Abstract
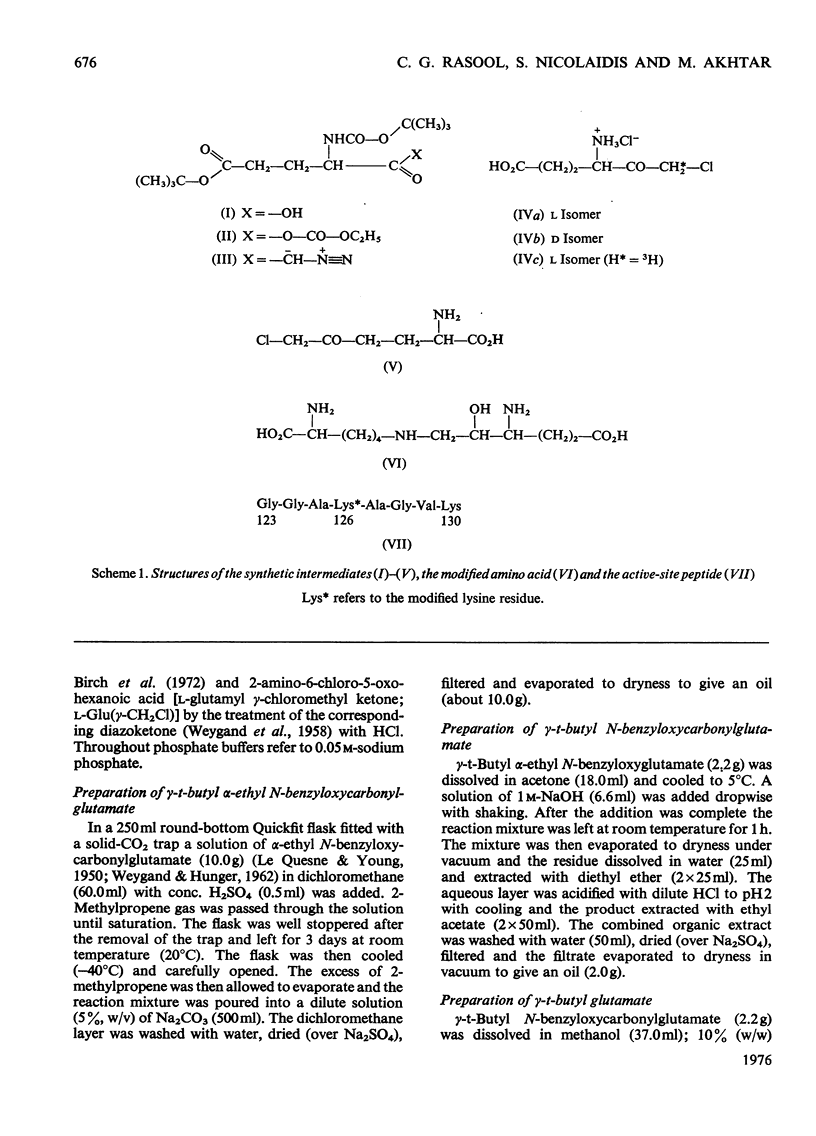
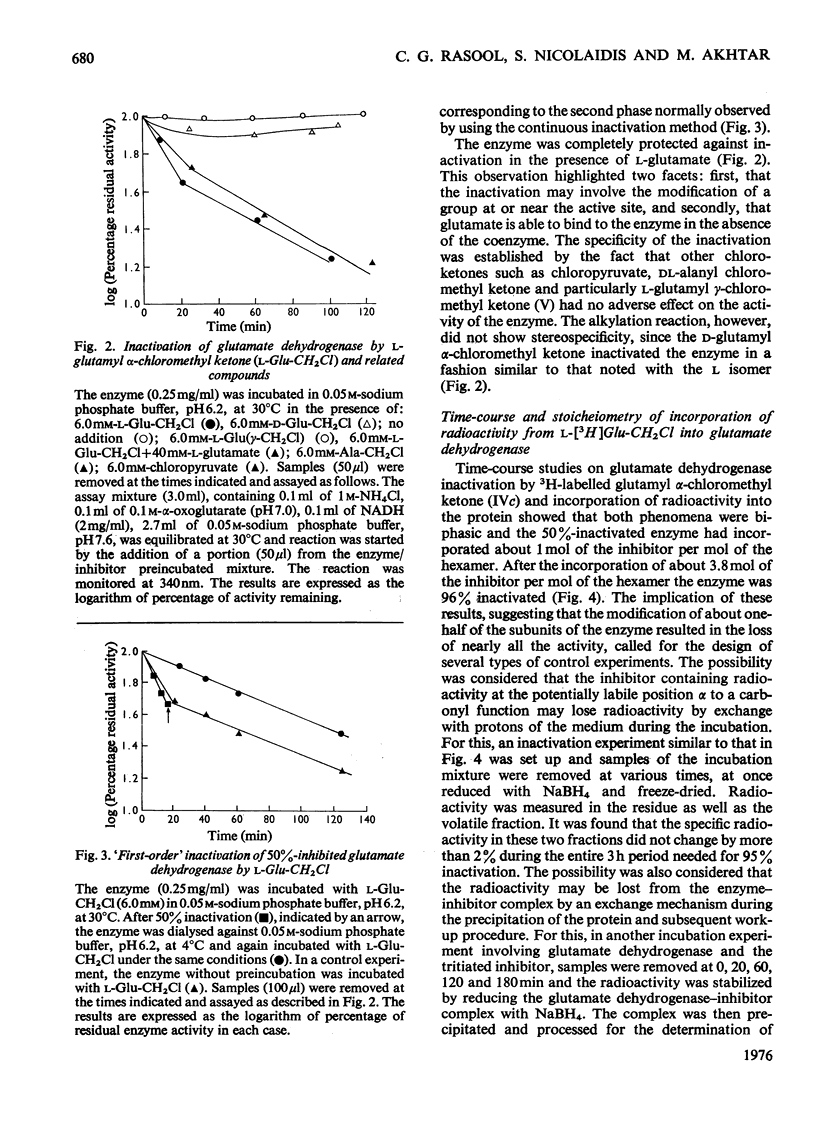
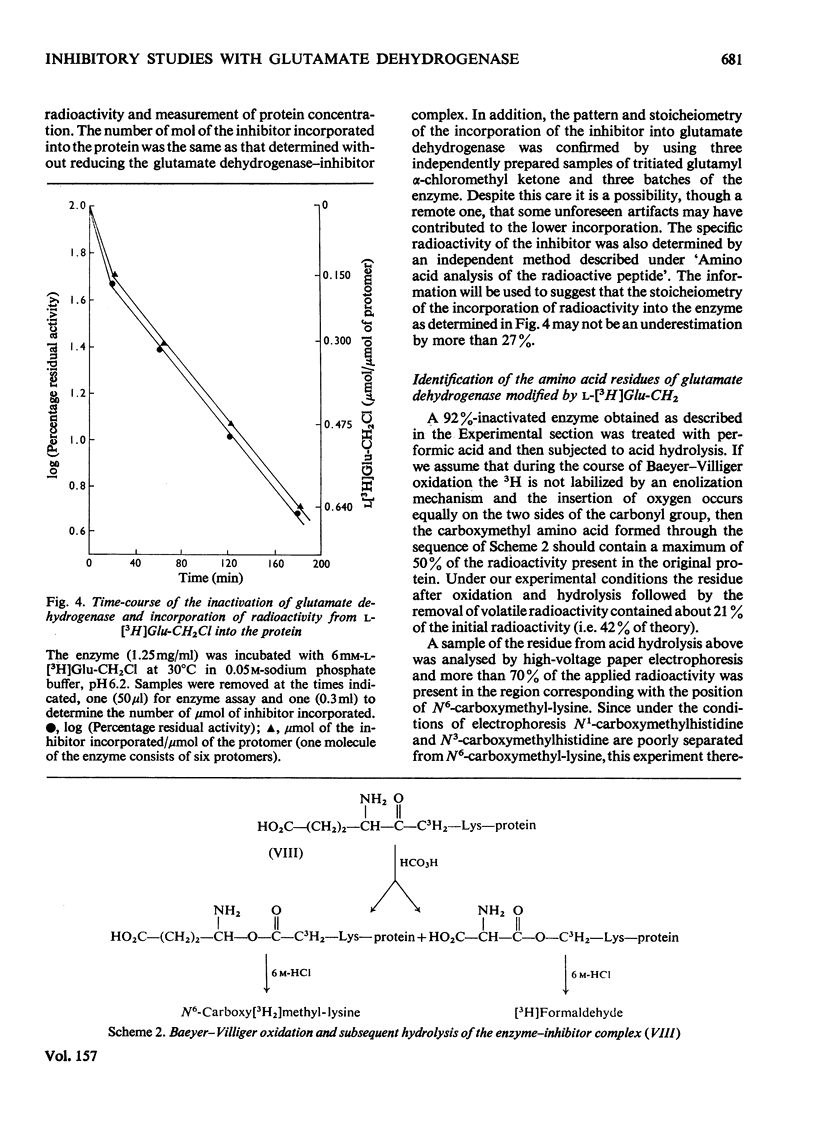
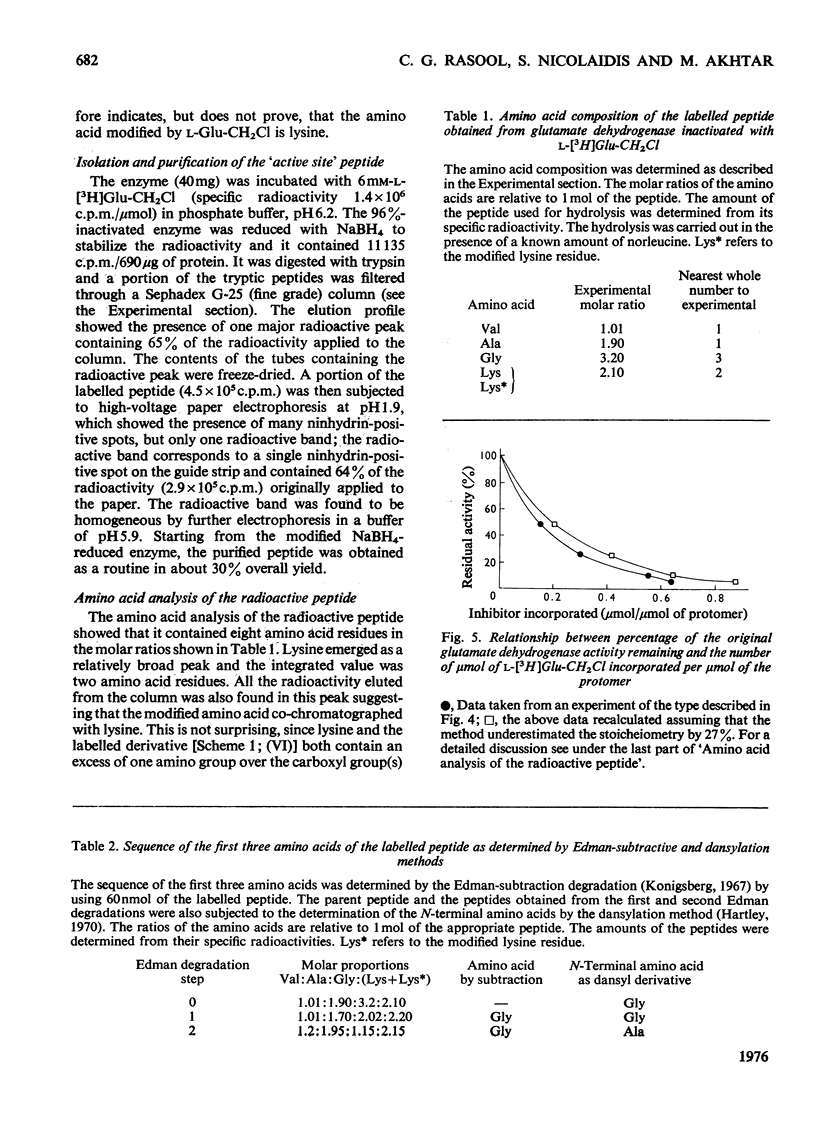
A method for the preparation of D- and L-glutamyl alpha-chloromethyl ketones (4-amino-6-chloro-5-oxohexanoic acid) is described. These chloromethyl ketones irreversibly inactivated bovine glutamate dehydrogenase, whereas several other related compounds had no adverse effect on the activity of the enzyme. The inactivation process was shown to be due to the modification of lysine-126. The time-courses for the inactivation and the incorporation of radioactivity from tritiated L-glutamyl alpha-chloromethyl ketone into the glutamate dehydrogenase were biphasic. The results were interpreted to suggest the involvement of 'negative co-operative' interactions in the reactivity of lysine-126. From the cumulative evidence it is argued that the first subunit of the enzyme, which takes part in catalysis, makes the largest, and the last the smallest, contribution to the overall catalysis. It is emphasized that three of the six subunits of the enzyme may possess as much as 80% of the total activity of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Tomkins G. M. The subunits of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase: demonstration of a single peptide chain. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. E., Dalziel K. A conformational transition of the oligomer of glutamate dehydrogenase induced by half-saturation with NAD + or NADP + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 5;309(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. L., el-Obeid H. A., Akhtar M. The preparation of chloromethylketone analogues of amino acids: inhibition of leucine aminopeptidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):447–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Bradshaw R. A., Goldin B. R., Frieden C. Identification of the sites of modification of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase reacted with trinitrobenzenesulfonate. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3516–3526. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggins J. R., Kray W., Shaw E. Affinity labelling of proteinases with tryptic specificity by peptides with C-terminal lysine chloromethyl ketone. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):579–585. doi: 10.1042/bj1370579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Franco A., Iwatsubo M. Reaction mechanism of L-glutamate dehydrogenase. Characterization of optical and kinetic properties of various enzyme-reduced-coenzyme complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 7;30(3):517–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R., Frieden C. Effect of trinitrophenylation of specific lysyl residues on the catalytic, regulatory, and molecular properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3527–3534. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Roberts P. A., Wallis R. B. The site at which 4-iodoacetamidosalicylate reacts with glutamate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):165–171. doi: 10.1042/bj1330165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Janda M. Investigation of the quaternary structure of beef liver glutamate dehydrogenase with bifunctional reagents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1080–1088. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90807-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Powers J. C., Wilcox P. E. Kinetics of the reaction of chymotrypsin A with peptide chloromethyl ketones in relation to its subsite specificity. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):771–777. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. The reaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with 4-iodoacetamido salicylic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon K., Piszkiewicz D., Smith E. L. Glutamate dehydrogenase: amino-acid sequence of the bovine enzyme and comparison with that from chicken liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1380–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON J. A., ANFINSEN C. B. The crystallization and characterization of L-glutamic acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):67–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal P. K., Wechter W. J., Colman R. F. Affinity labeling of the inhibitory DPNH site of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase by 5'-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8140–8147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Bovine liver flutamate dehydrogenase. Sequence of a hexadecapeptide containing a lysyl residue reactive with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2622–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C., Tuhy P. M. Active-site specific inhibitors of elastase. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4767–4774. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen N. L., Bishop L., Burnett J. B., Bishop M., Colman R. F. Methionyl residue critical for activity and regulation of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7359–7369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw E. Selective chemical modification of proteins. Physiol Rev. 1970 Apr;50(2):244–296. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Blout E. R. Peptide chloromethyl ketones as irreversible inhibitors of elastase. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):44–47. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


