Abstract
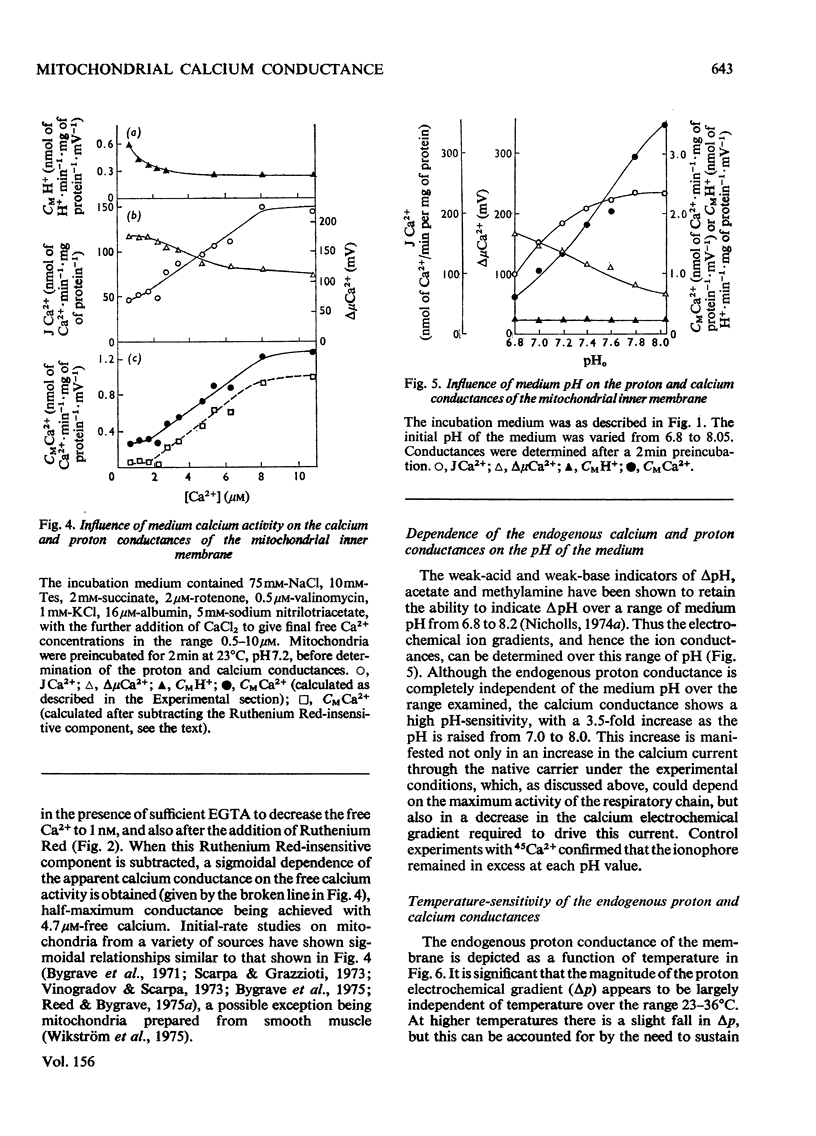
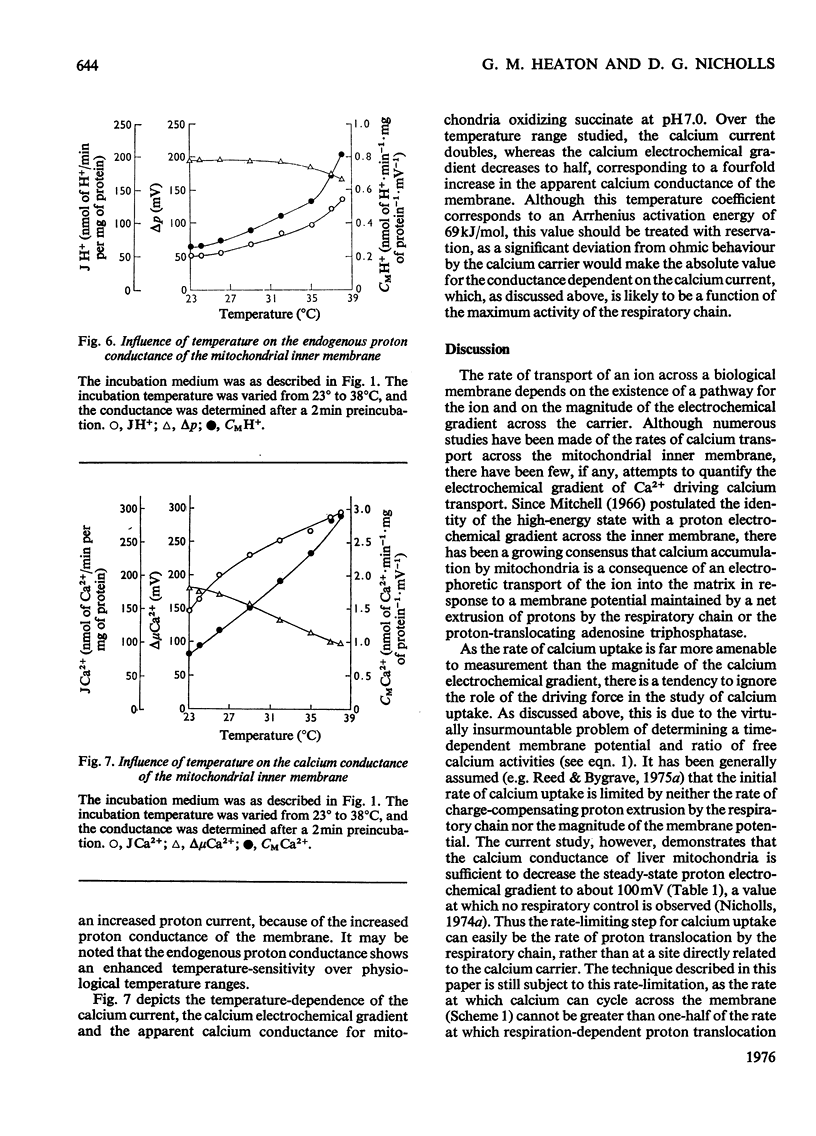
1. A method is described for establishing steady-state conditions of calcium transport across the inner membrane of rat liver mitochondria and for determining the current of Ca2+ flowing across the membrane, together with the Ca2+ electrochemical gradient across the native Ca2+ carrier. These parameters were used to quantify the apparent Ca2+ conductance of the native carrier. 2. At 23 degrees C and pH7.0, the apparent Ca2+ conductance of the carrier is close to 1 nmol of Ca2+-min-1-mg of protein-1 mV-1. Proton extrusion by the respiratory chain, rather than the Ca2+ carrier itself, may often be rate-limiting in studies of initial rates of Ca2+ uptake. 3. Under parallel conditions, the endogenous H+ conductance of the membrane is 0.3 nmol of H+-min-1-mg of protein-1-mV-1. 4. Ruthenium Red and La3+ both strongly inhibit the Ca2+ conductance of the carrier, but are without effect on the H+ conductance of the membrane. 5. The apparent Ca2+ conductance of the carrier shows a sigmoidal dependence on the activity of Ca2+ in the medium. At 23 degrees C and pH7.2, half-maximum conductance is obtained at a Ca2+ activity of 4.7 muM. 6. The apparent Ca2+ conductance and the H+ conductance of the inner membrane increase fourfold from 23 degrees to 38 degrees C. The apparent Arrhenius activation energy for Ca2+ transport is 69kJ/mol. The H+ electrochemical gradient maintained in the absence of Ca2+ transport does not vary significantly with temperature. 7. The apparent Ca2+ conductance increases fivefold on increasing the pH of the medium from 6.8 to 8.0. The H+ conductance of the membrane does not vary significantly with pH over this range. 8. Mg2+ has no effect on the apparent Ca2+ conductance when added at concentration up to 1 mM. 9. Results are compared with classical methods of studying Ca2+ transport across the mitochondrial inner membrane.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand M. D., Lehninger A. L. Superstoichiometric Ca2+ uptake supported by hydrolysis of endogenous ATP in rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7958–7960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L., Daday A. A., Doy F. A. Evidence of a calcium-ion-transport system in mitochondria isolated from flight muscle of the developing sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1460601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L., Reed K. C., Spencer T. Cooperative interactions in energy-dependent accumulation of Ca2+ by isolated rat liver mitochondria. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):89–89. doi: 10.1038/newbio230089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Azzi A. The affinity of mitochondria for Ca ++ . Experientia. 1972 Aug 15;28(8):906–908. doi: 10.1007/BF01924937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Gamble R. L., Lehninger A. L. On the maximum stoichiometry of energy-linked Ca++ accumulation during electron transport in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 8;21(3):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Gamble R. L., Rossi C. S., Lehninger A. L. Super-stoichiometric ratios between ion movements and electron transport in rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1199–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Lehninger A. L. A survey of the interaction of calcium ions with mitochondria from different tissues and species. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):681–690. doi: 10.1042/bj1220681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Mitochondrial uptake of calcium ions and the regulation of cell function. Biochem Soc Symp. 1974;(39):89–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Mela L. Hydrogen ion concentration changes in mitochondrial membranes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4588–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Schoener B. High and low energy states of cytochromes. 