Abstract
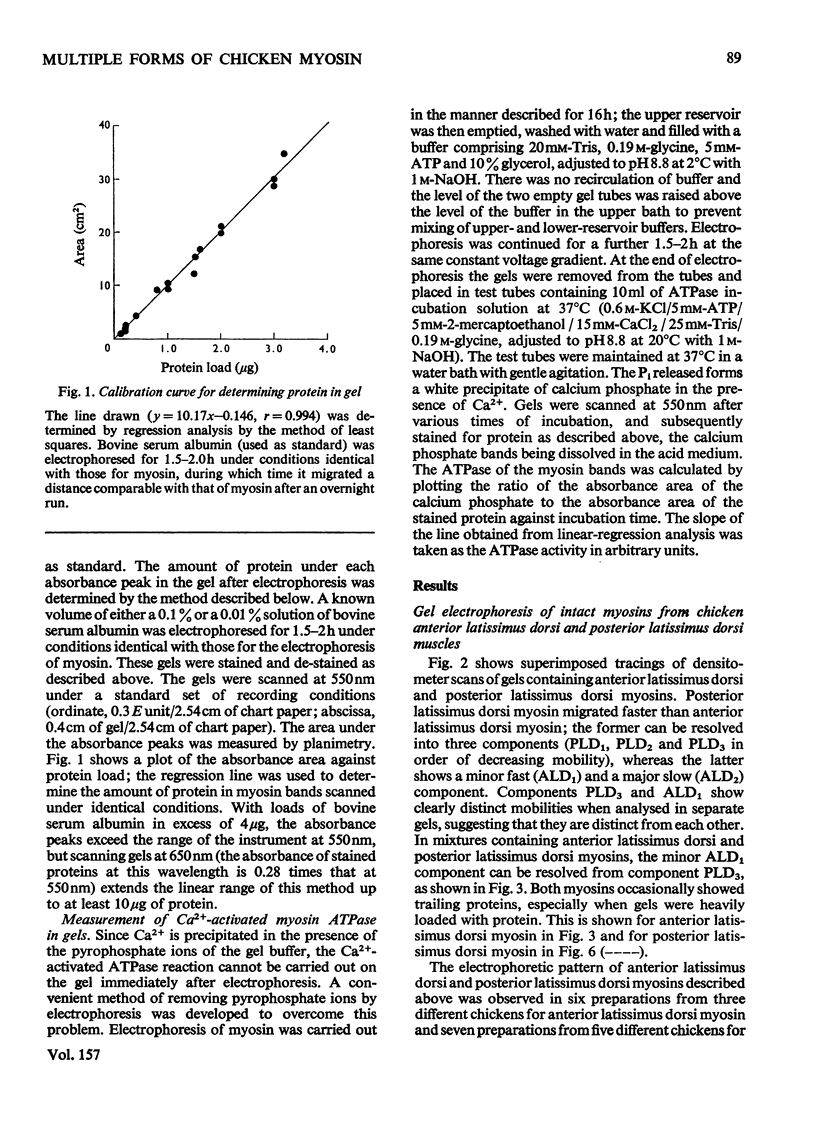
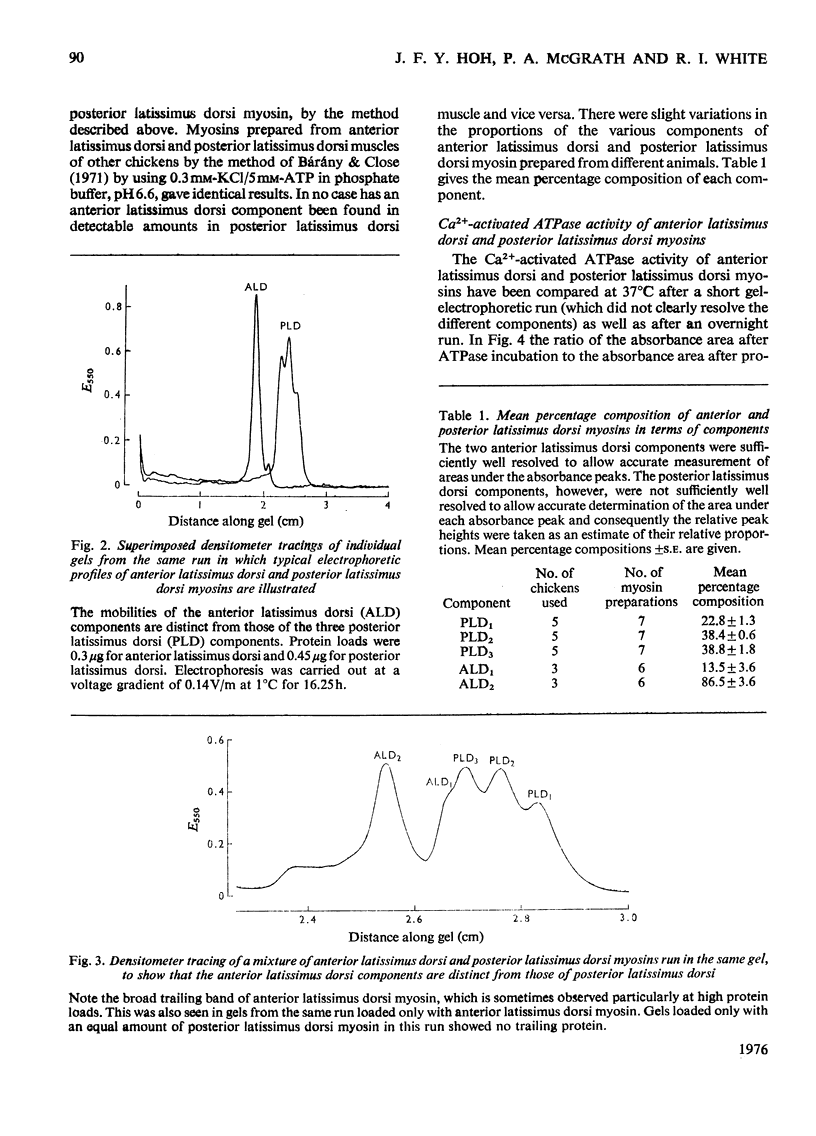
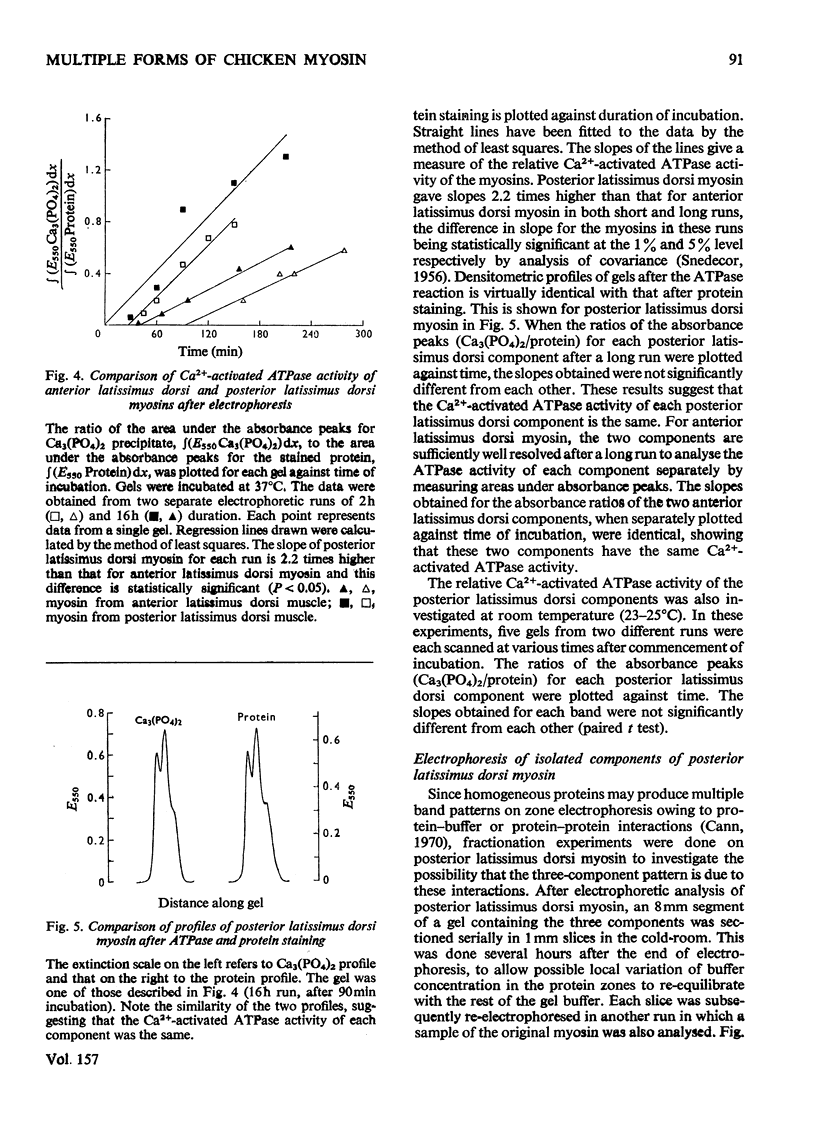
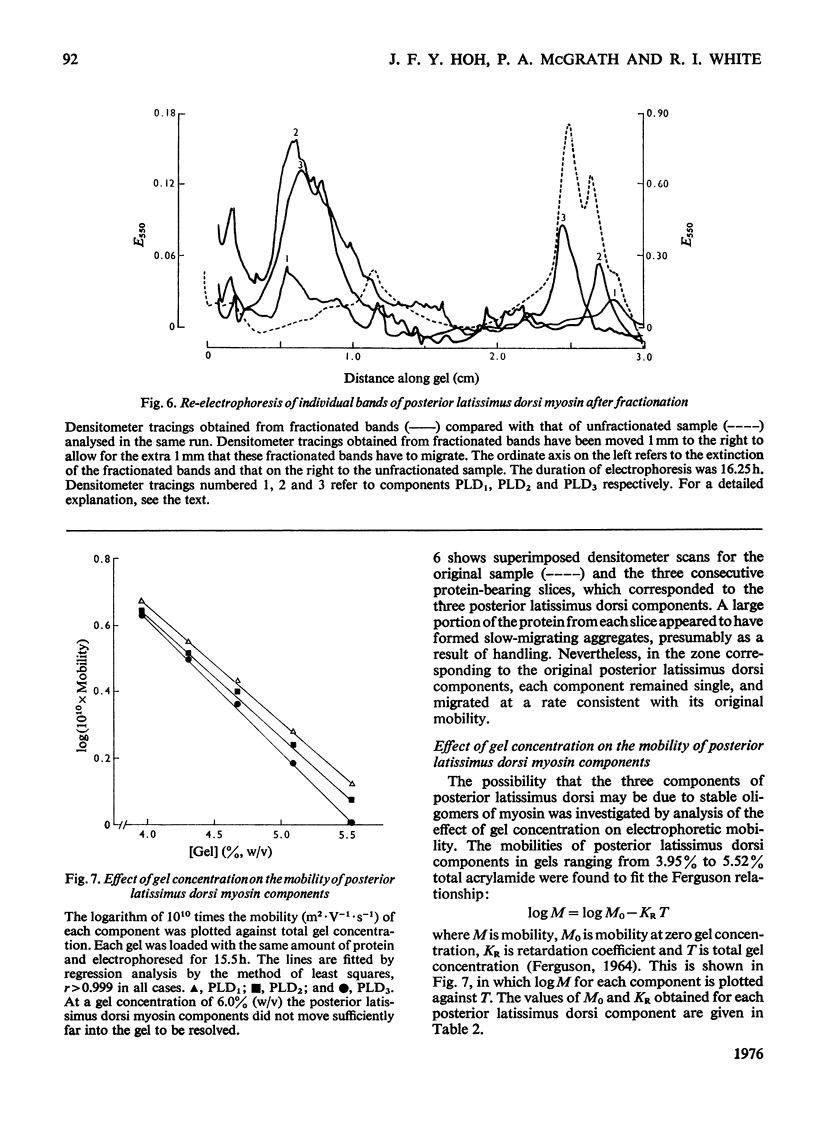
1. A method is described for the electrophoretic analysis of intact myosin in polyacrylamide gel in a buffer system containing 0.02 M-pyrophosphate and 10% (v/v) glycerol, pH 8.8. 2. In this system chicken skeletal-muscle myosins reveal five distinct electrophoretic components, three components from the fast-twitch posterior latissimus dorsi muscle and two slower-migrating components from the slow-twitch anterior latissimus dorsi muscle. 3. The Ca2+-activated ATPase (adenosine triphosphatase) activity of myosin components was measured by densitometric scanning of the gel for the Ca3(PO4)2 precipitate formed during the ATPase reaction and subsequently for stained protein. Each component from the same muscle appears to have identical ATPase activity, but components from the fast-twitch muscle had an activity 2.2 times higher than those from the slow-twitch muscle. 4. On re-electrophoresis in the same buffer system, individual fractions of fast-twitch myosin did not reproduce the three-band pattern of the original myosin, but migrated at rates consistent with their original mobility. 5. Analysis of the mobility of the three fast-twitch myosin components in gels of different concentrations suggests that they are not stable oligomers of each other. 