Abstract
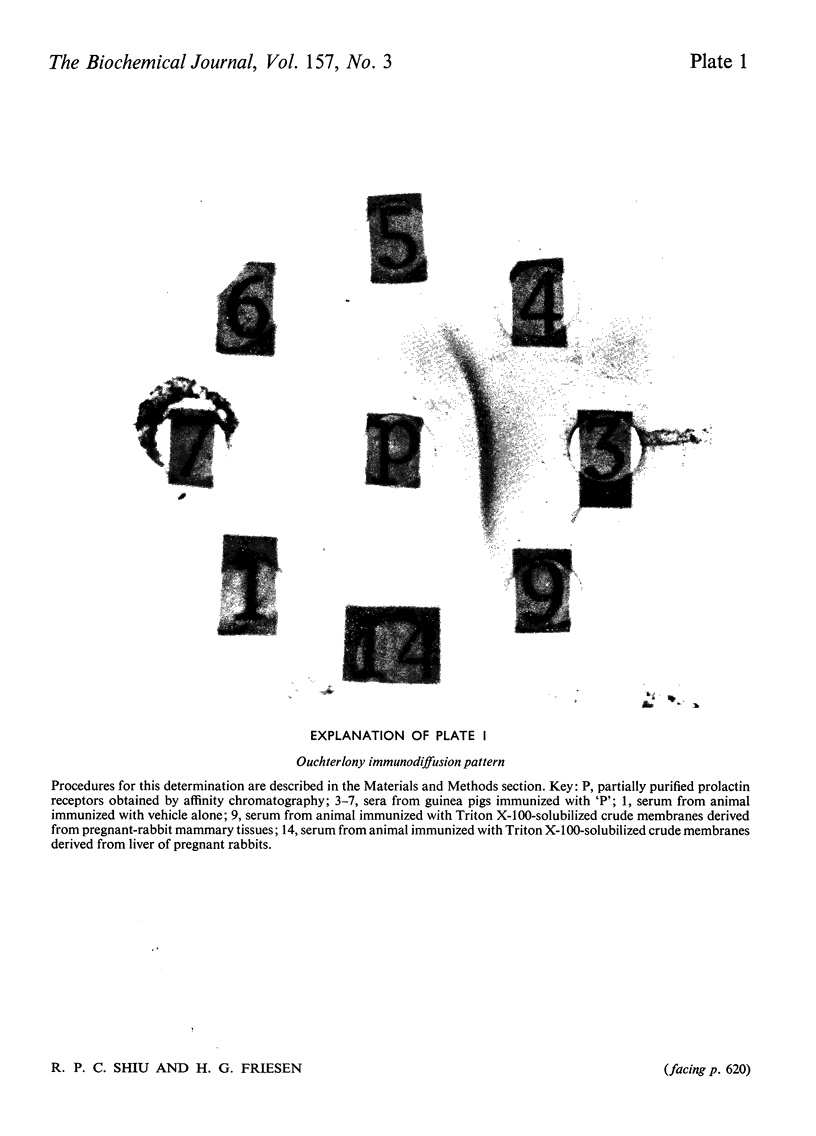
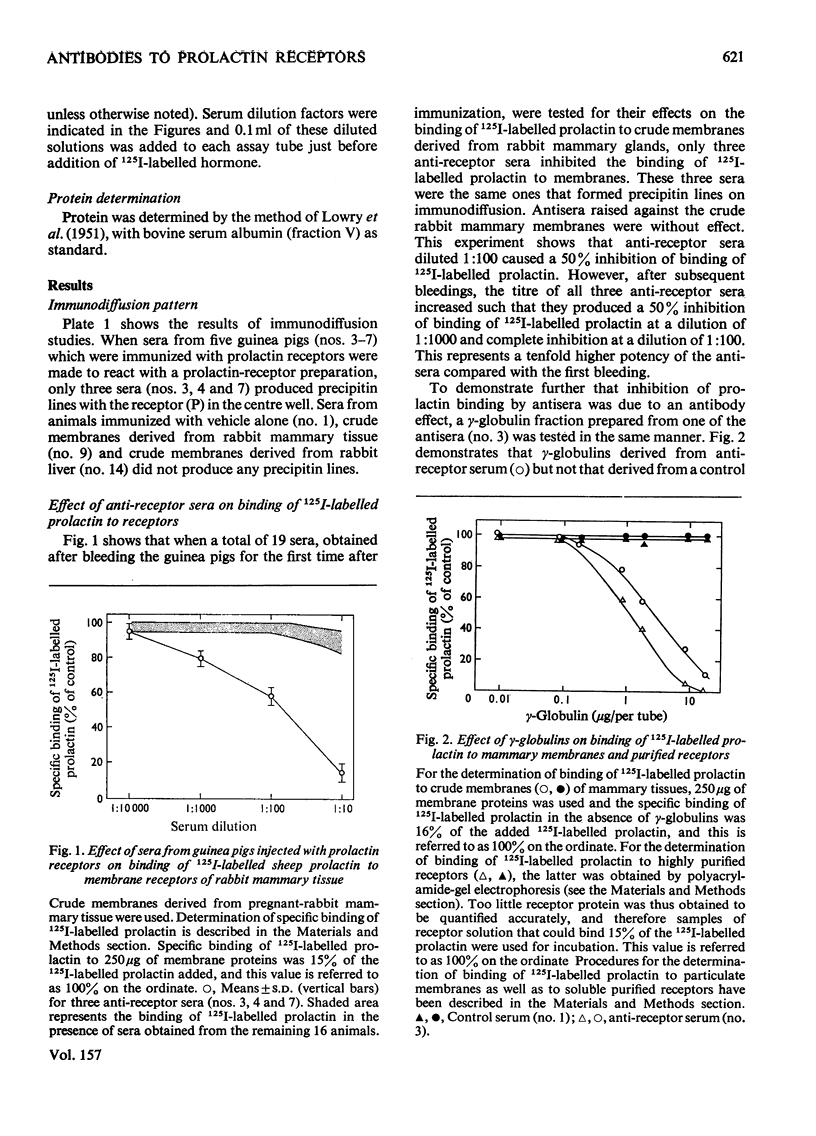
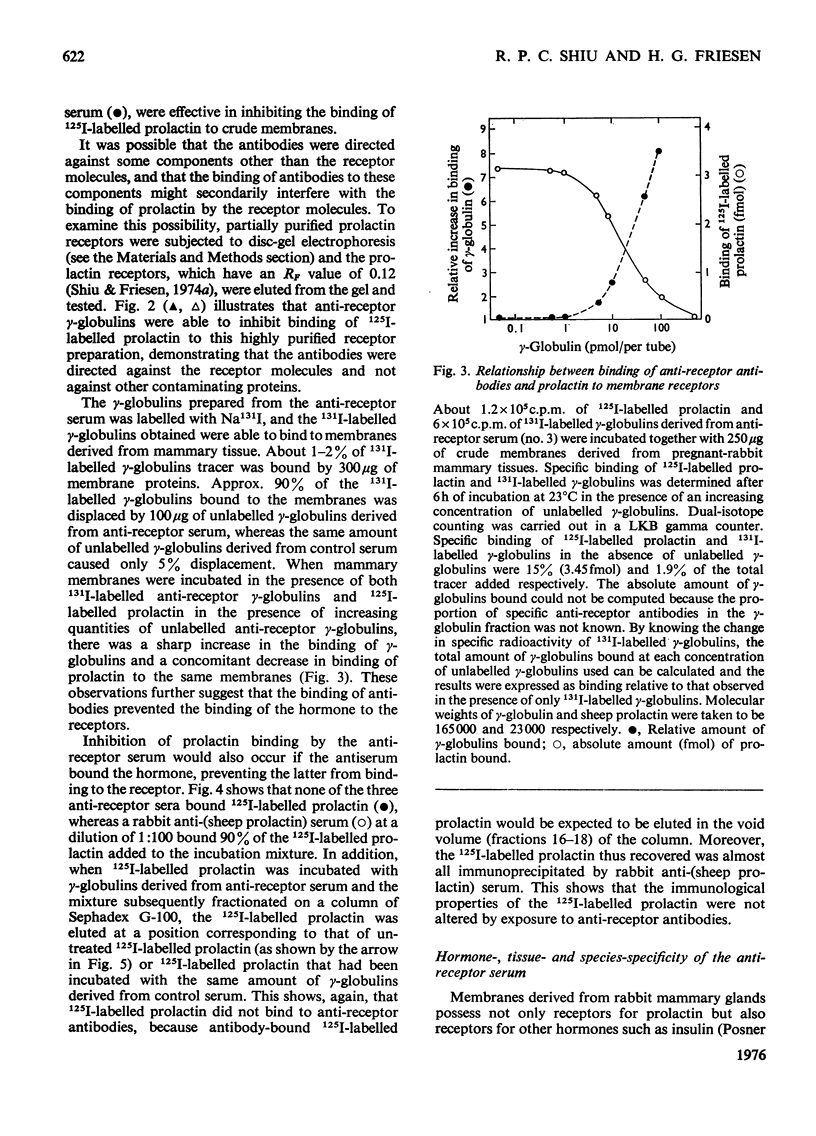
Antisera against a partially purified prolactin-receptor preparation derived from pregnant-rabbit mammary glands were generated in guinea pigs. On double immuno-diffusion, each antiserum produced a single precipitin line with the prolactin receptors. The anti-receptor sera also specifically inhibited the binding of 125I-labelled sheep prolactin to membrane particles as well as to highly purified prolactin receptors derived from the rabbit mammary glands. The same antisera, however, had no effect on the binding of 125I-labelled insulin to the same membranes. These antisera did not bind or destroy prolactin. Moreover, the binding of 125I-LABELLED PROLACTIN TO MEMBRANE PARTICLES DErived from different tissues from a number of species was also inhibited by the antisera, thus suggesting that the immunological determinants of the prolactin receptors are