Abstract
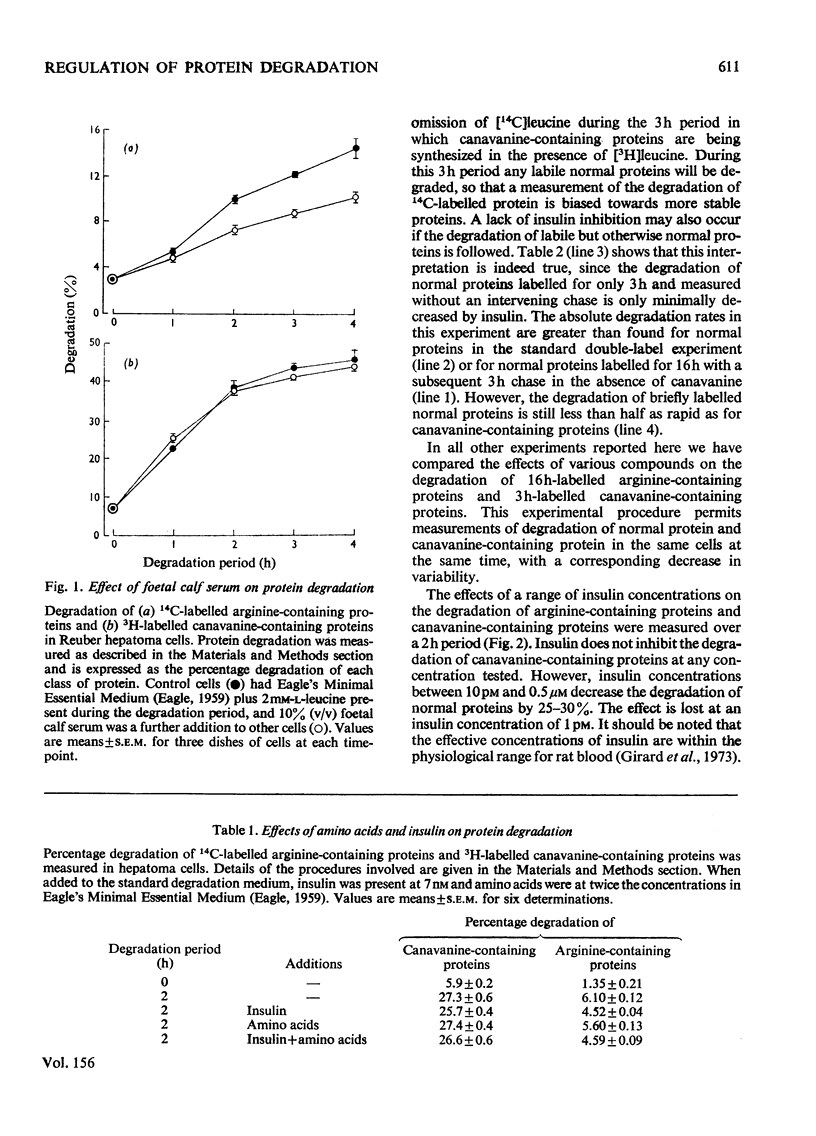
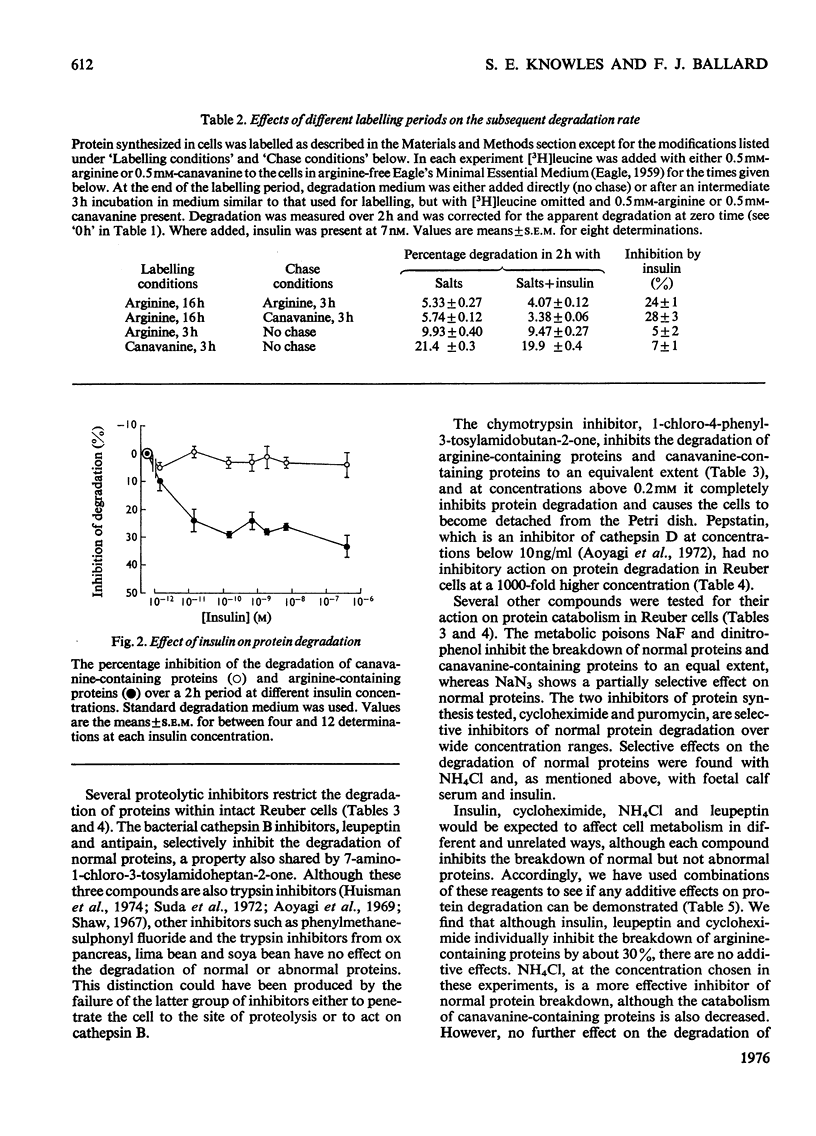
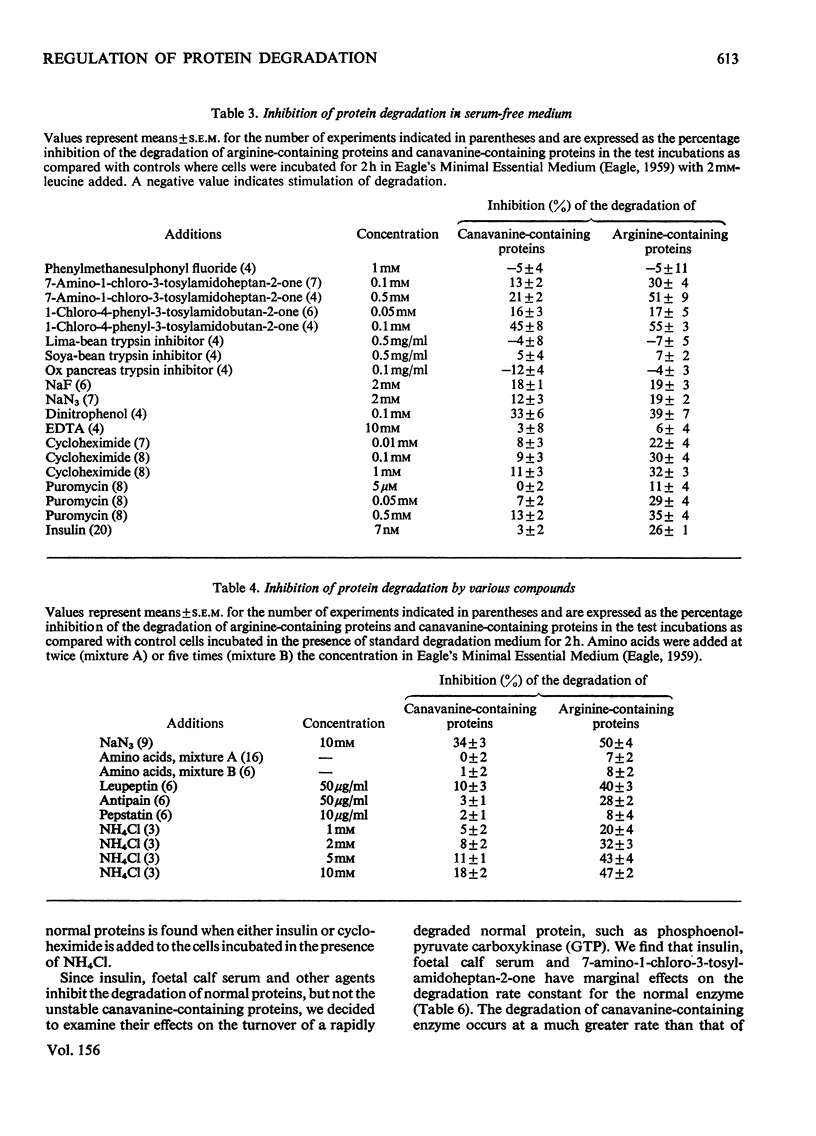
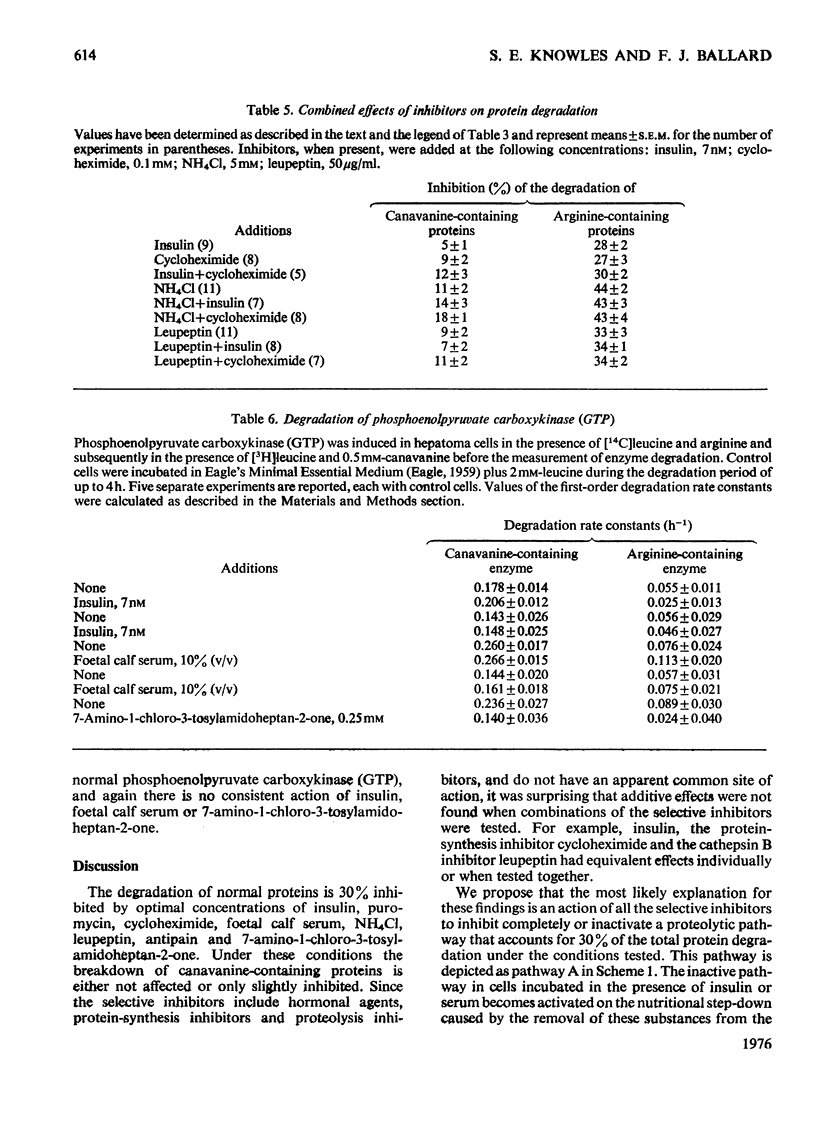
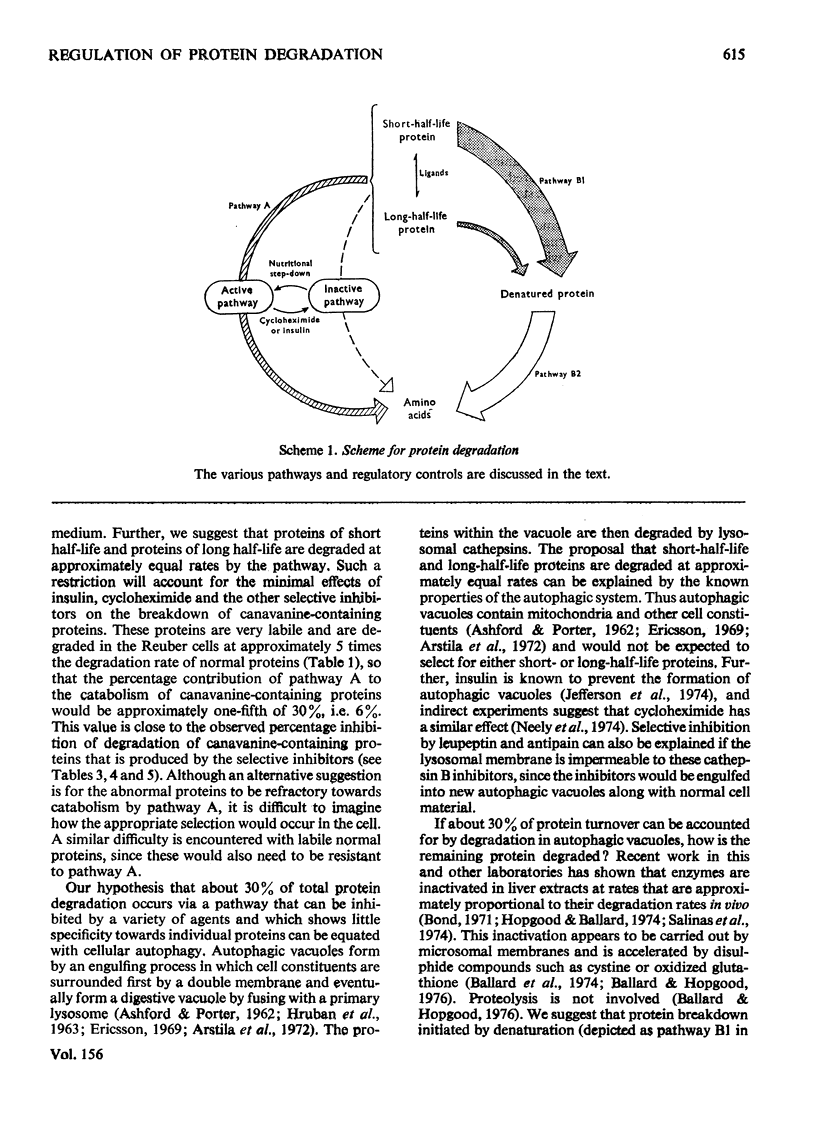
1. Rates of degradation of normal and abnormal protein were measured in hepatoma cells after labelling first for 16h with [14C]leucine plus L-arginine and then for 3h with [3H]-leucine plus the arginine analogue, L-canavanine. 2. Over the first 2h of the degradation period, canavanine-containing proteins were degraded at approximately 5 times the average degradation rate of normal proteins. 3. Degradation of normal proteins was inhibited by about 30% by insulin, cycloheximide, puromycin, leupeptin, antipain and foetal calf serum, whereas these agents had a negligible effect on the breakdown of canavanine-containing proteins. 4. Other compounds inhibited degradation of both classes of protein to equal extents. 5. Combination experiments showed no additional inhibitory effects on the degradation of normal proteins over degradation measured in the presence of a single selective inhibitor. 6. In contrast with the results with a 16 h labelling period, the degradation of normal proteins labelled for only 3 h was not inhibited by insulin. 