6. It is suggested that these components of fast-twitch myosin and slow-twitch myosin are isoenzymes of myosin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril E. F., Love D. S., Herrmann H. Investigation of myosin heterogeneity observed during chromatography on diethylaminoethyl cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):822–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel P. J., Pearson A. M., Bodwell C. E. Isoelectric focusing of S- -(4-pyridylethyl)-L-cysteine myosin components on polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M., Close R. I. The transformation of myosin in cross-innervated rat muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(2):455–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield S. P. The mechanical properties and heat production of chicken latissimus dorsi muscles during tetanic contractions. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I., Luff A. R. Dynamic properties of inferior rectus muscle of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):259–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Properties of motor units in fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):45–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. The isometric responses of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1930 Jun 27;69(4):377–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Brivio R. P., Battelle B. A. Isoelectric focusing of myosin in dilute polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Apr;40(2):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Brivio R. P. Disc electrophoresis of myosin and myosin derivatives in dilute polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazith J., Himmelfarb S., Harrington W. F. Studies on the subunit structure of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershman L. C., Stracher A., Dreizen P. Subunit structure of myosin. 3. A proposed model for rabbit skeletal myosin. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 25;244(10):2726–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S. "Molecular sieve" chromatography on polyacrylamide gels, prepared according to a simplified method. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale R. G., Beecher G. R. Electrophoretic separation of myosin large subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80455-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Craggs E. C. The contraction times and enzyme activity of two rabbit laryngeal muscles. J Anat. 1968 Jan;102(Pt 2):241–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F. Neural regulation of mammalian fast and slow muscle myosins: an electrophoretic analysis. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):742–747. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G. Amino acid sequences around the two -N-trimethyllysine residues in rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4057–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G., Elzinga M. Amino acid sequence around the single 3-methylhistidine residue in rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):229–236. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. The absence of 3-methylhistidine in red, cardiac and fetal myosins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jun 5;39(5):956–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Risby D. Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):81–85. doi: 10.1038/234081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melichna J., Gutmann E., Syrový I. Developmental changes in contraction properties, adenosine-triphosphatase activity and muscle fibre pattern of fast and slow chicken muscle. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1974;23(6):511–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Light chains of myosins from white, red, and cardiac muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polarity of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrový I., Gutmann E. ATPase activity of 2 rabbit laryngeal muscles. Experientia. 1971 Mar 15;27(3):248–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02138124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Cody F. W., Bosley M. A. Histochemical and mechanical properties of the jaw muscles of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1973 Jan;38(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Albis A., Gratzer W. B. Electrophoretic examination of native myosin. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 1;29(3):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


