Abstract
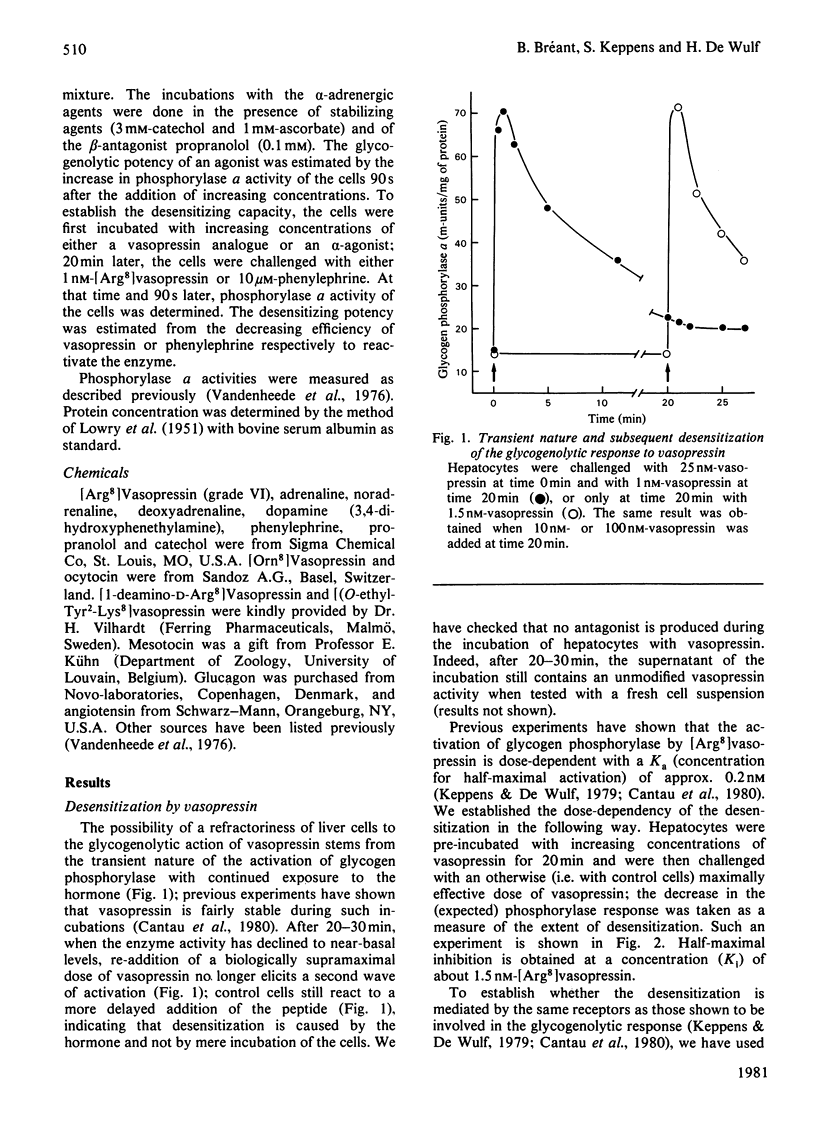
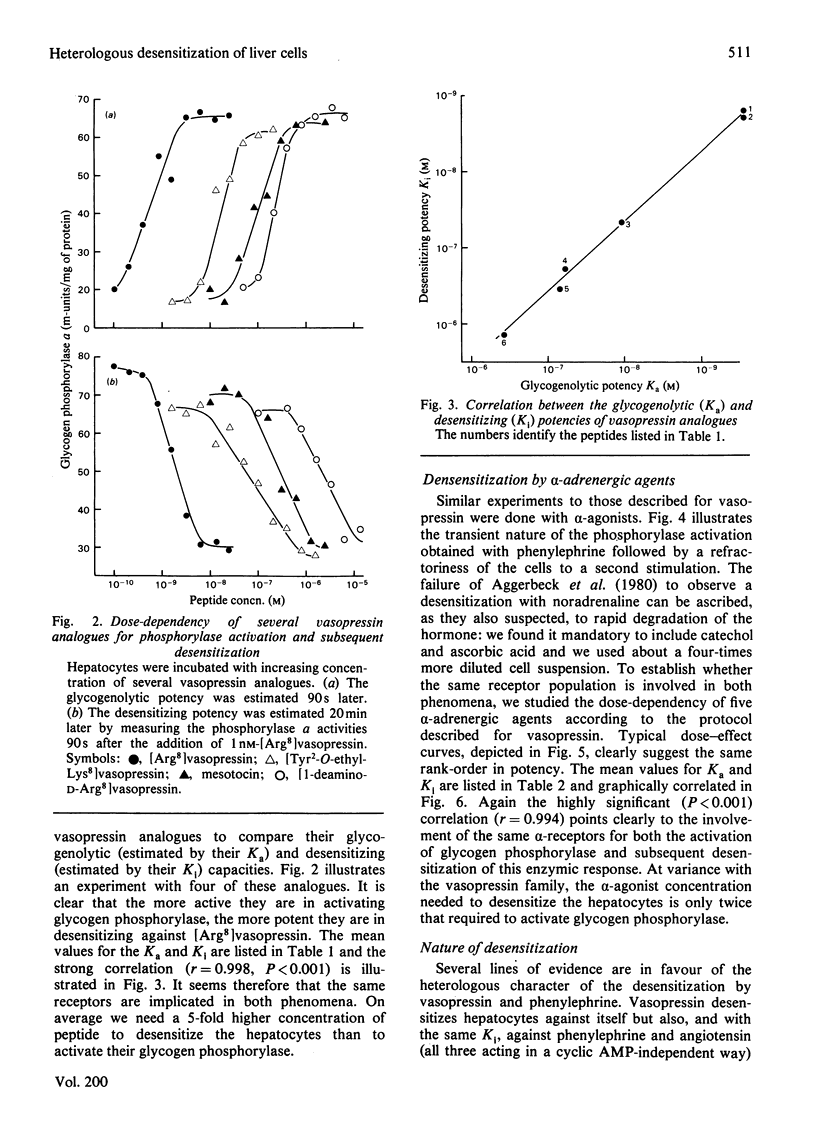
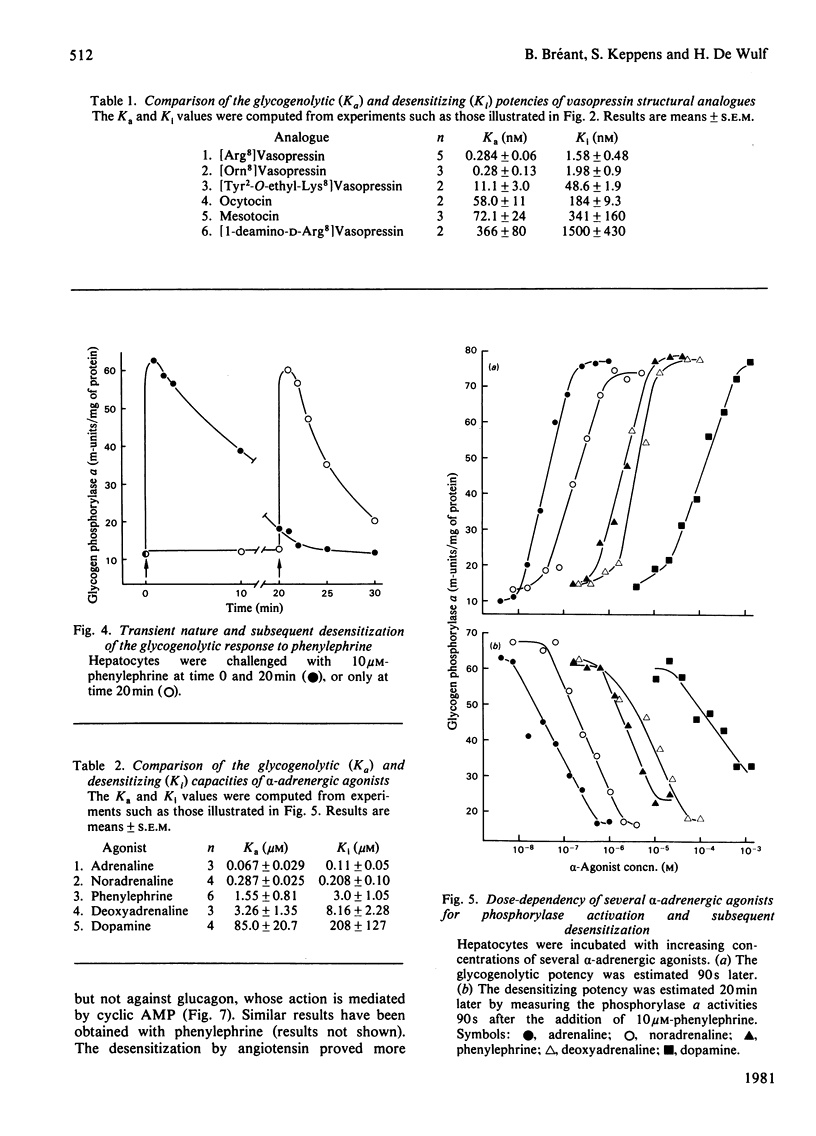
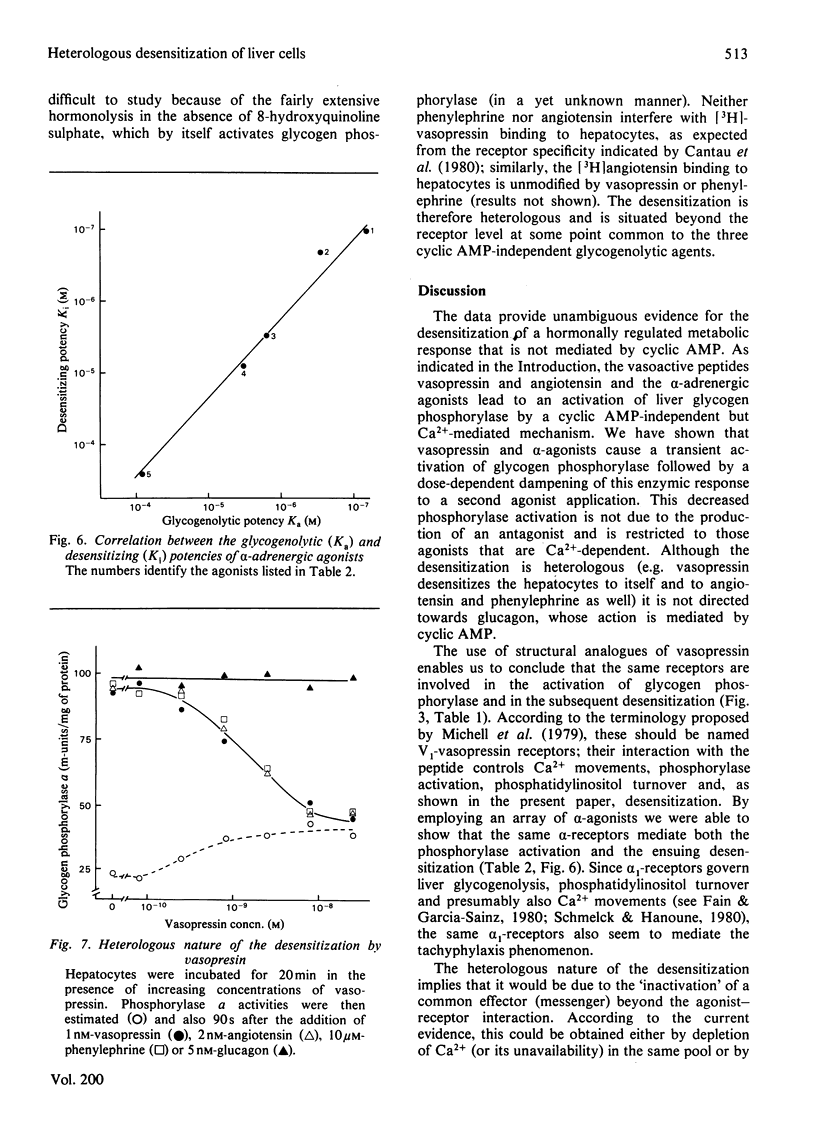
Vasopressin and alpha-adrenergic agonists are known to be potent cyclic AMP-independent Ca2+-dependent activators of liver glycogen phosphorylase. When hepatocytes are pre-incubated with increasing concentrations of vasopressin or of the alpha-agonist phenylephrine, they become progressively unresponsive to a second addition of the respective agonist. The relative abilities of six vasopressin analogues and of five alpha-agonists to activate glycogen phosphorylase and to cause subsequent desensitization are highly correlated, indicating that the same vasopressin and alpha-adrenergic receptors are involved in both responses. About 5-times-higher peptide concentrations are needed to desensitize the cells than to activate their glycogen phosphorylase, whereas the concentrations of alpha-agonists required for the desensitization are only twice those needed for the activation of phosphorylase. The desensitization is not mediated by a perturbation in the agonist-receptor interaction. It is clearly heterologous, i.e. it is not agonist-specific, and must therefore involve a mechanism common to both series of agonists. The evidence for a role of Ca2+ movements or phosphatidylinositol turnover is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Guellaen