Abstract
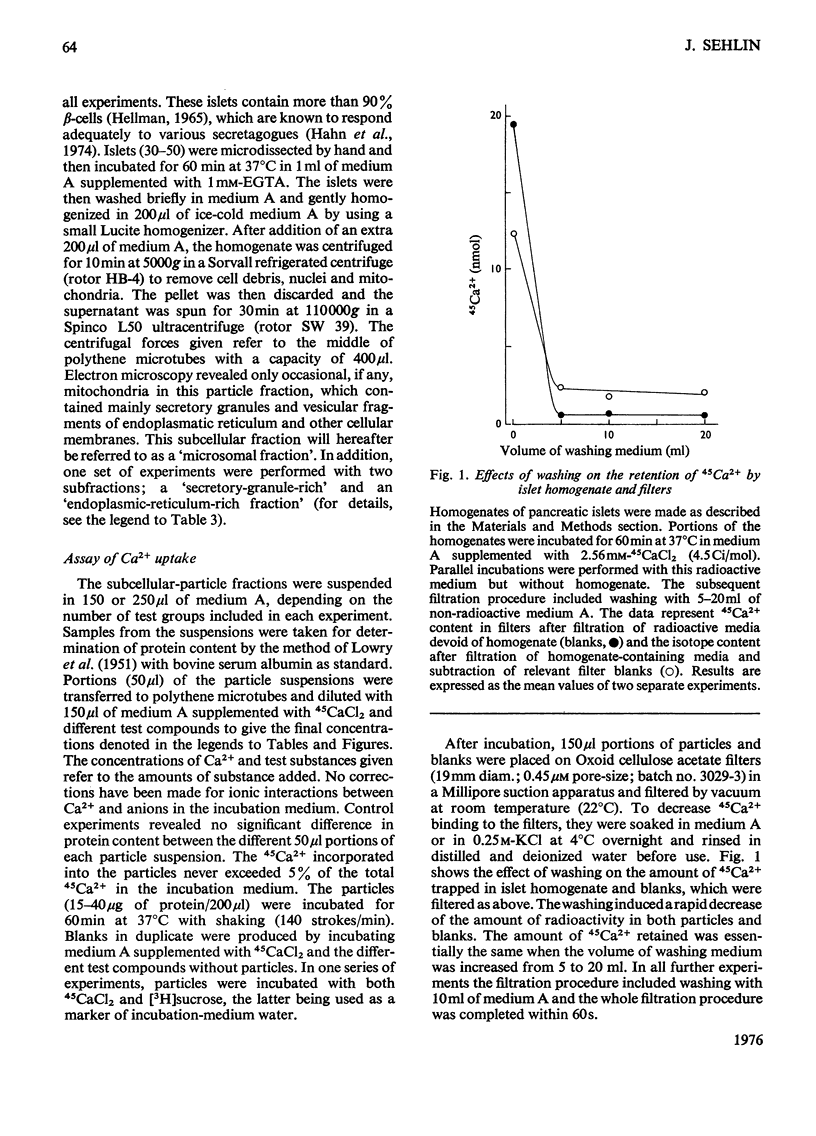
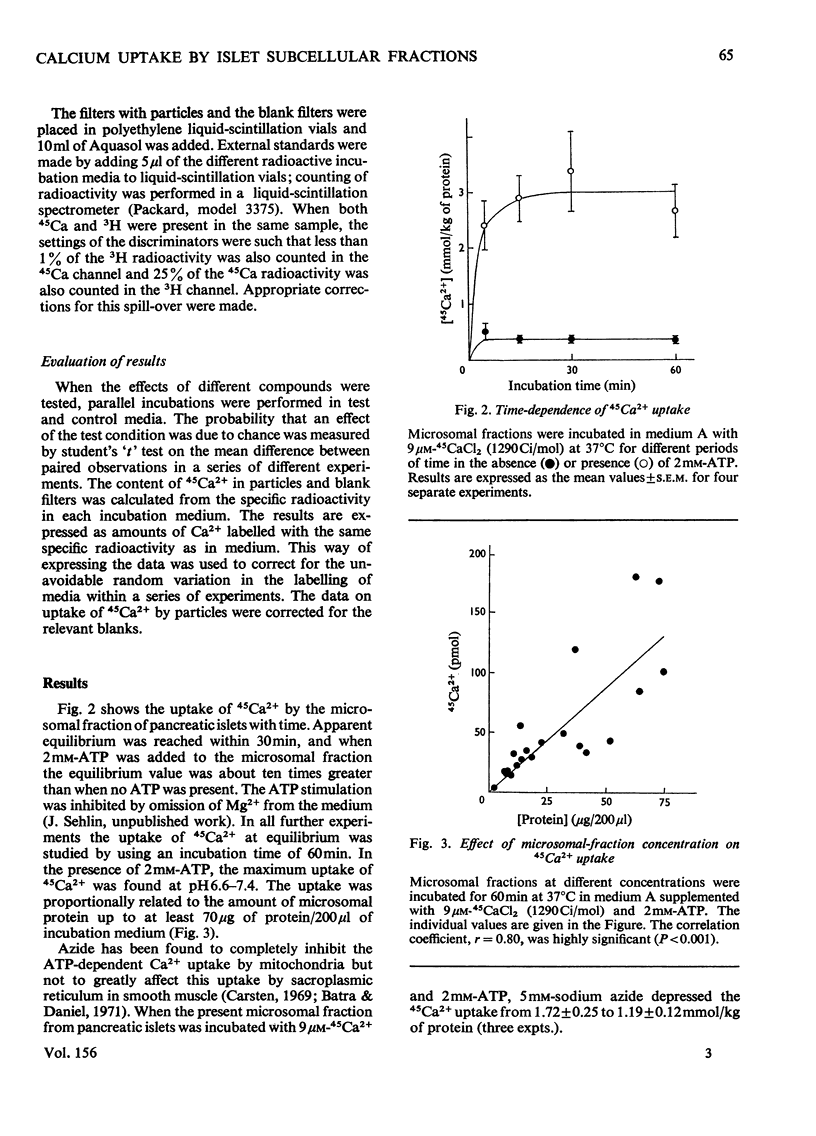
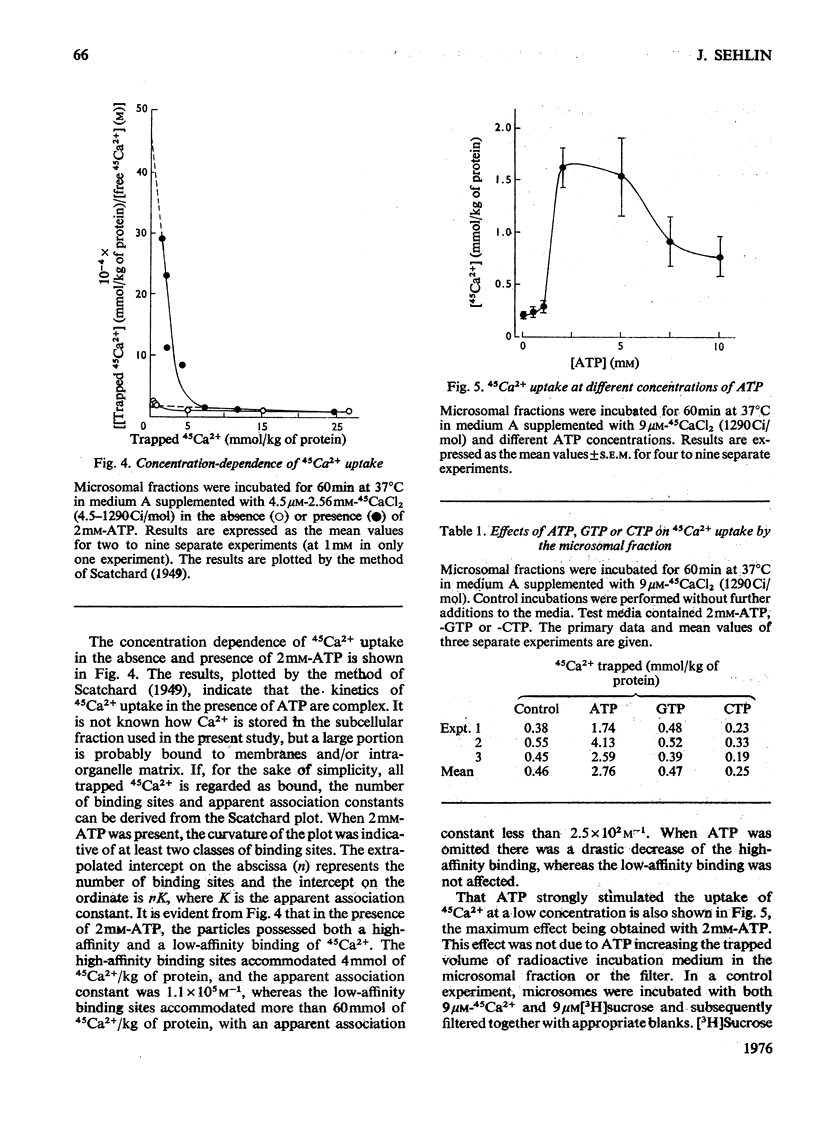
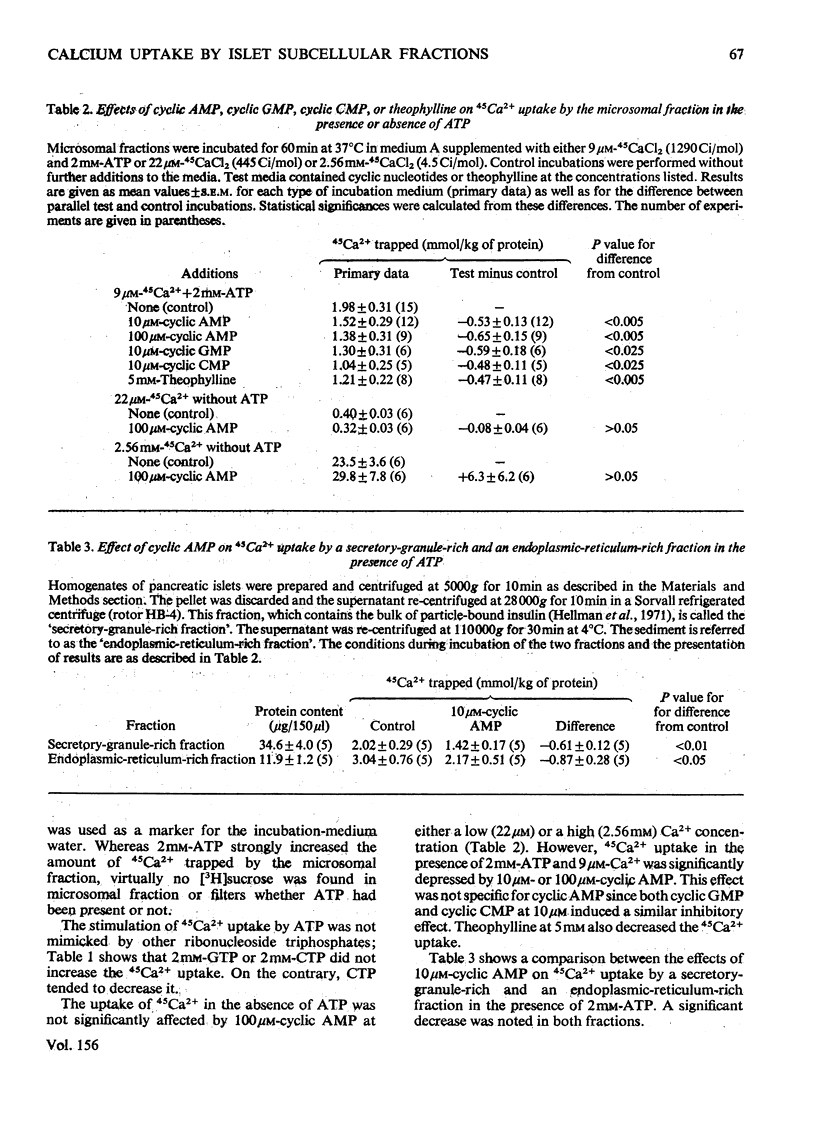
Uptake of 45Ca2+ by a microsomal fraction isolated pancreatic islets of non-inbred ob/ob mice was studied. ATP strongly stimulated 45Ca2+ uptake, the maximum effect being obtained with 2mM-ATP. GTP and CTP at this concentration did not increase the uptake. Scatchard analysis revealed at least two types of uptake mechanisms in the presence of 2mM-ATP; the apparent association constants were 1.1 x 10(5)m(-1) and less than 2.5 x 10(2)m(-1). In contradistinction to an unaffected low-affinity uptake, the high-affinity uptake was drastically decreased on ommission of ATP. The ATP-dependent and high-affinity uptake was half-saturated at about 10-20mum-Ca(2+) and was inhibited by 10 or 100mum cyclic AMP, 10mum cyclic GMP, 10 mum cyclic GMP, or 5mm-theophylline. 45ca2+ uptake in the absence of ATP was not affected by 100mum-cyclic AMP. In view of its sensitivity to ATP and cyclic nucleotides, the high-affinity Ca2+-uptake mechaniam may play a role in stimulus-secretion coupling in the beta-cells by regulating the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood L. G. Interrelationships between phosphates and calcium in bioelectric phenomena. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1966;9:223–261. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batra S. C., Daniel E. E. ATP-dependent Ca uptake by subcellular fractions of uterine smooth muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1971 Feb 1;38(2):369–385. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(71)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batra S. The effects of drugs on calcium uptake and calcium release by mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog skeletal muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jan 1;23(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Calcium metabolism at the cellular level. Fed Proc. 1973 Sep;32(9):1944–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson G. R., Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. VII. A