Abstract
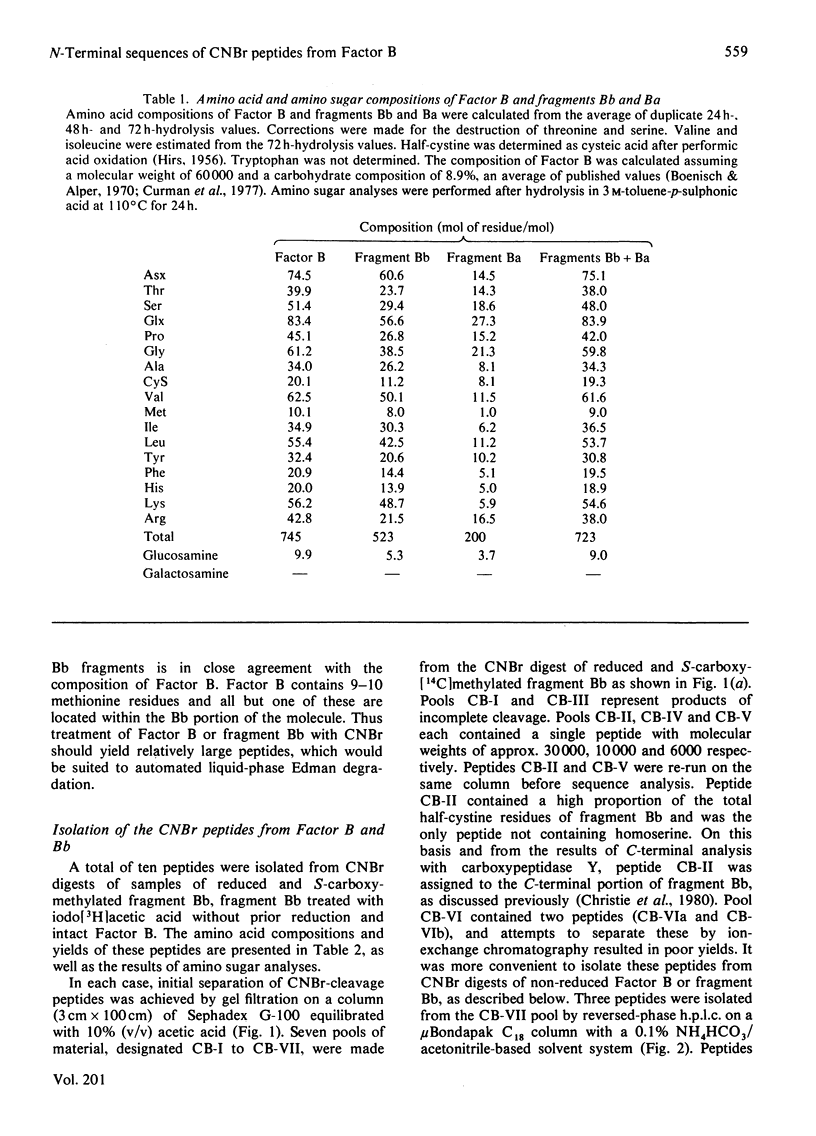
Nine CNBr-cleavage peptides from Factor B (a component of the alternative pathway of complement) were isolated. Each was characterized by amino acid analysis and automated Edman degradation. One peptide contained a methionyl bond resistant to cleavage by CNBr. The number of CNBr-cleavage peptides is in agreement with the results of amino acid analysis of Factor B and the fragments Ba and Bb. A total of 358 unique residues were identified from the N-terminal sequences of the CNBr-cleavage peptides. These represent approx. 50% and 60% of the total residues of Factor B and fragment Bb respectively. Alignment of two CNBr-cleavage peptides (CB-VIc and CB-IV) provided a continuous segment of 140 residues. This sequence contained the site cleaved by Factor D to generate the Ba and Bb fragments during the activation of complement. Peptide CB-IV contained a free thiol group at a position corresponding to residue 33 of fragment Bb. Amino sugar analyses of Factor B and of fragments Bb and Ba indicated that all the carbohydrate structures of factor B are N-linked to asparagine through N-acetylglucosamine. The two carbohydrate-attachment sites of the Bb fragment were identified.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. K., Neuberger A. The quantitation of glucosamine and galactosamine in glycoproteins after hydrolysis in p-toluenesulphonic acid. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball C. B. HEALTH DEPARTMENTS AND HOUSING. Am J Public Health (N Y) 1913 Jan;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.2105/ajph.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhown A. S., Bennett J. C., Morgan P. H., Mole J. E. Use of fluorescamine as an effective blocking reagent to reduce the background in protein sequence analyses by the Beckman automated sequencer. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 15;112(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boenisch T., Alper C. A. Isolation and properties of a glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen P. J., Cross G. A., Bridgen J. N-terminal amino acid sequences of variant-specific surface antigens from Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1976 Oct 14;263(5578):613–614. doi: 10.1038/263613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. Partial sequence of human complement component factor B: novel type of serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4923–4927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Sandberg-Trägårdh L., Peterson P. A. Chemical characterization of human factor B of the alternate pathway of complement activation. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5368–5375. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dognin M. J., Wittmann-Liebold B. The primary structure of L11, the most heavily methylated protein from Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 15;84(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80721-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fothergill J. E., Anderson W. H. A molecular approach to the complement system. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;13:259–311. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152813-3.50012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. A cheap and simple method to achieve and maintain the necessary purity of reagents and solvents for automated amino acid sequence determination with the sequenator. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Jul;360(7):997–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