3. In reactions with cations. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4577–4587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAHOTA Z., CARAFOLI E., ROSSI C. S., GAMBLE R. L., LEHNINGER A. L. THE STEADY STATE MAINTENANCE OF ACCUMULATED CA++ IN RAT LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2712–2720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear A. R., Lehninger A. L. Rapid, respiration-independent binding of alkali metal cations by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3953–3962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E., Rossi C. S. Energy-linked ion movements in mitochondrial systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:259–320. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E. The interaction of La 3+ with mitochondria in relation to respiration-coupled Ca 2+ transport. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):506–515. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L. Mitochondria and calcium ion transport. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1190129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L. Interactions of La3+ and local anesthetic drugs with mitochondrial Ca++ and Mn++ uptake. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Feb;123(2):286–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Estimation of membrane potential and pH difference across the cristae membrane of rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):471–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Respiration-driven proton translocation in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1147–1162. doi: 10.1042/bj1051147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Translocation of some anions cations and acids in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L. Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Hamster brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria. The chloride permeability of the inner membrane under respiring conditions, the influence of purine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 2;49(3):585–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Hamster brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria. The control of respiration and the proton electrochemical potential gradient by possible physiological effectors of the proton conductance of the inner membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 2;49(3):573–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The influence of respiration and ATP hydrolysis on the proton-electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria as determined by ion distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. Ultraviolet and fluorescent spectral properties of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 and its metal ion complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4007–4014. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskin J. S., Gunter T. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance of copper ion and manganese ion complexes with the ionophore A23187. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):187–191. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. A kinetic study of mitochondrial calcium transport. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. Accumulation of lanthanum by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):239–252. doi: 10.1042/bj1380239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. Methodology for in vitro studies of Ca-2+ transport. