Abstract
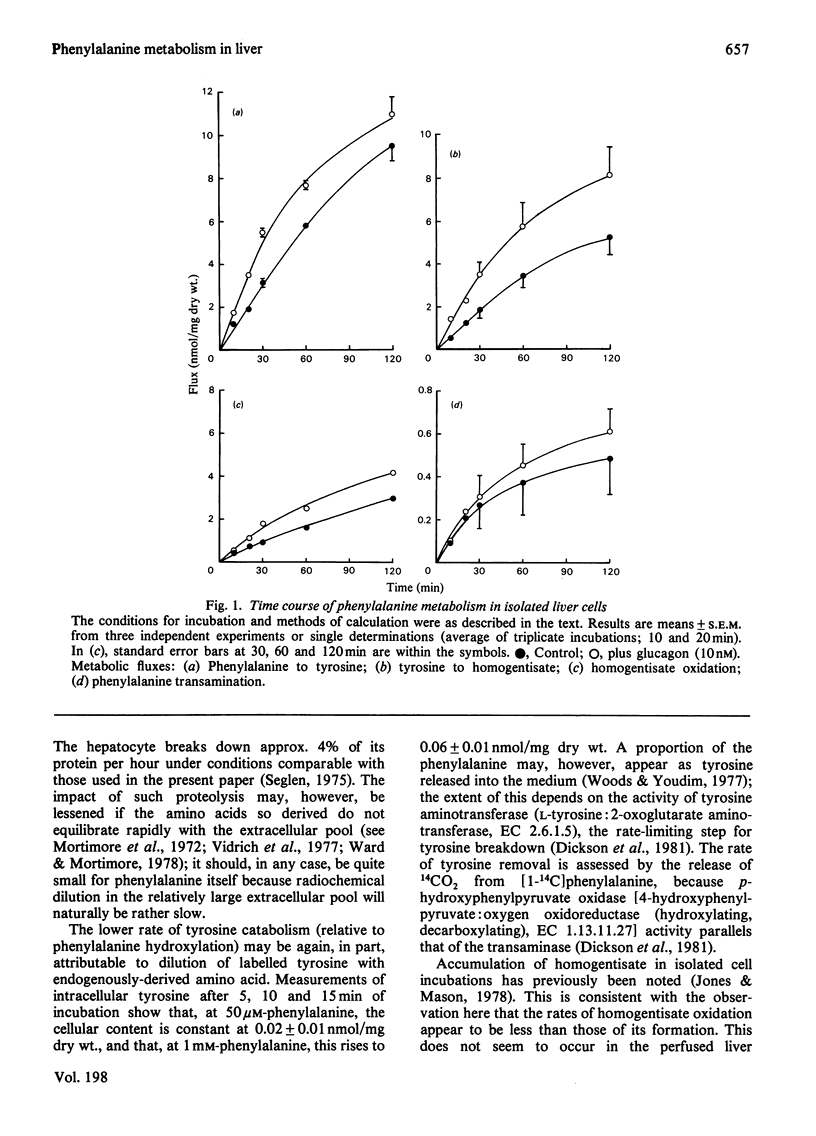
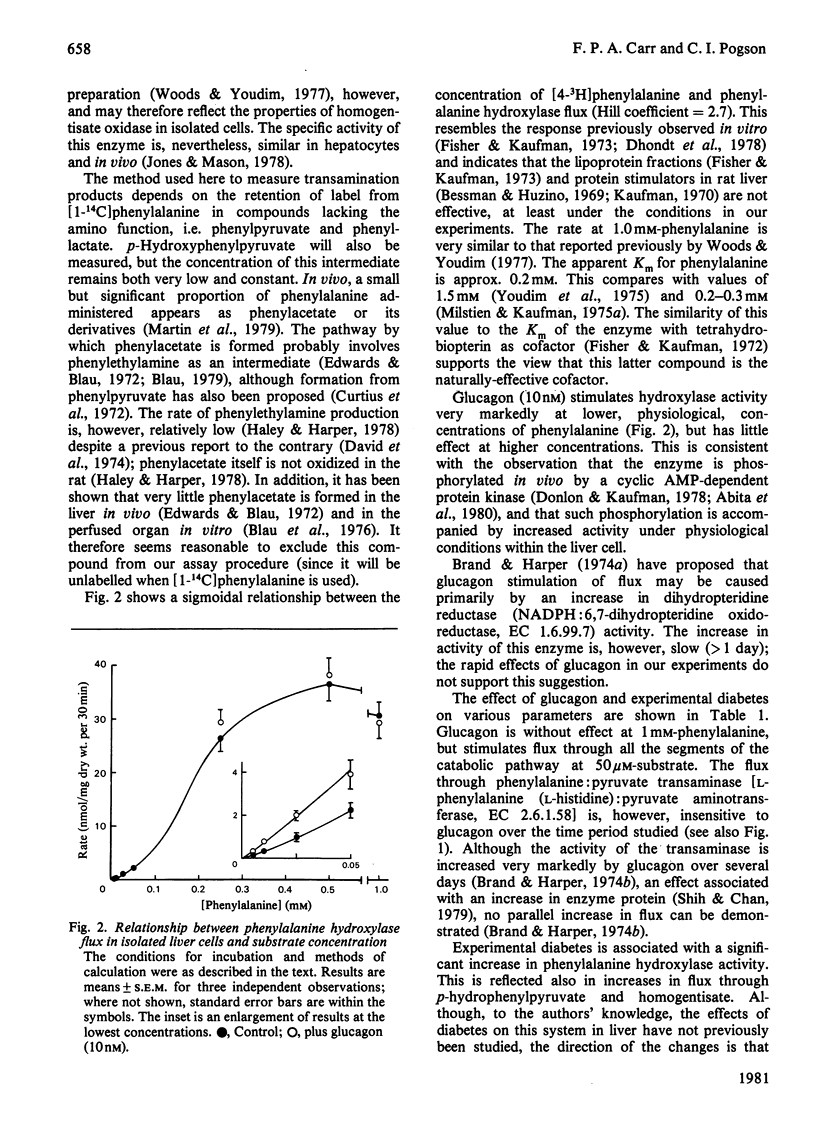
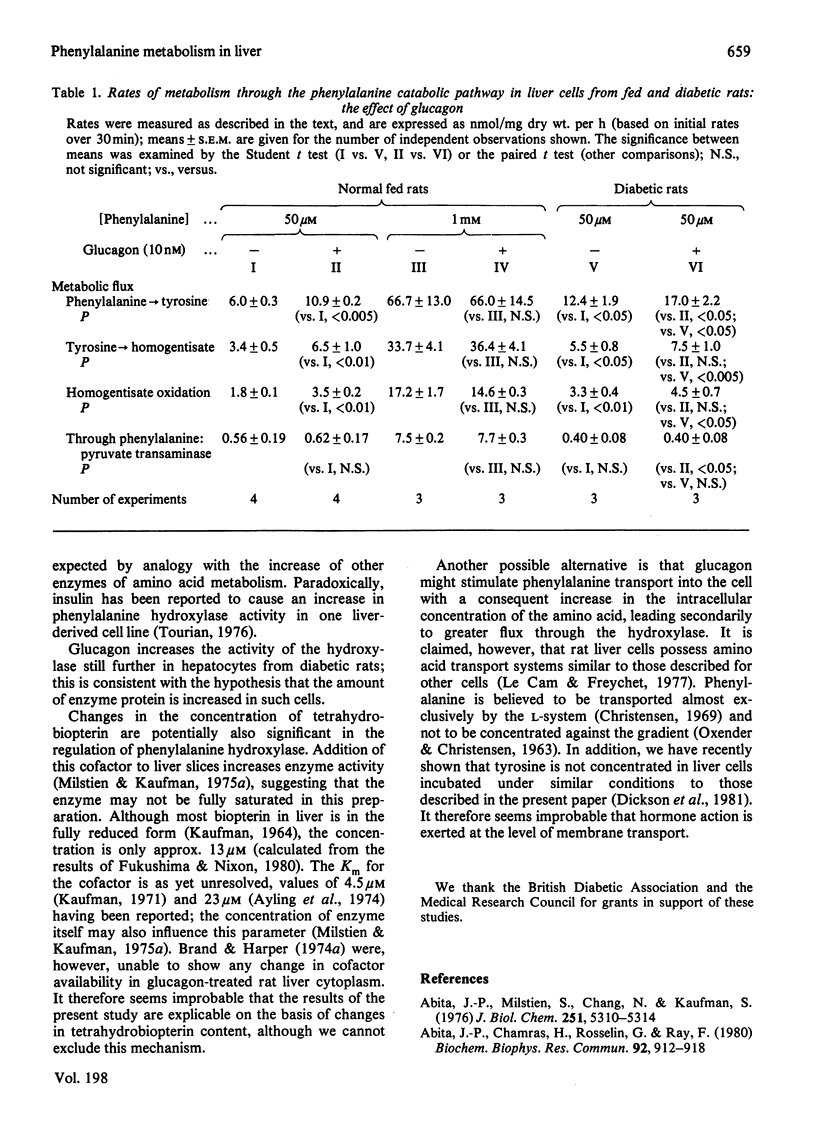
1. Methods are described for monitoring the metabolic flux through phenylalanine hydroxylase, the tyrosine catabolic pathway and phenylalanine: pyruvate transaminase in isolated liver cell incubations. 2. The relationship between hydroxylase flux and phenylalanine concentration is sigmoidal. 3. Glucagon increases hydroxylase activity at low, near-physiological, substrate concentrations only. The hormone does not affect the rate of formation of phenylpyruvate. 4. Experimental diabetes (for 10 days) increases phenylalanine catabolism, and this is further increased by glucagon. 5. These results are discussed in the light of the known mechanisms for control of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abita J. P., Chamras H., Rosselin G., Rey F. Hormonal control of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):912–918. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90789-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abita J. P., Milstien S., Chang N., Kaufman S. In vitro activation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5310–5314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayling J. E., Pirson W. D., al-Janabi J. M., Helfand G. D. Kidney phenylalanine hydroxylase from man and rat. Comparison with the liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):78–85. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L. M., Harper A. E. Effect of glucagon on phenylalanine metabolism and phenylalanine-degrading enzymes in the rat. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):231–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1420231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L. M., Harper A. E. Studies on the functional significance of rat liver phenylalanine:pyruvate aminotransferase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):211–215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Some special kinetic problems of transport. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:1–20. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtius H. C., Völlmin J. A., Baerlocher K. The use of deuterated phenylalanine for the elucidation of the phenylalanine-tyrosine metabolism. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:277–285. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. C., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. On the importance of decarboxylation in the metabolism of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhondt J. L., Dautrevaux M., Biserte G., Farriaux J. P. Phenylalanine analogues as inhibitors of phenylalanine-hydroxylase from rat liver. New conclusions concerning kinetic behaviors of the enzyme. Biochimie. 1978;60(8):787–794. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson A. J., Marston F. A., Pogson C. I. Tyrosine aminotransferase as the rate-limiting step for tyrosine catabolism in isolated rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 5;127(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson A. J., Pogson C. I. The metabolic integrity of hepatocytes in sustained incubations. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon J., Kaufman S. Glucagon stimulation of rat hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase through phosphorylation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6657–6659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon J., Kaufman S. Relationship between the multiple forms of rat hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase and degree of phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2146–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. J., Blau K. Aromatic acids derived from phenylalanine in the tissues of rats with experimentally induced phenylketonuria-like characteristics. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):495–503. doi: 10.1042/bj1300495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kaufman S. The stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by lysolecithin and -chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4345–4353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kaufman S. The stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2250–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima T., Nixon J. C. Analysis of reduced forms of biopterin in biological tissues and fluids. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):176–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Abramowitz A. A simple radioisotope assay for phenylalanine hydroxylase. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jun;19(3):548–555. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Daly J. W., Jerina D. M., Renson J., Witkop B., Udenfriend S. Hydroxylation-induced migration: the NIH shift. Recent experiments reveal an unexpected and general result of enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1524–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3796.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley C. J., Harper A. E. The importance of transamination and decarboxylation in phenylalanine metabolism in vivo in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Aug;189(2):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. D., Coulson R. A., Hernandez T. Free amino acids in the caiman and rat. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1966 Feb;17(2):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(66)90589-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. P., Mason H. S. Metabolic hypoxia: accumulation of tyrosine metabolites in hepatocytes at low pO2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. A protein that stimulates rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4751–4759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. The phenylalanine hydroxylating system from mammalian liver. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;35:245–319. doi: 10.1002/9780470122808.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Neutral amino acid transport. Characterization of the A and L systems in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Karoum F., Wyatt R. J. Phenylacetic acid excretion in man. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien S., Kaufman S. Studies on the phenylalanine hydroxylase system in liver slices. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4777–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien S., Kaufman S. Studies on the phenylalanine hydroxylase system in vivo. An in vivo assay based on the liberation of deuterium or tritium into the body water from ring-labeled L-phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4782–4785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Woodside K. H., Henry J. E. Compartmentation of free valine and its relation to protein turnover in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2776–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OXENDER D. L., CHRISTENSEN H. N. DISTINCT MEDIATING SYSTEMS FOR THE TRANSPORT OF NEUTRAL AMINO ACIDS BY THE EHRLICH CELL. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3686–3699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes is inhibited by ammonia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih J. C., Chan Y. L. Direct evidence for de novo synthesis of rat liver phenylalanine: pyruvate transaminase after glucagon treatment. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Feb;192(2):414–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Elliott K. R., Pogson C. I. Differential effects of tryptophan on glucose synthesis in rats and guinea pigs. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):817–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1760817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Pogson C. I. The metabolism of L-tryptophan by isolated rat liver cells. Effect of albumin binding and amino acid competition on oxidatin of tryptophan by tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):977–986. doi: 10.1042/bj1860977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourian A. Control of phenylalanine hydroxylase synthesis in tissue culture by serum and insulin. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jan;87(1):15–24. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040870104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trefz F. K., Erlenmaier T., Hunneman D. H., Bartholomé K., Lutz P. Sensitive in vivo assay of the phenylalanine hydroxylating system with a small intravenous dose of heptadeutero L-phenylalanine using high pressure liquid chromatography and capillary gas chromatography/mass fragmentography. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Dec 17;99(3):211–230. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidrich A., Airhart J., Bruno M. K., Khairallah E. A. Compartmentation of free amino acids for protein biosynthesis. Influence of diurnal changes in hepatic amino acid concentrations of the composition of the precursor pool charging aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):257–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1620257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. F., Mortimore G. E. Compartmentation of intracellular amino acids in rat liver. Evidence for an intralysosomal pool derived from protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3581–3587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim M. B., Mitchell B., Woods H. F. The effect of increasing phenylalanine concentration on phenylalanine metabolism in perfused rat liver. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):683–684. doi: 10.1042/bst0030683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