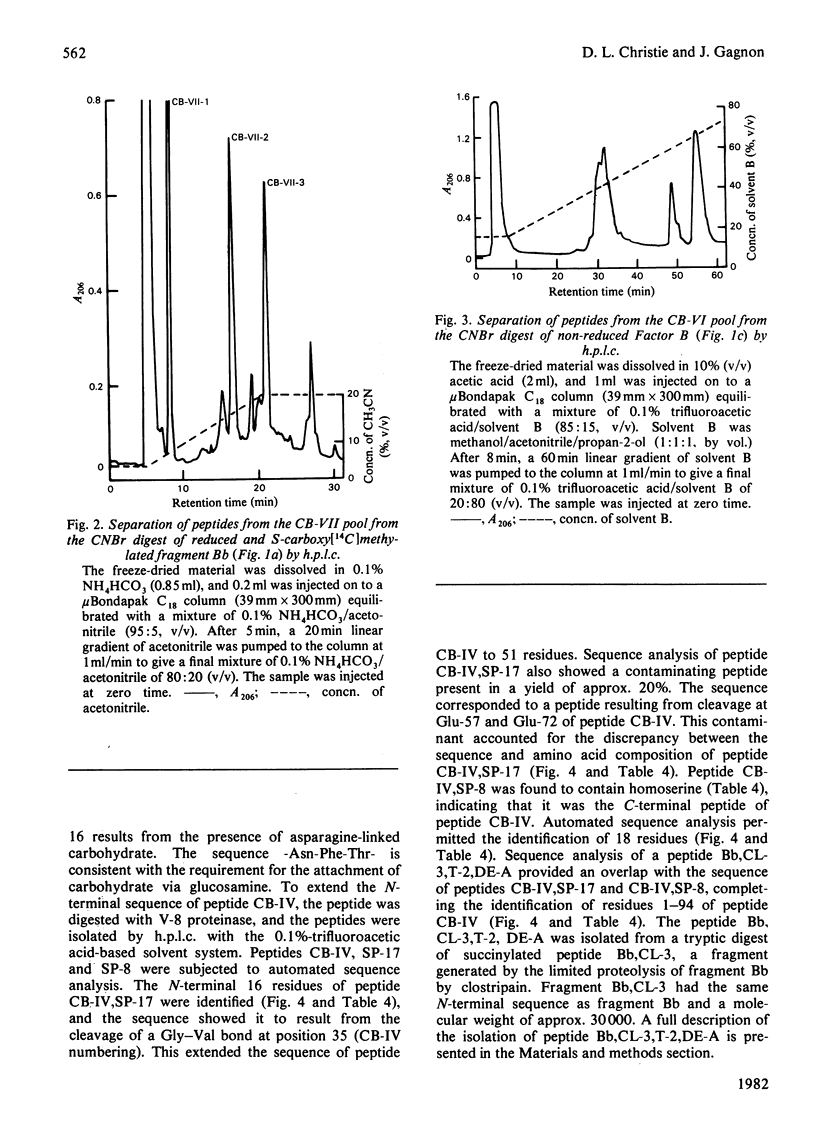
- Goodkofsky I., Lepow I. H. Functional relationship of factor B in the properdin system to C3 proactivator of human serum. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1200–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Direct microsequence analysis of polypeptides using an improved sequenator, a nonprotein carrier (polybrene), and high pressure liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2124–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. M., Gagnon J., Reid K. B. Factor D of the alternative pathway of human complement. Purification, alignment and N-terminal amino acid sequences of the major cyanogen bromide fragments, and localization of the serine residue at the active site. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):863–874. doi: 10.1042/bj1870863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A. Limited proteolysis of complement components C2 and factor B. Structural analogy and limited sequence homology. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1830615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Porter R. R. The purification and properties of the second component of human complement. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):99–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1710099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide A., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Kumar S., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Sequence of the amino-terminal 349 residues of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase including the sites of covalent and allosteric control. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5657–5672. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Comparative aspects of glycoprotein structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:217–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P. H., Hugli T. E., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway C3/C5 convertase: chemical basis of factor B activation. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The serine protease nature of the C3 and C5 convertases of the classical and alternative complement pathways. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(9):1049–1055. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole J. E., Niemann M. A. Structural evidence that complement factor B constitutes a novel class of serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8472–8476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Schreiber R. D. Molecular biology and chemistry of the alternative pathway of complement. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Role of proteolytic enzymes in biological regulation (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3825–3832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann M. A., Volanakis J. E., Mole J. E. Amino-terminal sequence of human factor B of the alternative complement pathway and its cleavage fragments, Ba and Bb. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1576–1583. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. B., Shelton J. R. An examination of conditions for the cleavage of polypeptide chains with cyanogen bromide: application to catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Twose T. M., Paterson D. S., Sim E. The covalent-binding reaction of complement component C3. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1930115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