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. The inhibition of mitochondrial calcium transport by lanthanides and ruthenium red. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):143–155. doi: 10.1042/bj1400143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. A quantitative analysis of super-stoichiometric H+ ejection and Ca 2+ uptake in respiring rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6067–6073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. The cause of superstoichiometric Ca2+ uptake and H+ ejection in L1210 mouse ascites tumor mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C., Azzi A., Azzone G. F. Ion transport in liver mitochondria. I. Metabolism-independent Ca++ binding and H+ release. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):951–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C., Azzone G. F. H+/O ratio during ca2+ uptake in rat-liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 22;110(2):434–436. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Scarpa A. Calcium uptake and membrane potential in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4811–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of transmembrane electrochemical proton gradients. J Bioenerg. 1975 May;7(2):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01558427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Azzone G. F. Ion transport in liver mitochondria. VI. The role of surface binding on aerobic Ca++translocation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5132–5138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Azzone G. F. The mechanism of ion translocation in mitochondria. 4. Coupling of K+ efflux with Ca2+ uptake. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):328–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Graziotti P. Mechanisms for intracellular calcium regulation in heart. I. Stopped-flow measurements of Ca++ uptake by cardiac mitochondria. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Dec;62(6):756–772. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.6.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Dunnett S. J. Calcium transport in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 18;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordahl L. A. Effects of magnesium, Ruthenium red and the antibiotic ionophore A-23187 on initial rates of calcium uptake and release by heart mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):104–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer T., Bygrave F. L. The role of mitochondria in modifying the cellular ionic environment: studies of the kinetic accumulation of calcium by rat liver mitochondria. J Bioenerg. 1973 Apr;4(3):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01648977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stucki J. W., Ineichen E. A. Energy dissipation by calcium recycling and the efficiency of calcium transport in rat-liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 2;48(2):365–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasington F. D., Gazzotti P., Tiozzo R., Carafoli E. The effect of ruthenium red on Ca 2+ transport and respiration in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 21;256(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov A., Scarpa A. The initial velocities of calcium uptake by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5527–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Ahonen P., Luukkainen T. The role of mitochondria in uterine contractions. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab H. Respiration-linked calcium ion uptake by flight muscle mitochondria from the blowfly Sarcophaga bullata. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4014–4018. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


