Abstract
The interaction of Factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor with phospholipid vesicles has been studied by using sucrose-density-gradient ultracentrifugation. When purified Factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor was run alone. Factor VIII activity and Factor VIIIR-Ag sedimented together to the lower half of the tube. Addition of phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylethanolamine vesicles at concentrations above 250 microgram/ml resulted in complete separation of Factor VIII activity and Factor VIIIR-Ag, the former appearing with the phospholipid on the top of the tube and the latter sedimenting as before. This separation was obtained even in the presence of proteinase inhibitors. Activation of Factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor by thrombin resulted in formation of a slow sedimenting component containing essentially all the Factor VIII activity, whereas the Factor VIIIR-Ag sedimented towards the bottom of the tube as before. The thrombin-induced Factor VIII activity was strongly bound to phospholipid vesicles as determined by density-gradient centrifugations at various Factor VIII concentrations and low concentrations of phospholipid. Based on certain assumptions a dissociation constant of 2.5 nM was calculated, a mechanism for the formation in vivo of the Factor X-activator complex is suggested.
Full text
PDF

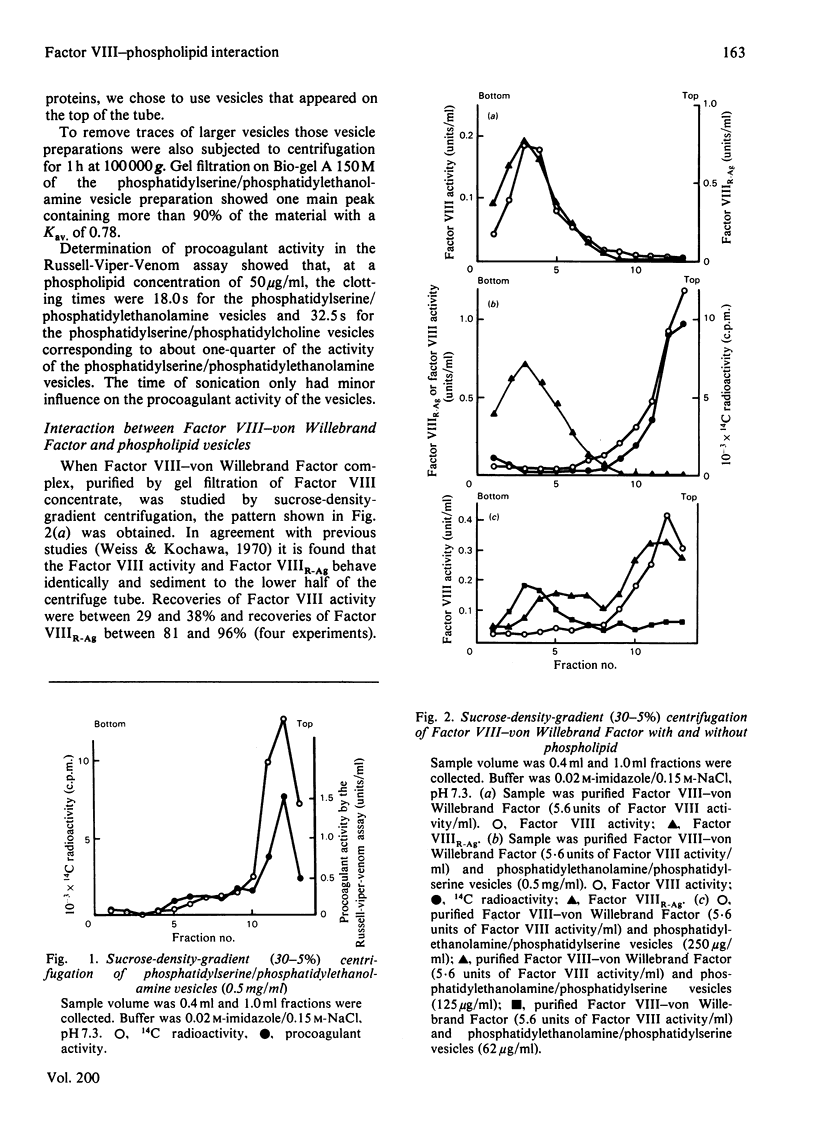
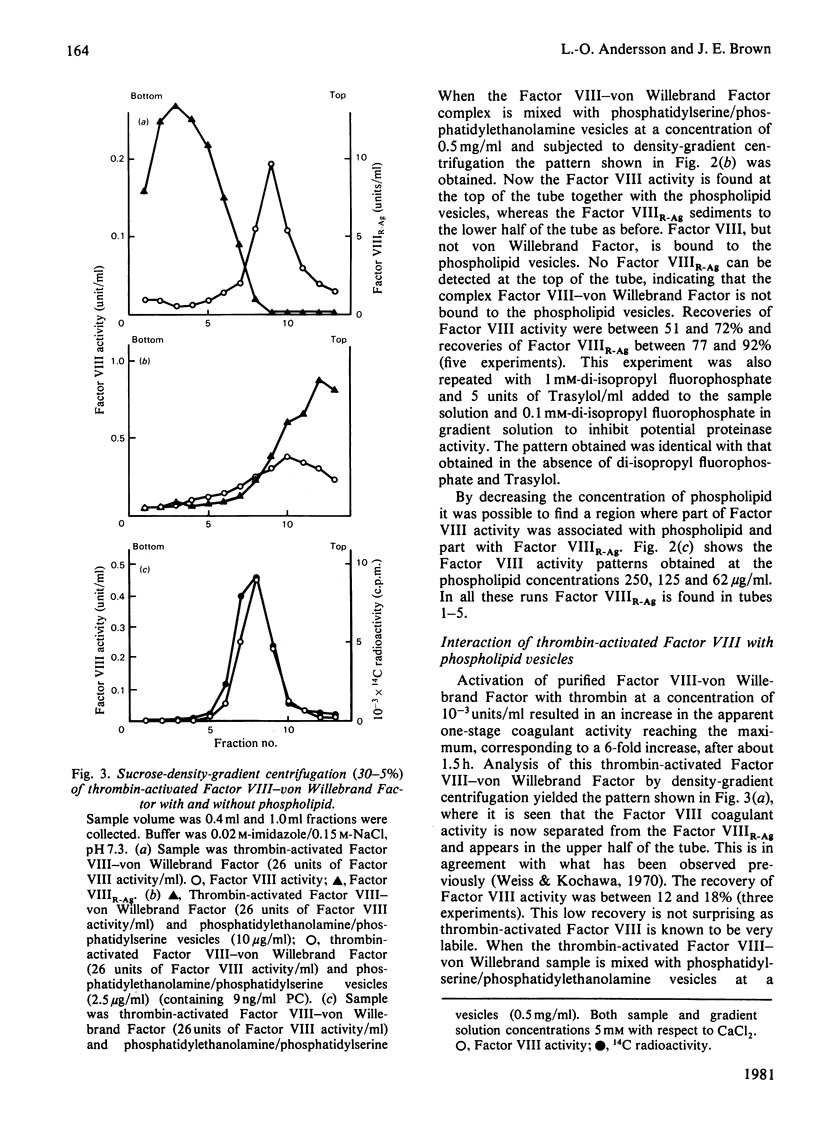
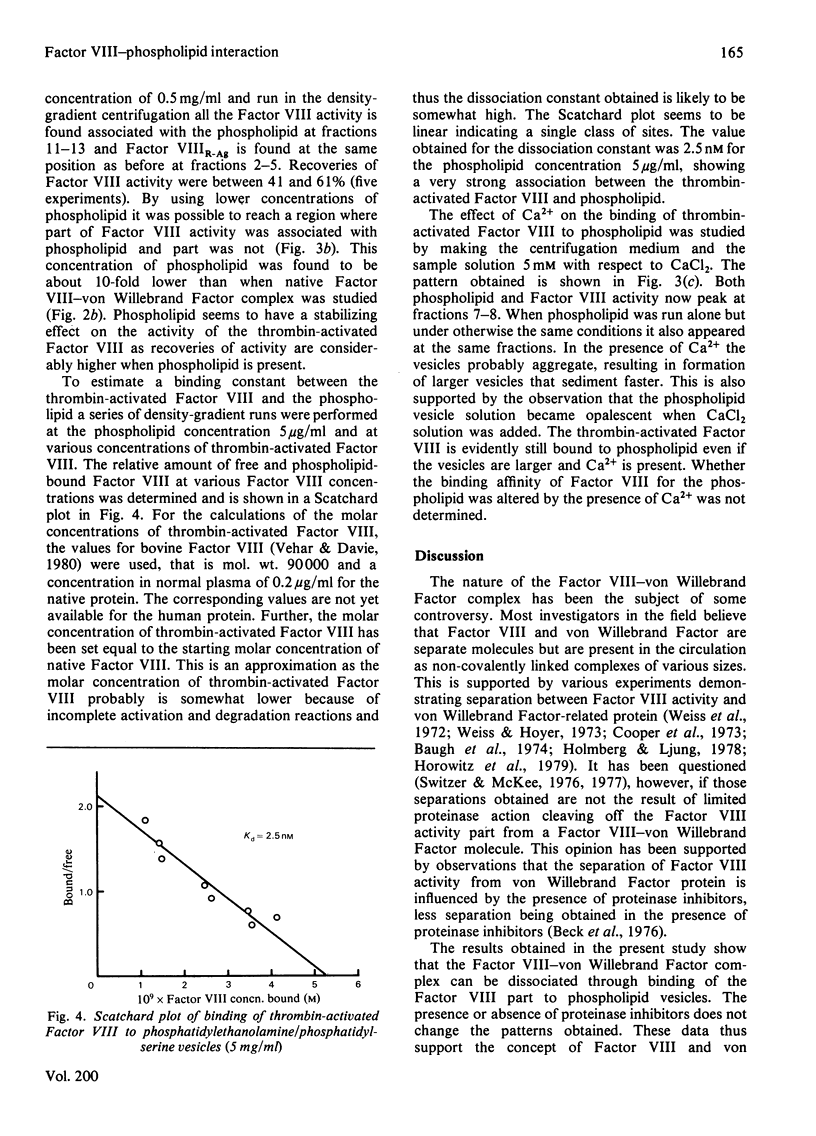


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baugh R., Brown J., Sargeant R., Hougie C. Separation of human factor VIII activity from the von Willebrand's antigen and ristocetin platelet aggregating activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E. A., Bachmann P., Barbier P., Furlan M. Importance of protease inhibition in studies on purified factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor). Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):186–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodén K., Andersson L. O., Sandberg H. Kinetics of activation of human factor VIII by thrombin. Thromb Res. 1980 Aug 1;19(3):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Griggs T. R., Wagner R. H. Factor VIII recombination after dissociation by CaCl12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2326–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemker H. C., Kahn M. J., Devilee P. P. The adsorption of coagulation factors onto phospholipids. Its role in the reaction mechanism of blood coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Oct 31;24(1):214–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Ljung R. Purification of F.VIII:C by antigen-antibody chromatography. Thromb Res. 1978 Apr;12(4):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz B., Lippin A., Woods K. R. Purification of low molecular weight factor VIII by affinity chromatography using factor VIII - sepharose. Thromb Res. 1979 Feb-Mar;14(2-3):463–475. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg H., Andersson L. O. Studies of the thromboplastic effect of human plasma lipoproteins. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Some effects of calcium on the activation of human factor VIII/Von Willebrand factor protein by thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):819–828. doi: 10.1172/JCI108836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer I. W. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Molecular forms of antihaemophilic globulin in plasma, cryoprecipitate and after thrombin activation. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Phillips L. L., Rosner W. Separation of sub-units of antihemophilic factor (AHF) by agarose gel chromatography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F. Membrane and lipid involvement in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):163–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


