KRETCHMER N. Factors influencing the development of tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase activity in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):609–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S., Litwack G. Effects of age and sex on 3H-cortisol uptake, binding and metabolism in liver and on enzyme induction capacity. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1448–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks W. D. Induction of tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase in fetal rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):900–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh G. C., Bennett F. A., Oliver I. T. Hepatocyte differentiation in culture. Appearance of tyrosine aminotransferase. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):153–160. doi: 10.1042/bj1800153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh G. C., Oliver I. T. The effect of cytosine arabinoside and bromodeoxyuridine on the appearance of tyrosine aminotransferase in cultured foetal hepatocytes of the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bj1880929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


