Abstract
1. Changes in the mean volume, the rate of fatty acid and acylglycerol glycerol synthesis, the activity of lipoprotein lipase and the numbers and affinities of insulin receptors of subcutaneous adipocytes are reported for sheep at different stages of pregnancy and lactation. In addition, the serum concentrations of insulin, progesterone, prolactin, choriomammotropin, somatotropin, glucose, acetate, L-lactate, glycerol and unesterified fatty acids are reported for these sheep. 2. A switch from lipid accumulation to net lipid mobilization accompanied by a decline in the capacity for lipid synthesis, occurred at the onset of the last third of pregnancy. Net lipid mobilization continued during lactation. 3. The changes that occurred in the serum concentrations of the various hormones listed above are discussed in relation to their possible roles in the modulation of adipose tissue metabolism in sheep during pregnancy and lactation. The observations are compared with those from previous studies on the hormonal control of adipose tissue metabolism in the rat during pregnancy and lactation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agius L., Robinson A. M., Girard J. R., Williamson D. H. Alterations in the rate of lipogenesis in vivo in maternal liver and adipose tissue on premature weaning of lactating rats: a possible regulatory role of prolactin. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):689–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1800689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby J. P., Shirling D., Baird J. D. Effect of progesterone on the secretion and peripheral action of insulin and glucagon in the intact rat. J Endocrinol. 1981 Jan;88(1):49–55. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0880049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett J. M., Thorburn G. D., Wallace A. L. The plasma growth hormone concentration of the foetal lamb. J Endocrinol. 1970 Oct;48(2):251–263. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0480251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman D. E., Currie W. B. Partitioning of nutrients during pregnancy and lactation: a review of mechanisms involving homeostasis and homeorhesis. J Dairy Sci. 1980 Sep;63(9):1514–1529. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(80)83111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck N. F., Tucker H. A. Mammary arterial and venous concentrations of serum insulin in lactating dairy cows. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Dec;159(3):394–396. doi: 10.3181/00379727-159-40355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom A. K., Hove K., Nedkvitne J. J. Plasma insulin and growth hormone concentrations in pregnant sheep II: post-absorptive levels in mid- and late pregnancy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Jul;82(3):553–560. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0820553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Frazier W. A. Hormone receptors as regulators of hormone action. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1977;12:1–37. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152812-6.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costrini N. V., Kalkhoff R. K. Relative effects of pregnancy, estradiol, and progesterone on plasma insulin and pancreatic islet insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):992–999. doi: 10.1172/JCI106593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint D. J., Clegg R. A., Vernon R. G. Prolactin and the regulation of adipose-tissue metabolism during lactation in rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 May;22(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
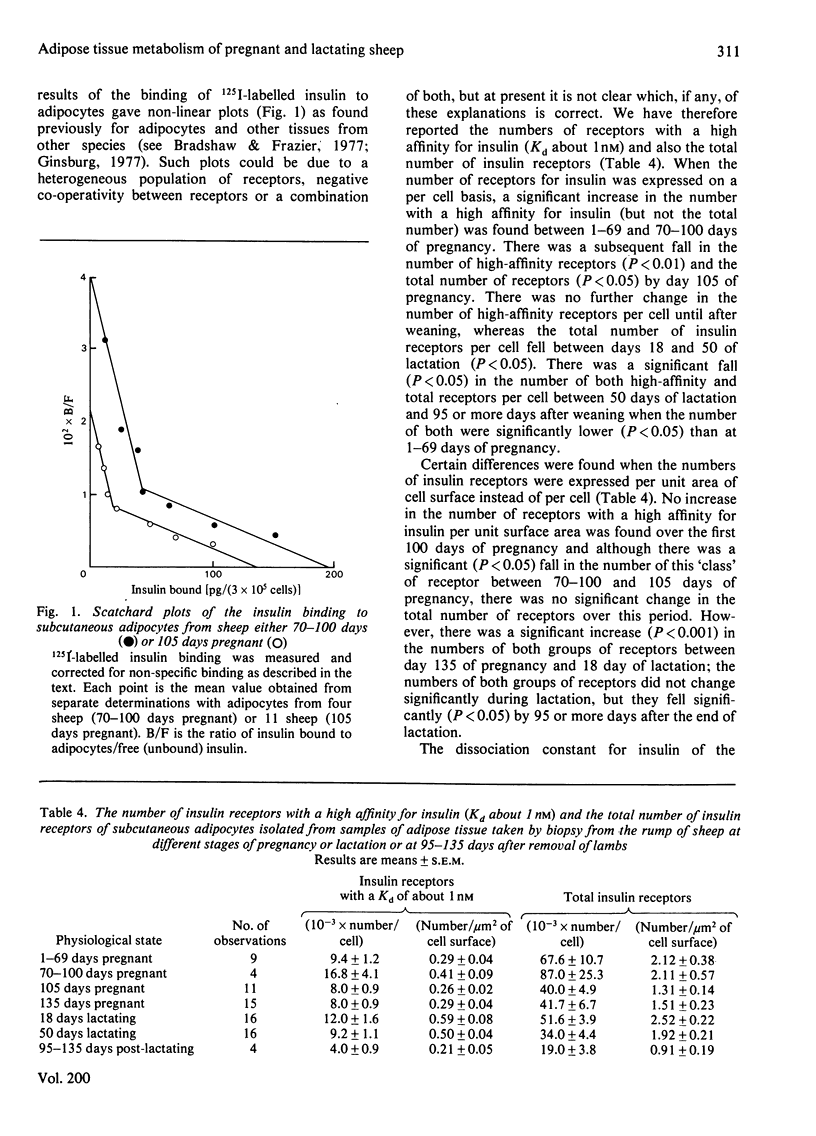