7. These results are explained by a model with two distinct pathways of protein turnover. The first of these pathways involves the formation of autophagic vacuoles and would be completely inhibited by each of the selective inhibitors. Normal and canavanine-containing proteins would be catabolized by this pathway at equal rates. We propose that degradation by a second pathway is not regulated by the agents tested, but by the inherent stability of each protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHFORD T. P., PORTER K. R. Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jan;12:198–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Miyata S., Nanbo M., Kojima F., Matsuzaki M. Biological activities of leupeptins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Nov;22(11):558–568. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Nishizawa R., Kunimoto S., Takeuchi T. Biological activity of pepstatins, pepstanone A and partial peptides on pepsin, cathepsin D and renin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):689–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arstila A. U., Shelburne J. D., Trump B. F. Studies on cellular autophagocytosis. A histochemical study on sequential alterations of mitochondria in the glucagon-induced autophagic vacuoles of rat liver. Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;27(3):317–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hopgood M. F. Inactivation of phosphoenolypyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) by liver extracts. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):717–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1540717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hopgood M. F., Reshef L., Hanson R. W. Degradation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (guanosine triphosphate) in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj1400531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Ansorge S., Hanson H. Intrazellulärer Proteinabbau. 3. Intrazelluläre Verteilung des Zytosolproteinabbaues bei neutralem p. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;27(2):229–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S. A comparison of the proteolytic susceptibility of several rat liver enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90757-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. R., Kervran A., Soufflet E., Assan R. Factors affecting the secretion of insulin and glucagon by the rat fetus. Diabetes. 1974 Apr;23(4):310–317. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. Degradation of abnormal proteins in Escherichia coli (protein breakdown-protein structure-mistranslation-amino acid analogs-puromycin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HRUBAN Z., SPARGO B., SWIFT H., WISSLER R. W., KLEINFELD R. G. Focal cytoplasmic degradation. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jun;42:657–683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Ballard F. J. The relative stability of liver cytosol enzymes incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):371–376. doi: 