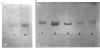
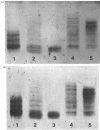
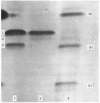
Abstract
Ferritin was purified from the serum of two patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis. The protein contained three types of subunit--the H and L subunits of tissue ferritins (although only a trace of H could be detected) and a third subunit, 'G', with the highest apparent molecular weight. Only the 'G' subunit band stained for carbohydrate, indicating that a proportion of the subunits of human serum ferritin are glycosylated. Although serum was obtained from patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis, it is probable that the 'G' subunit is a component of normal serum ferritin.
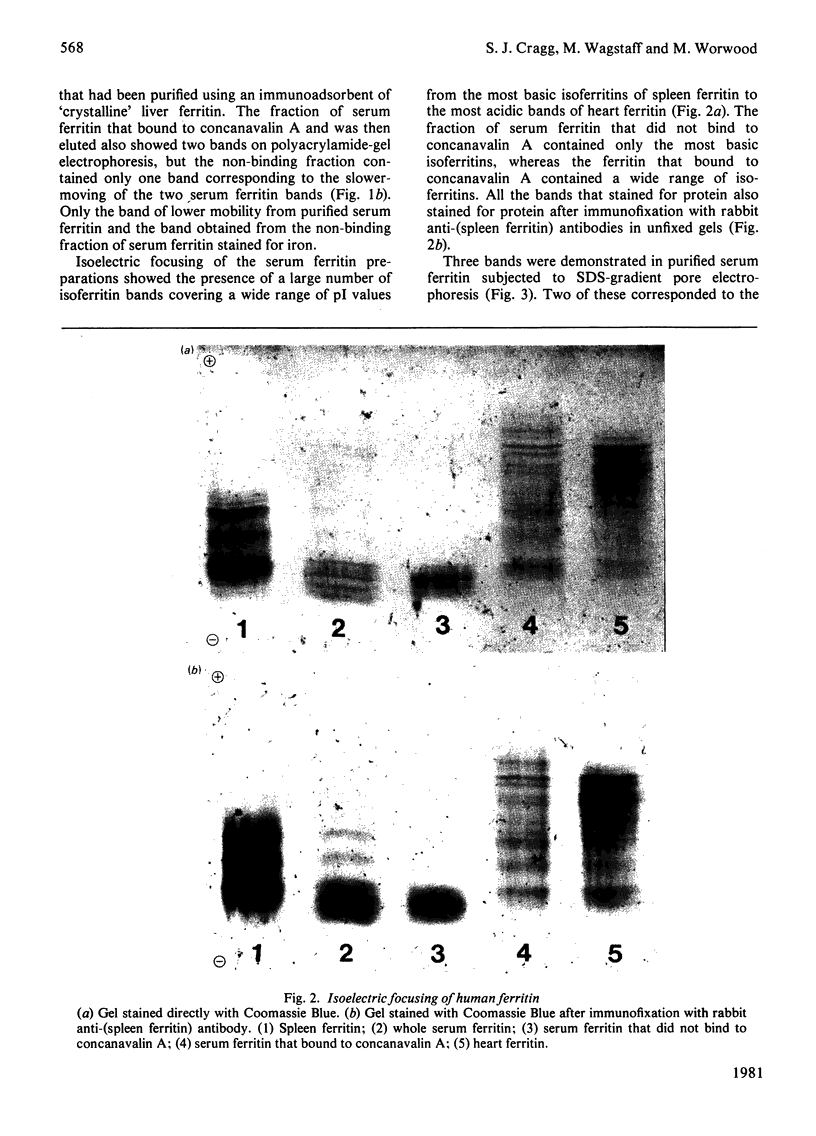
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arosio P., Adelman T. G., Drysdale J. W. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4451–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arosio P., Yokota M., Drysdale J. W. Characterization of serum ferritin in iron overload: possible identity to natural apoferritin. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg S. J., Wagstaff M., Worwood M. Sialic acid and the microheterogeneity of human serum ferritin. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Mar;58(3):259–262. doi: 10.1042/cs0580259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Perret B. A., Beck E. A. Staining of glycoproteins in polyacrylamide and agarose gels with fluorescent lectins. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görg A., Postel W., Westermeier R. Ultrathin-layer isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels on cellophane. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. M., Worwood M. An immunoradiometric assay for the acidic ferritin of human heart: application to human tissues, cells and serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Apr 3;85(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., Richter G. W. Ferritin synthesis by free and membrane-bound (poly)ribosomes of rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):399–403. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen D. Glycoprotein detection in polyacrylamide gel with thymol and sulfuric acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):474–476. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S., Watson L. R., Tavassoli M., Green R., Crosby W. H. Methods for establishing a working immunoradiometric assay for serum ferritin. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(4):375–386. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff M., Worwood M., Jacobs A. Properties of human tissue isoferritins. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):969–977. doi: 10.1042/bj1730969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Aherne W., Dawkins S., Jacobs A. The characteristics of ferritin from human tissues, serum and blood cells. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 May;48(5):441–451. doi: 10.1042/cs0480441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Cragg S. J., Wagstaff M., Jacobs A. Binding of human serum ferritin to concanavalin A. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Jan;56(1):83–87. doi: 10.1042/cs0560083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Dawkins S., Wagstaff M., Jacobs A. The purification and properties of ferritin from human serum. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):97–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1570097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]