similar in various tissues derived from different species. The factors in the antisera that were responsible for inhibiting the binding of 125I-labelled prolactin to its receptors were found to be associated with the gamma-globulin fraction. In addition, 131I-labelled gamma-globulins derived from one antiserum were shown to bind to membrane particles derived from mammary glands, and an increase in binding of gamma-globulin was accompanied by a decrease in binding of prolactin. Kinetic analyses of inhibition of 125I-labelled prolactin binding by antisera by using the methods of Lineweaver & Burk [J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1934) 56, 658-666] and Dixon [Biochem. J. (1953) 55, 170-171], revealed that the mechanism is a hyperbolic competitive inhibition. The demonstration of hormone-receptor-antibody complexes further favours this mechanism. The availability of anti-receptor sera should facilitate studies on the functional role as well as other biochemical, immunological and physiological properties of the prolactin receptors.
Full text
PDF

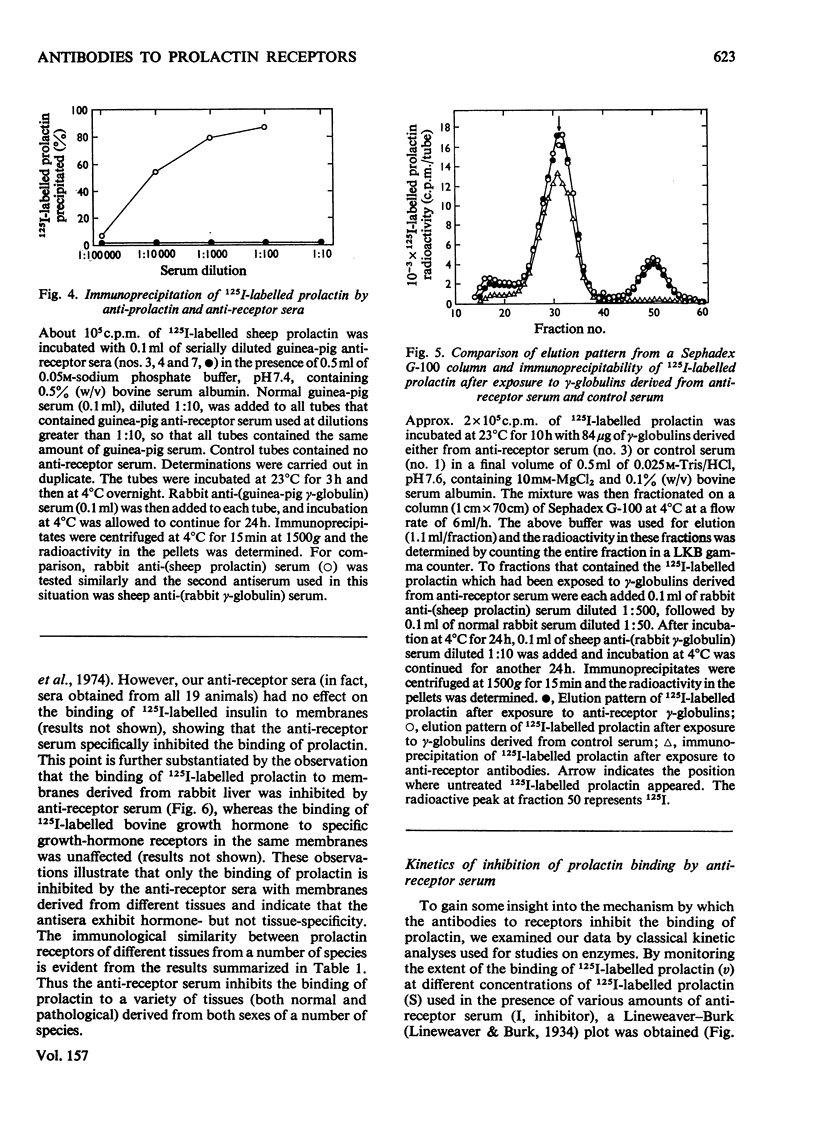
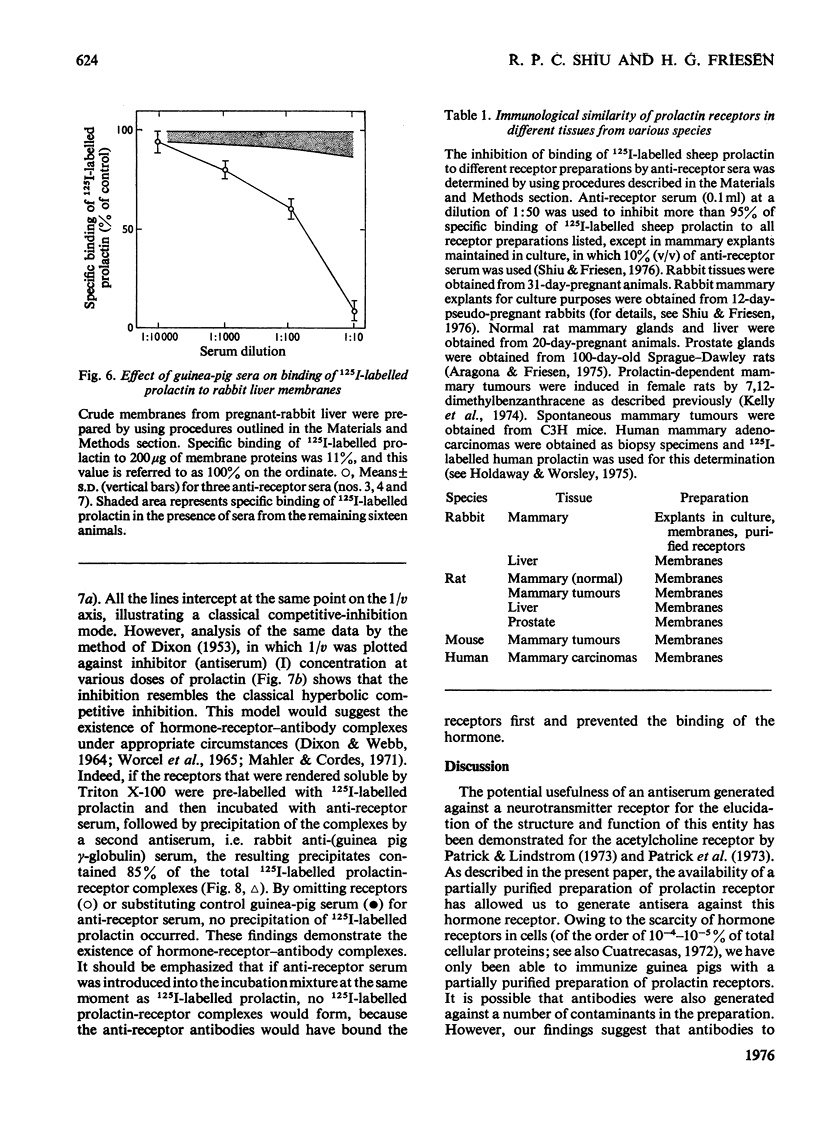
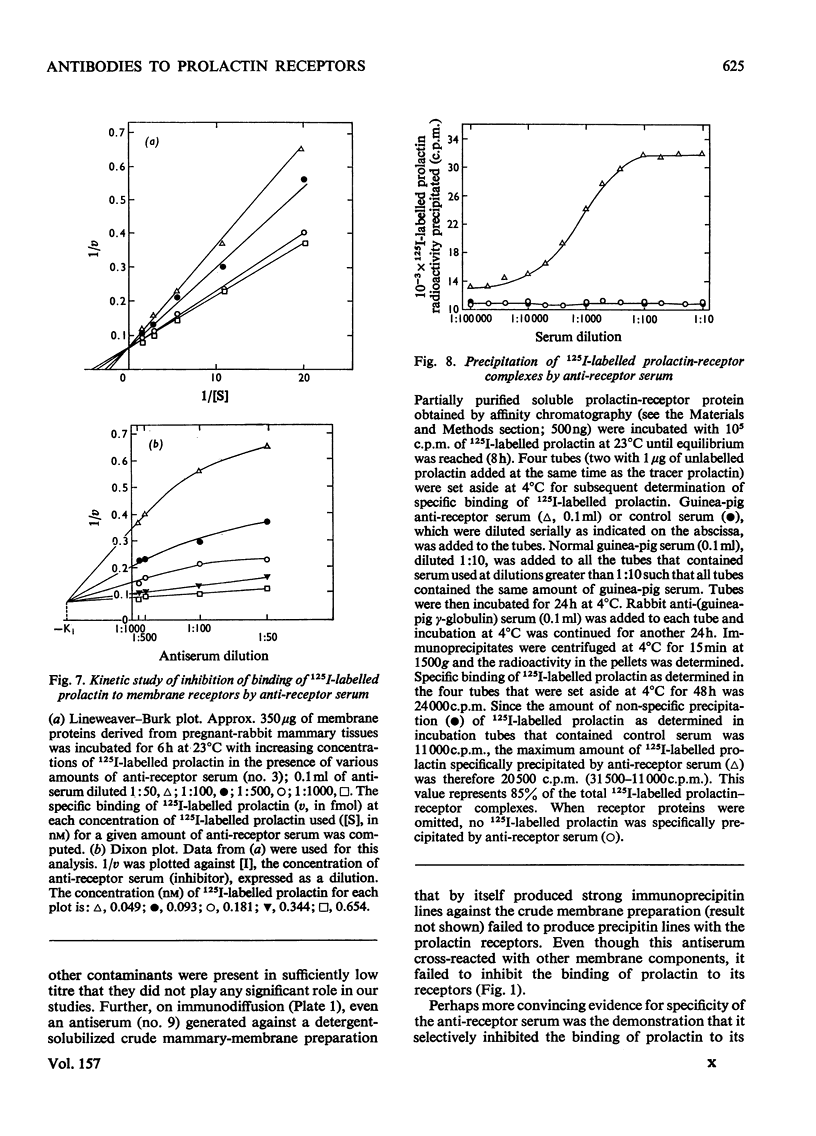

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aragona C., Friesen H. G. Specific prolactin binding sites in the prostate and testis of rats. Endocrinology. 1975 Sep;97(3):677–684. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-3-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Kaumann A. J. Receptors and acceptors: a necessary distinction in hormone binding studies. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1974;4(0):239–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography and purification of the insulin receptor of liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Hormone receptors - their function in cell membranes and some problems related to methodology. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:79–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Ryan D. W., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Gonadotropin receptors. Solubilization and purification by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4822–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgio N. A., Johnson C. B., Blecher M. Hormone receptors. 3. Properties of glucagon-binding proteins isolated from liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):428–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Bradley C., Shiu R. P., Meites J., Friesen H. G. Prolactin binding to rat mammary tumor tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):816–819. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J., Culp B., McMillan J. Studies on purified eel acetylcholine receptor and anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I., Kelly P. A., Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Studies of insulin, growth hormone and prolactin binding: tissue distribution, species variation and characterization. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):521–531. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Blockade of prolactin action by an antiserum to its receptors. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):259–261. doi: 10.1126/science.176727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Properties of a prolactin receptor from the rabbit mammary gland. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):301–311. doi: 10.1042/bj1400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Solubilization and purification of a prolactin receptor from the rabbit mammary gland. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7902–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORCEL A., GOLDMAN D. S., CLELAND W. W. AN ALLOSTERIC REDUCED NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE OXIDASE FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3399–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]