proposed site of action for adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):232–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI106808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson G. R., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XI. Effects of theophylline and epinephrine on Ca efflux from perifused islets. Metabolism. 1973 Mar;22(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsten M. E. Role of calcium binding by sarcoplasmic reticulum in the contraction and relaxation of uterine smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Apr;53(4):414–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.4.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Ashcroft S. J., Randle P. J. Concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in mouse pancreatic islets measured by a protein-binding radioassay. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):599–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1340599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Requirement for calcium ion in insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):174–178. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Goldberg A. L. Uptake and release of 45Ca by brain microsomes, synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1971 Aug;18(8):1419–1431. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entman M. L., Levey G. S., Epstein S. E. Mechanism of action of epinephrine and glucagon on the canine heart. Evidence for increase in sarcotubular calcium stores mediated by cyclic 3',5'-AMP. Circ Res. 1969 Oct;25(4):429–438. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.4.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann N., Park C. R. Early effects of 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate on the fluxes of calcium end potassium in the perfused liver of normal and adrenalectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. J., Hellman B., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic beta-cell recognition of insulin secretogogues. Influence of neuraminidase treatment on the release of insulin and the islet content of insulin, sialic acid, and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5275–5284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Luzio J. P., Chandler J. A., Herman L. Localization of calcium in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of rat isolated fat cells. J Cell Sci. 1974 Jun;15(1):1–15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Calcium uptake by pancreatic -cells as measured with the aid of 45 Ca and mannitol- 3 H. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1795–1801. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Studies in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):541–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman L., Sato T., Hales C. N. The electron microscopic localization of cations to pancreatic islets of Langerhans and their possible tole in insulin secretion. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Feb;42(3):298–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Montague W. Regulation by nucleotides of 45calcium uptake in homogenates of rat islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lain R. F., Hess M. L., Gertz E. W., Briggs F. N. Calcium uptake activity of canine myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum in the presence of anesthetic agents. Circ Res. 1968 Nov;23(5):597–604. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinose M. Phosphoprotein formation during osmo-chemical energy conversion in the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 1;25(1):113–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G. R., Baird L. E. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. X. Effect of glucose on 45 Ca efflux from perifused islets. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):389–394. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Donley J., Halpin R. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. 3. The role of phospholipids in the adenosine triphosphatase activity and Ca++ transport. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. VII. Properties of a phosphoprotein intermediate implicated in calcium transport. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Hales C. N. The role of calcium and magnesium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas studied in vitro. Diabetologia. 1967 Mar;3(1):47–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01269910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Konishi K. Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate-dependent Ca2+ uptake of brain microsomes. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1129–1133. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijjar M. S., Pritchard E. T. Calcium binding by a plasma membrane fraction isolated from rat submandibular glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y. Some properties of fragmented frog sarcoplasmic reticulum with particular reference to its response to caffeine. J Biochem. 1970 May;67(5):667–683. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. Cell communication, calcium ion, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):404–412. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robblee L. S., Shepro D., Belamarich F. A. Calcium uptake and associated adenosine triphosphatase activity of isolated platelet membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Apr;61(4):462–481. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Rossi G. L. (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )-activated membrane ATPases in human red cells and their possible relations to cation transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Vincenzi F. F. Calcium movements across the membrane of human red cells. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):369–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlatz L., Marinetti G. V. Calcium binding to the rat liver plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):70–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkiss K. Calcium translocation by cells. Endeavour. 1974 Sep;33(120):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(74)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland E. W., Robison G. A. The role of cyclic-3',5'-AMP in responses to catecholamines and other hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):145–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