- Flint D. J., Clegg R. A., Vernon R. G. Regulation of adipocyte insulin receptor number and metabolism during late-pregnancy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Nov;20(2):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint D. J., Sinnett-Smith P. A., Clegg R. A., Vernon R. G. Role of insulin receptors in the changing metabolism of adipose tissue during pregnancy and lactation in the rat. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1820421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND P. B., RANDLE P. J. A rapid enzymatic assay for glycerol. Nature. 1962 Dec 8;196:987–988. doi: 10.1038/196987a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Clary T. R., Chernick S. S., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase activity of adipose and mammary tissue and plasma triglyceride in pregnant and lactating rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 8;210(3):473–482. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. C. Basal levels of prolactin in goat blood measured throughout a 24-h period by a rapid double antibody-solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Dairy Res. 1973 Jun;40(2):235–245. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900014564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp R. H., Saudek C. D., Arky R. A., O'Sullivan J. B. 2 phases of adipose tissue metabolism in pregnancy: maternal adaptations for fetal growth. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):984–988. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax M. A., Baird G. D., Mallinson C. B., Symonds H. W. Differences between lactating and non-lactating dairy cows in concentration and secretion rate of insulin. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj1800281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqman W. A., Matej L. A., Smith M. L. Comparison of prolactin levels in human semen and seminal plasma. J Endocrinol. 1979 Apr;81(1):131–133. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0810131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otway S., Robinson D. S. The significance of changes in tissue clearing-factor lipase activity in relation to the lipaemia of pregnancy. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1060677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAY C. M. A study of some aspects of reproduction by means of chemical analysis. Br J Nutr. 1950;4(4):354–360. doi: 10.1079/bjn19500059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S., Reichlin S. Plasma growth hormone concentration in the rat determined by radioimmunoassay: influence of sex, pregnancy, lactation, anesthesia, hypophysectomy and extrasellar pituitary transplants. Endocrinology. 1966 Aug;79(2):275–280. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W. The effects of pregnancy, lactation and involution on the metabolism of glucose by rat parametrial adipose tissue. J Dairy Res. 1973 Oct;40(3):353–360. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900014722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson J. E., Felig P. Medical aspects of diabetes in pregnancy and the diabetogenic effects of oral contraceptives. Med Clin North Am. 1971 Jul;55(4):947–959. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32489-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Effect of dietary fats on ovine adipose tissue metabolism. Lipids. 1976 Sep;11(9):662–669. doi: 10.1007/BF02532883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Effect of dietary safflower oil upon lipogenesis in neonatal lamb. Lipids. 1975 May;10(5):284–289. doi: 10.1007/BF02532701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue of ruminant animals. Prog Lipid Res. 1980;19(1-2):23–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(80)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Lipogenesis in ovine adipose tissue in tissue culture. Ann Rech Vet. 1979;10(2-3):399–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Smith R. L. Lowry determination of protein in the presence of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


