Abstract
Cortex of rat kidney was homogenized and fractions enriched in plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum or brush border were prepared by several techniques of differential centrifugation. The identity and homogeneity of the membrane fragments were investigated by assaying marker enzymes and by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Kallikrein was present in both plasma-membrane- and endoplasmic-reticulum-enriched fractions isolated by two fractionation procedures. Kallikrein was highly concentrated in a plasma-membrane fraction but was absent from the brush-border membrane of proximal tubular cells. Cells of transplanted renal tumours of the rat, originating from the proximal tubule, had no kallikrein activity. Kininase activity, angiotensin I-converting enzyme (kininase II) and angiotensinase were found in a plasma-membrane-enriched fraction and especially in the fraction containing isolated brush border. It is suggested that after renal kallikrein is synthesized on endoplasmic reticulum, it is subsequently reoriented to a surface membrane for activation and release. Renal kallikrein may enter the tubular filtrate distal to the proximal tubules. The brush-border membrane of proximal tubule is the major site of inactivation of kinins and angiotensin II..
Full text
PDF



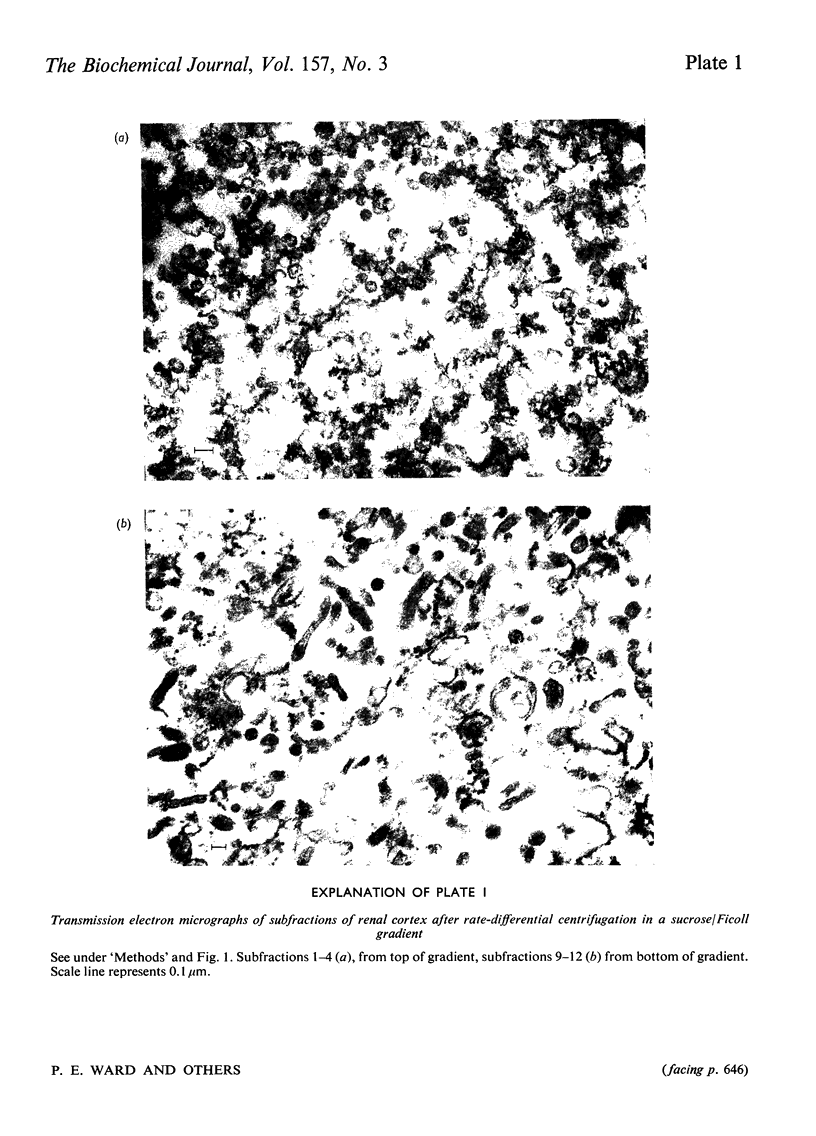

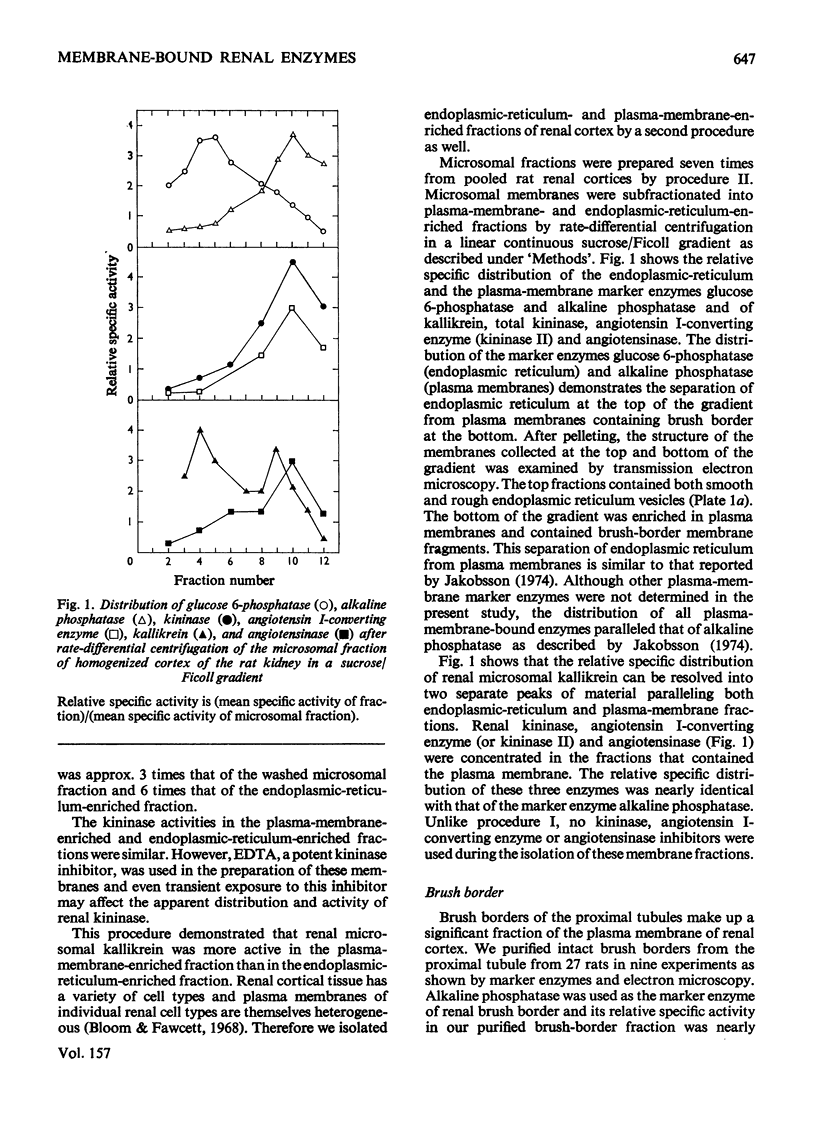



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K. Urinary excretion of kinin in man with special reference to its origin. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 25;87(2):175–184. doi: 10.1620/tjem.87.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An ethical consideration of large-scale clinical trials in cardiovascular diseases. Report of the Committee on Ethics of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1975 Sep;52(3):5–9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.3.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRACLOUGH M. A., MILLS I. H. EFFECT OF BRADYKININ ON RENAL FUNCTION. Clin Sci. 1965 Feb;28:69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven V. H., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. A sensitive isotopic procedure for the assay of esterase activity: measurement of human urinary kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birckbichler P. J., Dowben R. M., Matacic S., Loewy A. G. Isopeptide bonds in membrane proteins from eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 2;291(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. Renal kallikrein: its localization and possible role in renal function. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho I. F., Diniz C. R. Kinin-forming enzyme (kininogenin) in homogenates of rat kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 17;128(1):136–148. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS E. G., SLOANE E. M. An enzyme in human blood plasma that inactivates bradykinin and kallidins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Jul;11:585–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdos E. G., Yang H. Y. An enzyme in microsomal fraction of kidney that inactivates bradykinin. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 15;6(6):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBSCHER G., WEST G. R. SPECIFIC ASSAYS OF SOME PHOSPHATASES IN SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Nature. 1965 Feb 20;205:799–800. doi: 10.1038/205799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Mochizuki Y., Morris H. P., Slesers A. Ultrastructure of Morris renal tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jun;50(6):1487–1495. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.6.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson S. V. Subfractionation and properties of rat kidney cortex microsomal fraction. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertensive man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):820–825. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga M., Kira J., Saito N., Ogino K., Takayasu M. Acid angiotensinase, renin, and acid adenosine triphosphatase in rat kidney lysosomes. Jpn Circ J. 1968 Feb;32(2):137–143. doi: 10.1253/jcj.32.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Itskovitz H. D., Terragno A., Wong P. Y. Modulation and mediation of the action of the renal kallikrein-kinin system by prostaglandins. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa I., Erdös E. G., Seki T. Presence of three peptides in urinary kinin (substance Z) preparations. Life Sci. 1968 Dec 15;7(24):1339–1343. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa I., Erdös E. G., Seki T. Separation of peptide components of urinary kinin (substance Z). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):768–772. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Colina-Chourio J., McGiff J. C. Disappearance of bradykinin in the renal circulation of dogs. Effects of kininase inhibition. Circ Res. 1975 Jul;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K. Localization of kininogenase in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 May;39(1):87–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima G., Gecse A., Erdös E. G. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme of the kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman T. N., Oparil S., Carone F. A. Fate of labeled angiotensin II microinfused into individual nephrons in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Mar;228(3):747–751. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.3.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. J., Robinson G. B. Isolation and characterization of rabbit kidney brush borders. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1319–1328. doi: 10.1042/bj1281319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., GILMORE J. P. INFLUENCE OF KALLIDIN-L0 ON RENAL FUNCTION. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:714–718. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., ERDOS E. G. Uber eine neue blutdrucksenkende, darm- und uteruserregende Substanz im menschlichen Urin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1954;223(3):234–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., VOGEL R. [On the excretion of kallikrein in urine after experimental kidney injury]. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Jun 1;126:171–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Erdös E. G. Isolation of membrane-bound renal kallikrein and kininase. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1510755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfong R. F., Neville D. M., Jr The isolation of a brush border membrane fraction from rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6106–6112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. A dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase that converts angiotensin I and inactivates bradykinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 21;214(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II: angiotensin I converting enzyme). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]