Abstract
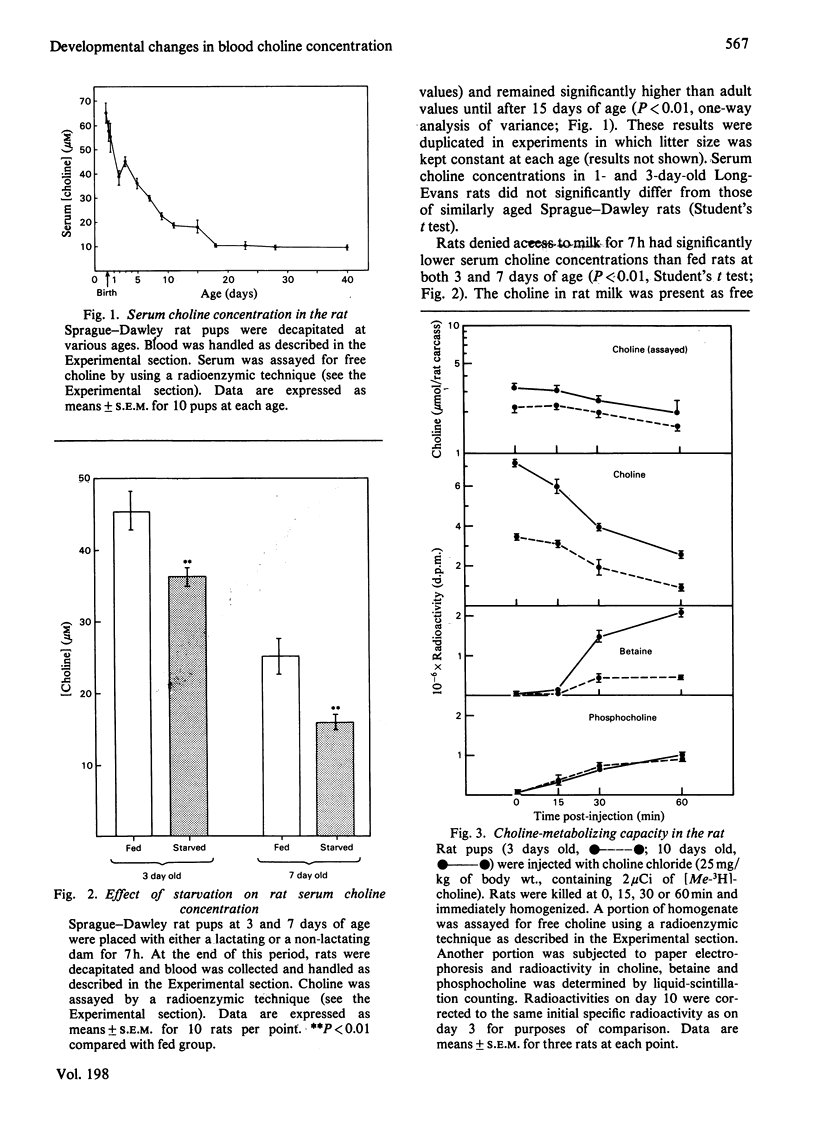
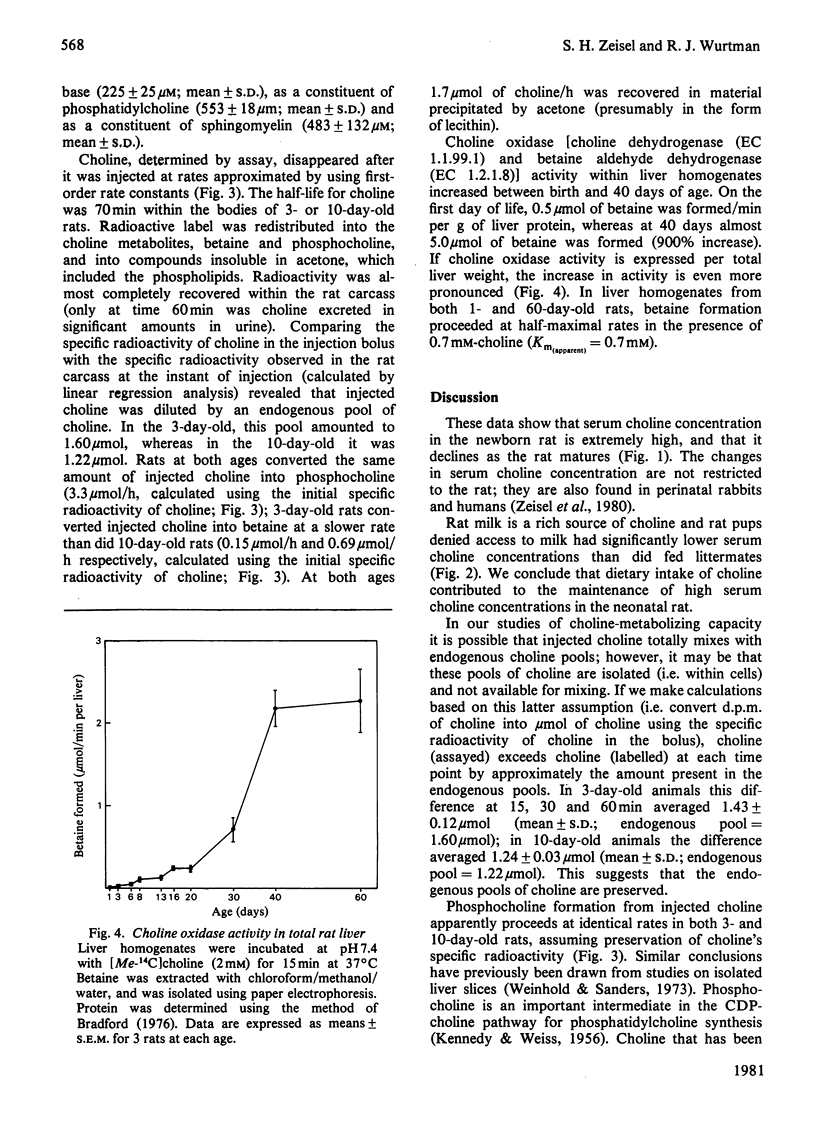
1. Serum choline concentration in the newborn rat is extremely high and declines as the rat matures until adult values are attained at 20 days of age. 2. Rat milk is a rich source of choline, and rat pups denied access to milk had significantly lower serum choline concentrations than did fed littermates. We conclude that dietary intake of choline contributes to the maintenance of high serum choline concentrations in the neonatal rat. 3. In vivo, choline disappears with a half-life of 70 min. It is converted into betaine, phosphocholine and phosphatidylcholine. The rate of phosphocholine formation is identical in 3- and 10-day-old rats (3.3 mumol/h), whereas the rate of betaine formation is slower in younger animals (0.15 mumol/h at 3 days versus 0.69 mumol/h at 10 days). In vitro, choline oxidase activity [choline dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.99.1) and betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.8)] increased between birth and 40 days of age. The age-related acceleration in choline's conversion into betaine probably tends to diminish unesterified choline concentration in the rat.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. J., Cornatzer W. E. Rat kidney glycerylphosphorylcholine diesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Wurtman R. J. Brain acetylcholine: increase after systemic choline administration. Life Sci. 1975 Apr 1;16(7):1095–1102. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. F., Farrell P. M. The choline incorporation pathway: primary mechanism for de novo lecithin synthesis in fetal primate lung. Pediatr Res. 1975 Aug;9(8):658–665. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197508000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck L., Kulovich M. V., Eidelman A. I., Cordero L., Khazin A. F. Biochemical development of surface activity in mammalian lung. IV. Pulmonary lecithin synthesis in the human fetus and newborn and etiology of the respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1972 Feb;6(2):81–99. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197202000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. M., McCaman R. E. The determination of picomole amounts of acetylcholine in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubrich D. R., Wang P. F., Chippendale T., Proctor E. Choline and acetylcholine in rats: effect of dietary choline. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1305–1313. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. R., Cornatzer W. E., Duerre J. A. Relationship between tissue levels of S-adenosylmethionine, S-adenylhomocysteine, and transmethylation reactions. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jan;57(1):56–65. doi: 10.1139/o79-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth D. R., Portman O. W. Formation of choline from phospholipid precursors: a comparison of the enzymes involved in phospholipid catabolism in the brain of the rhesus monkey. Physiol Chem Phys. 1973;5(5):365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Lombardi B. Effects of dietary choline and N,N-dimethylaminoethanol on lung phospholipid and surfactant of newborn rats. Pediatr Res. 1978 Sep;12(9):952–955. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197809000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladinsky H., Consolo S., Peri G., Garattini S. Acetylcholine, choline and choline acetyltransferase activity in the developing brain of normal and hypothyroid rats. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1947–1952. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Patterson L. M., Robison R. The phosphatase activity of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1934;28(2):720–724. doi: 10.1042/bj0280720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann P. J., Quastel J. H. The oxidation of choline by rat liver. Biochem J. 1937 Jun;31(6):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj0310869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Murphy W. Electrophoresis of acetylcholine, choline and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jul 7;16(7):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. J., Armstrong M. J. Billiary lecithin secretion. II. Effects of dietary choline and biliary lecithin synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter A., Field P. M., Raisman G. Muscarinic receptofs in the central nervous system of the rat. III. Postnatal development of binding of [3H]propylbenzilylcholine mustard. Brain Res. 1979;180(2):185–205. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(79)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Kanfer J. Phosphatidohydrolase activity in a solubilized preparation from rat brain particulate fraction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jul;169(1):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorimachi M., Kataoka K. High affinity choline uptake: an early index of cholinergic innervation in rat brain. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 29;94(2):325–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Arvidson G., Akesson B. Pathways for the incorporation of choline into rat liver phosphatidylcholines in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 8;280(4):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel S. H., Epstein M. F., Wurtman R. J. Elevated choline concentration in neonatal plasma. Life Sci. 1980 May 26;26(21):1827–1831. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90585-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


