Abstract
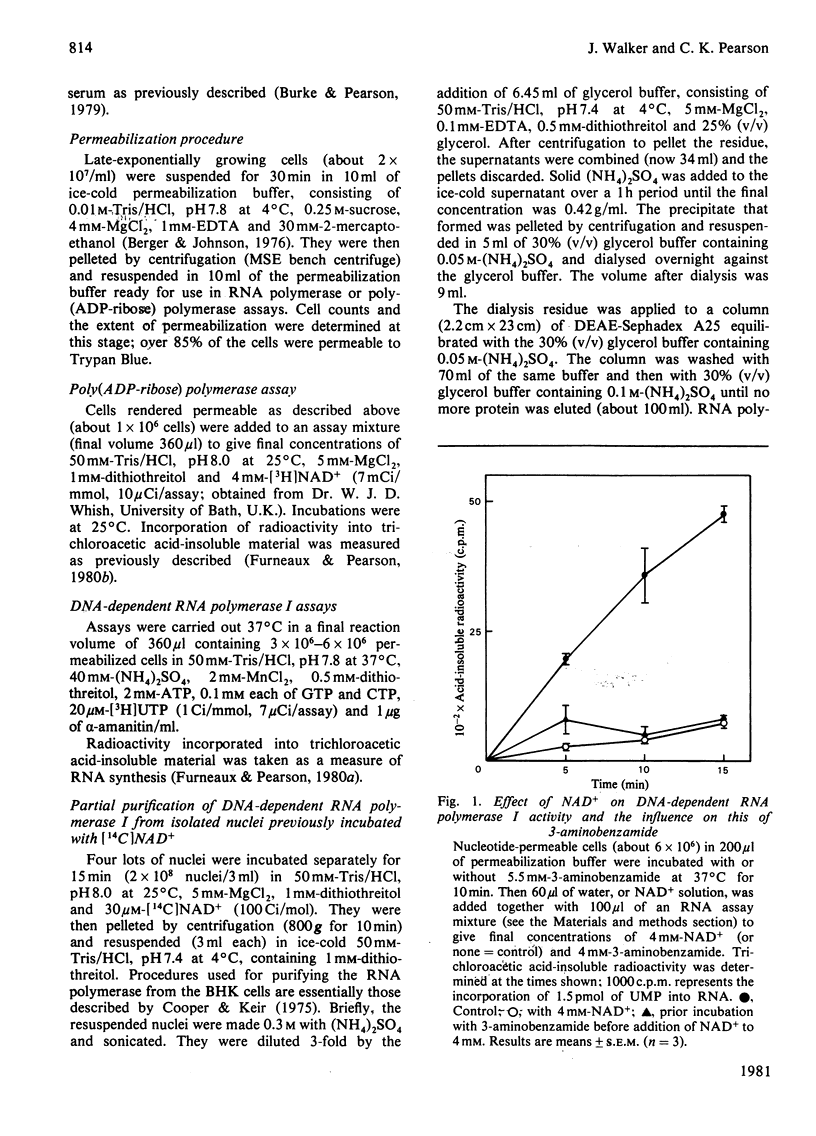
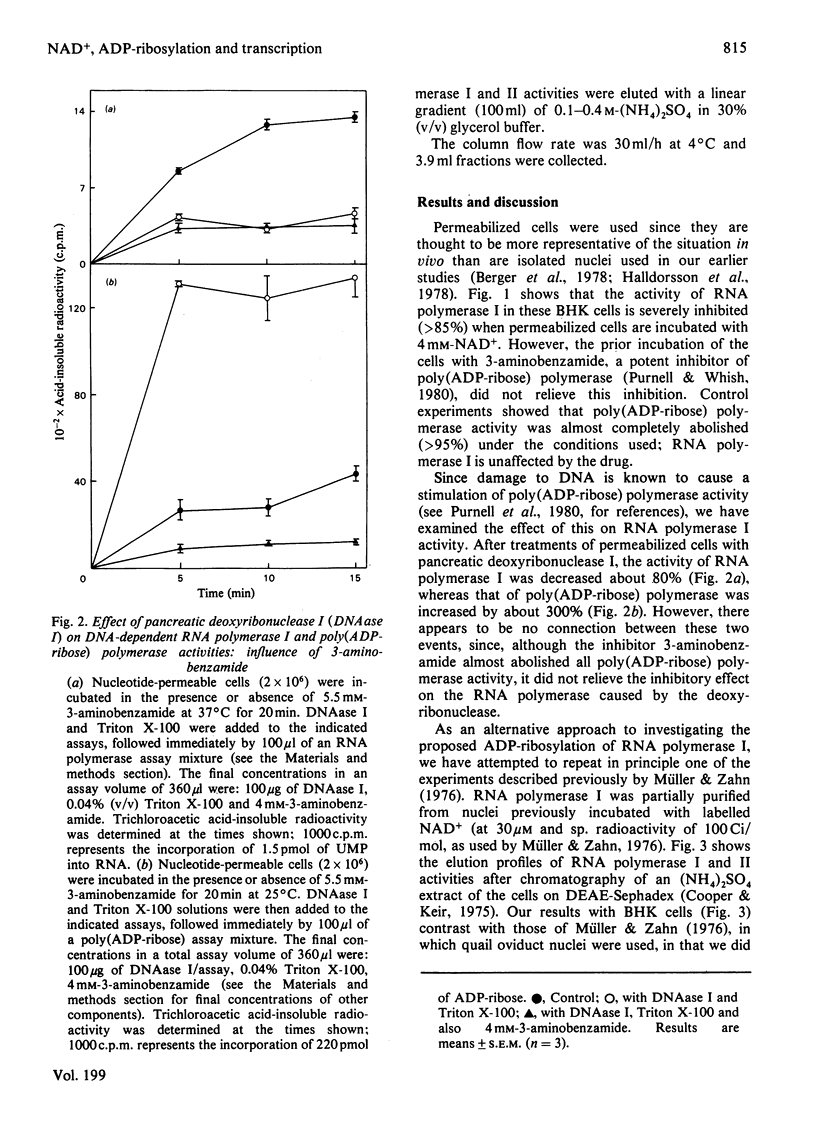
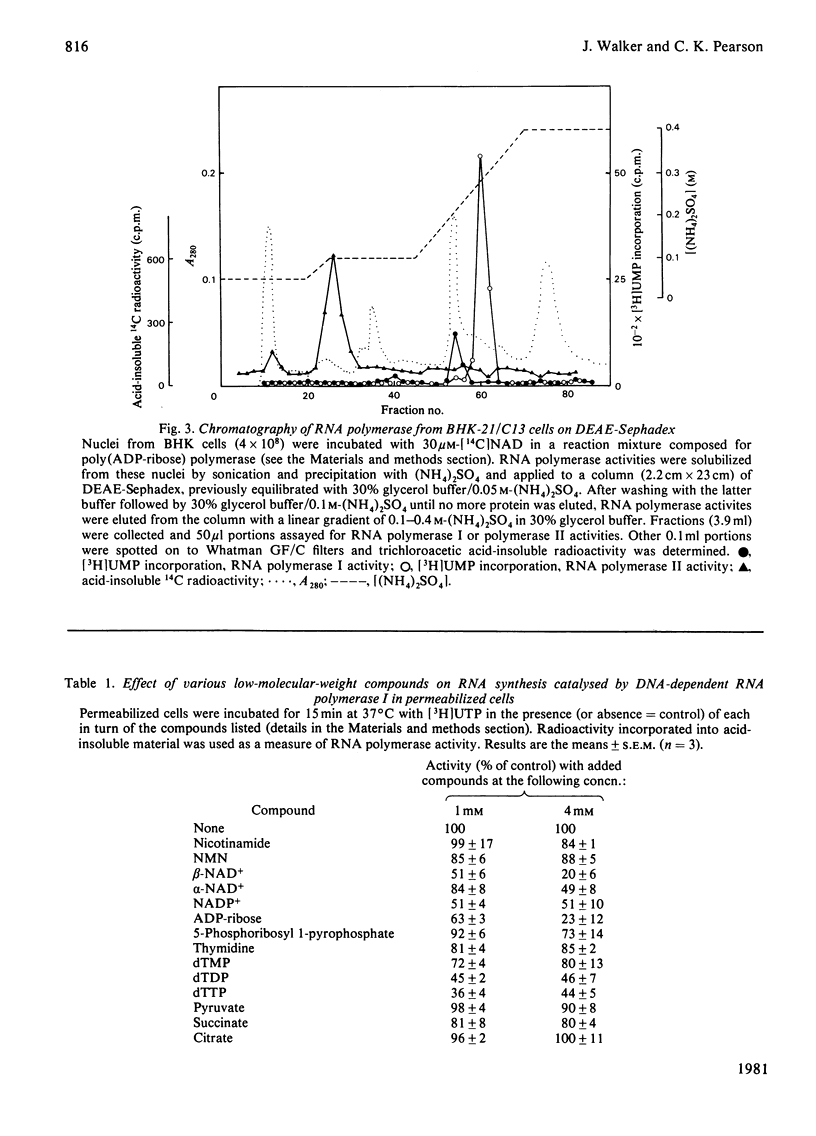
When permeabilized hamster fibroblasts were incubated with 4 mM-NAD+, the substrate for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, RNA polymerase I activity was inhibited by about 85%. This inhibition was not relieved by prior incubation of cells with 3-aminobenzamide, a potent inhibitor of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Digestion of cells with pancreatic deoxyribonuclease I resulted in the inhibition of RNA polymerase I by 80% and the activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by up to 300%; prior incubation with 3-aminobenzamide did not prevent the inhibition of the RNA polymerase activity. No radioactivity was found associated with RNA polymerase I during later stages of purification of this enzyme from permeabilized cells previously incubated with [14C]NAD+. The inhibitory effect of NAD+ on RNA polymerase I was not specific for NAD+, as other small, negatively charged molecules with a nuclear location also inhibited the enzyme. The results do not support the concept of a role for ADP-ribosylation in transcription catalysed by RNA polymerase I.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger N. A., Johnson E. S. DNA synthesis in permeabilized mouse L cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 18;425(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger N. A., Weber G., Kaichi A. S. Characterization and comparison of poly(adenosine dephosphoribose) synthesis and DNA synthesis in nucleotide-permeable cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):87–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F., Pearson C. K. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated nuclei from baby-hamster kidney cells (BHK-21/C13). Characterization of the system. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):613–620. doi: 10.1042/bj1780613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. J., Keir H. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from normal and polyoma-transformed BHK-21/C13 cells. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):509–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1450509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furneaux H. M., Pearson C. K. Adenosine diphosphate ribose transferase from baby-hamster kidney cells (BHK-21/C13). Characterization of the reaction and product. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):91–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1870091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furneaux H. M., Pearson C. K. Intracellular NAD+ content and ADP-ribose polymerase activity of serum-stimulated baby hamster kidney fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Dec;105(3):401–407. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halldorsson H., Gray D. A., Shall S. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase activity in nucleotide permeable cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 15;85(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilz H., Kittler M. Lack of correlation between poly ADP-ribose formation and DNA synthesis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Dec;352(12):1693–1704. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. W., Jr, Giri C. P., Smulson M. Poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase: the distribution of a chromosome-associated enzyme within the chromatin substructure. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):506–513. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Zahn R. K. Poly ADP-ribosylation of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I from quail oviduct. Dependence on progesterone stimulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Sep 30;12(3):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01741713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell M. R., Stone P. R., Whish W. J. ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Apr;8(2):215–227. doi: 10.1042/bst0080215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell M. R., Whish W. J. Novel inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):775–777. doi: 10.1042/bj1850775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsopanakis C., Leer J. C., Nielsen O. F., Gocke E., Shall S., Westergaard O. Poly (ADP-Ribose) metabolizing enzymes in nuclei and nucleoli of Tetrahymena pyriformis. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukioka M., Okai Y., Hasuma T., Inoue A. Non-preferential localization of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase activity in transcriptionally active chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


