Abstract
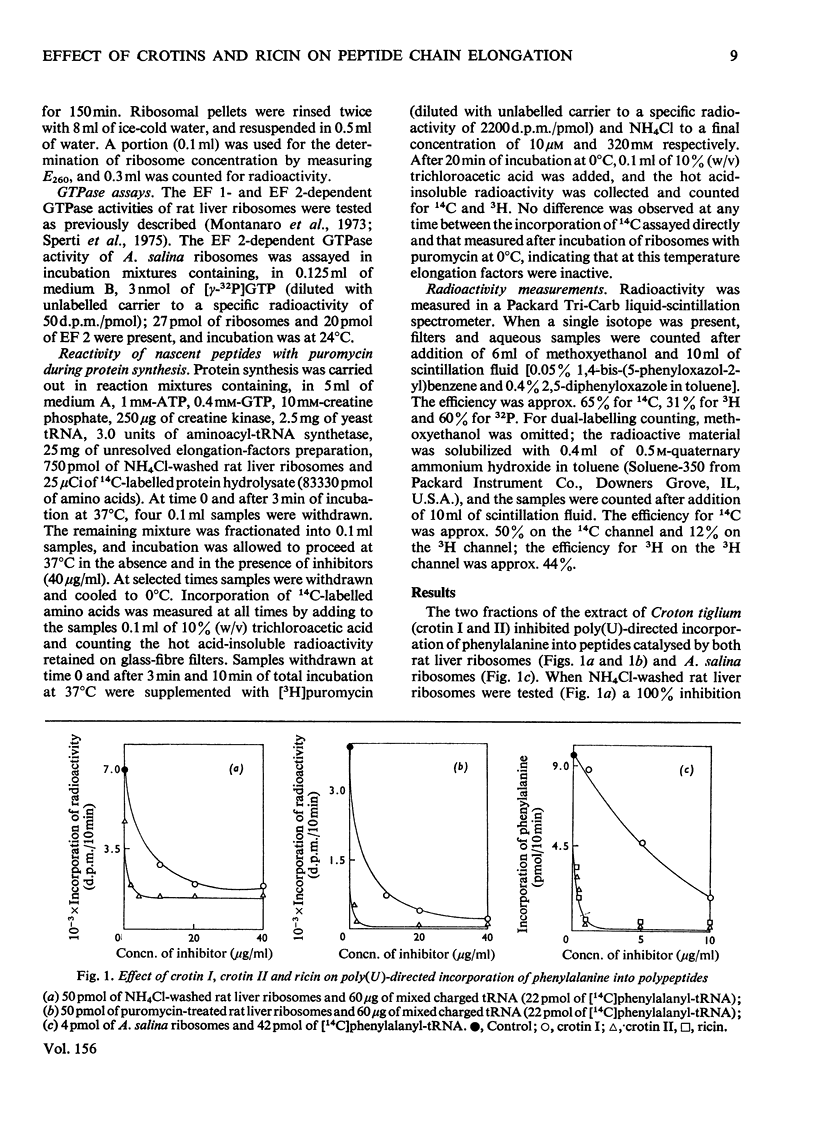
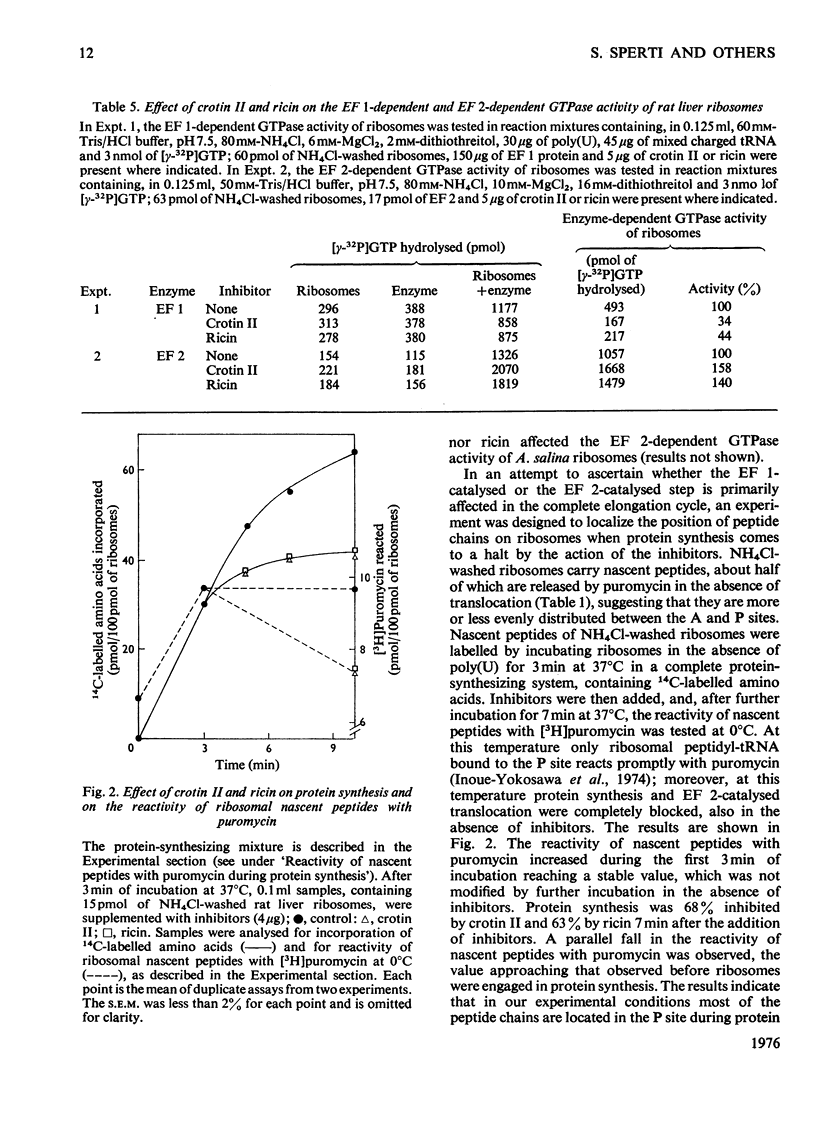
The effects of crotin I and crotin II on the partial reactions of polypeptide chain elongation were investigated and compared with the known effects of ricin. Crotin II was a more powerful inhibitor than crotin I, but no qualitative differences between the two crotins were found. Rat liver ribosomes, preincubated with crotins and washed through sucrose gradients, remained inactive in protein synthesis. Among the individual steps of elongation, the peptidyltransferase reaction was unaffected by crotins, but some of the reactions that involve the interaction of elongation factors 1 and 2 with ribosomes were modified. A strong inhibition of the binding of elongation factor 2 to ribosomes and a stimulation of the elongation factor2-dependent GTP hydrolysis were observed; this indicates the formation of a very unstable elongation factor 2--GDP--ribosome complex, which, however, allows a single round of translocation to take place in the presence ofelongation factor 2 and added GTP. The elongation factor 1-dependent GTP hydrolysis was inhibited by crotins, whereas the enzymic binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, to both rat liver and Artemia salina ribosomes, was scarcely affected. In a protein-synthesizing system the inhibition by crotins and by ricin leads to a block of the nascent peptides on the ribosomal aminoacyl-tRNA site, an effect consistent with inhibition at the level of translocation. The mechanism of action of crotins appears to be very similar to that of ricin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermek E. Formation of a complex involving ADP-ribosylated human translocation factor, guanosine nucleotide and ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Fernandez-Puentes C., Vazquez D. Effects of ricin on the ribosomal sites involved in the interaction of the elongation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felicetti L., Lipmann F. Comparison of amino acid polymerization factors isolated from rat liver and rabbit reticulocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):548–557. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90613-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Morris J. E. The ribosomes of encysted embryos of Artemia salina during cryptobiosis and resumption of development. Dev Biol. 1968 Feb;17(2):143–164. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue-Yokosawa N., Ishikawa C., Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine triphosphate in translocation reaction catalyzed by elongation factor G. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4321–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A., Jr, Rich A. Studies on crystalline abrin: X-ray diffraction data, molecular weight, carbohydrate content and subunit structure. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Mattioli A., Testoni G., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Inhibition of the binding of elongation factor 2 and of adenosine diphosphate-ribosylated elongation factor 2 to ribosomes. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):127–131. doi: 10.1042/bj1460127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Ribosomes as the target of the toxin. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1360677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J., Etzler M. E. Characterization of two plant lectins from Ricinus communis and their quantitative interaction with a murine lymphoma. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):196–204. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Irvin J. D., Hardesty B. The effect of an antiviral peptide on the ribosomal reactions of the peptide elongation enzymes, EF-I and EF-II. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Apr;155(2):278–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Meren R. Lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. II. Hybrid toxins and their interaction with chain-specific antibodies. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):842–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Ricin - a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 15;20(3):327–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Pihl A. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):627–631. doi: 10.1038/249627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The purification of diphtheria toxin and the isolation of crystalline toxin-protein. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Apr;39(2):139–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Olsnes S., Harper A. A. Lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. I. Immunochemical relationships between toxins and agglutinins. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):835–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refsnes K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. On the toxic proteins abrin and ricin. Studies of their binding to and entry into Ehrlich ascites cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3557–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Competition between the elongation factors 1 and 2, and phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid for the ribosomal binding sites in a polypeptide-synthesizing system from brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2853–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Maxwell E. S. Peptidylpuromycin formation on mammalian polysomes. Studies on transpeptidation and translocation. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):475–481. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Testoni G. Relationship between elongation factor I- and elongation factor II- dependent guanosine triphosphatase activities of ribosomes. Inhibition of both activities by ricin. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):447–451. doi: 10.1042/bj1480447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Baliga B. S., Munro H. N. Available sulphydryl groups of mammalian ribosomes in different functional states. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):895–911. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Pession-Brizzi A., Lorenzoni E., Strocchi P., Montanaro L., Sperti S. Studies on the proteins from the seeds of Croton tiglium and of Jatropha curcas. Toxic properties and inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):1–6. doi: 10.1042/bj1560001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