10.1042/bj1440371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman W., Lanting L., Doddema H. J., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. Role of individual cathepsins in lysosomal protein digestion as tested by specific inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Rannels D. E., Munger B. L., Morgan H. E. Insulin in the regulation of protein turnover in heart and skeletal muscle. Fed Proc. 1974 Apr;33(4):1098–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles S. E., Gunn J. M., Hanson R. W., Ballard F. J. Increased degradation rates of protein synthesized in hepatoma cells in the presence of amino acid analogues. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):595–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1460595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles S. E., Gunn J. M., Reshef L., Hanson R. W., Ballard F. J. Properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (guanosine triphosphate) synthesized in hepatoma cells in the presence of amino acid analogues. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):585–593. doi: 10.1042/bj1460585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. HEPATOMAS IN TISSUE CULTURE COMPARED WITH ADAPTING LIVER IN VIVO. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 Apr;13:229–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Response of intracellular proteolysis to alteration of bacterial protein and the implications in metabolic regulation. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1527–1533. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1527-1533.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole B., Wibo M. Protein degradation in cultured cells. The effect of fresh medium, fluoride, and iodoacetate on the digestion of cellular protein of rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6221–6226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouty W. F., Goldberg A. L. Fate of abnormal proteins in E. coli accumulation in intracellular granules before catabolism. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 29;240(100):147–150. doi: 10.1038/newbio240147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouty W. F., Karnovsky M. J., Goldberg A. L. Degradation of abnormal proteins in Escherichia coli. Formation of protein inclusions in cells exposed to amino acid analogs. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1112–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas M., Wallace R., Grisolia S. Comparative studies in vivo and in vitro of rat-liver enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):375–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda H., Aoyagi T., Hamada M., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Antipain, a new protease inhibitor isolated from actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):263–266. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