G., Hanoune J. The alpha-adrenergic mediated effect in rat liver. Correlation between [3H]-dihydroergocryptine binding to plasma membranes and glycogen phosphorylase activation in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 15;29(12):1653–1662. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Althaus-Salzmann M., Carafoli E., Jakob A. Ca2+, K+ redistributions and alpha-adrenergic activation of glycogenolysis in perfused rat livers. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. F., Chen J. L., Yip B. P., Lardy H. A. Evidence for mitochondrial localization of the hormone-responsive pool of Ca2+ in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8117–8120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barritt G. J., Parker J. C., Wadsworth J. C. A kinetic analysis of the effects of adrenaline on calcium distribution in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:29–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Dehaye J. P., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. The role of mitochondrial calcium release in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6945–6950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantau B., Keppens S., De Wulf H., Jard S. (3H)-vasopressin binding to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes: regulation by GTP and relation to glycogen phosphorylase activation. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):137–168. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Refai M. F., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Evidence for two alpha-adrenergic binding sites in liver plasma membranes. Studies with [3H]epinephrine and [3H]dihydroergocryptine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4375–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., García-Sáinz J. A. Role of phosphatidylinositol turnover in alpha 1 and of adenylate cyclase inhibition in alpha 2 effects of catecholamines. Life Sci. 1980 Apr 14;26(15):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., de Wulf H. The nature of the hepatic receptors involved in vasopressin-induced glycogenolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 15;588(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Michell R. H., Hems D. A. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):155–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1940155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Rodrigues L. M., Hems D. A. The influence of vasopressin and related peptides on glycogen phosphorylase activity and phosphatidylinositol metabolism in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):493–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1780493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Wessels M. R., Stadel J. M. Hormones, receptors, and cyclic AMP: their role in target cell refractoriness. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;17:205–230. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152817-1.50011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Billah M. M. Hormonal stimulation of phosphatidylinositol breakdown with particular reference to the hepatic effects of vasopressin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):861–865. doi: 10.1042/bst0070861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Coll K., Rich T. L., Williamson J. R. Hormonal effects on calcium homeostasis in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6600–6608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Berthon B., Claret M. Calcium movements in in situ mitochondria following activation of alpha-adrenergic receptors in rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelck P. H., Hanoune J. The hepatic adrenergic receptors. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Dec 10;33(1-2):35–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00224570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., White A. C., Aspry K., Cutts J., Fain J. N. Stimulation by vasopressin and alpha-catecholamines of phosphatidylinositol formation in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1938–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Keppens S., De Wulf H. The activation of liver phosphorylase b kinase by glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



