Abstract
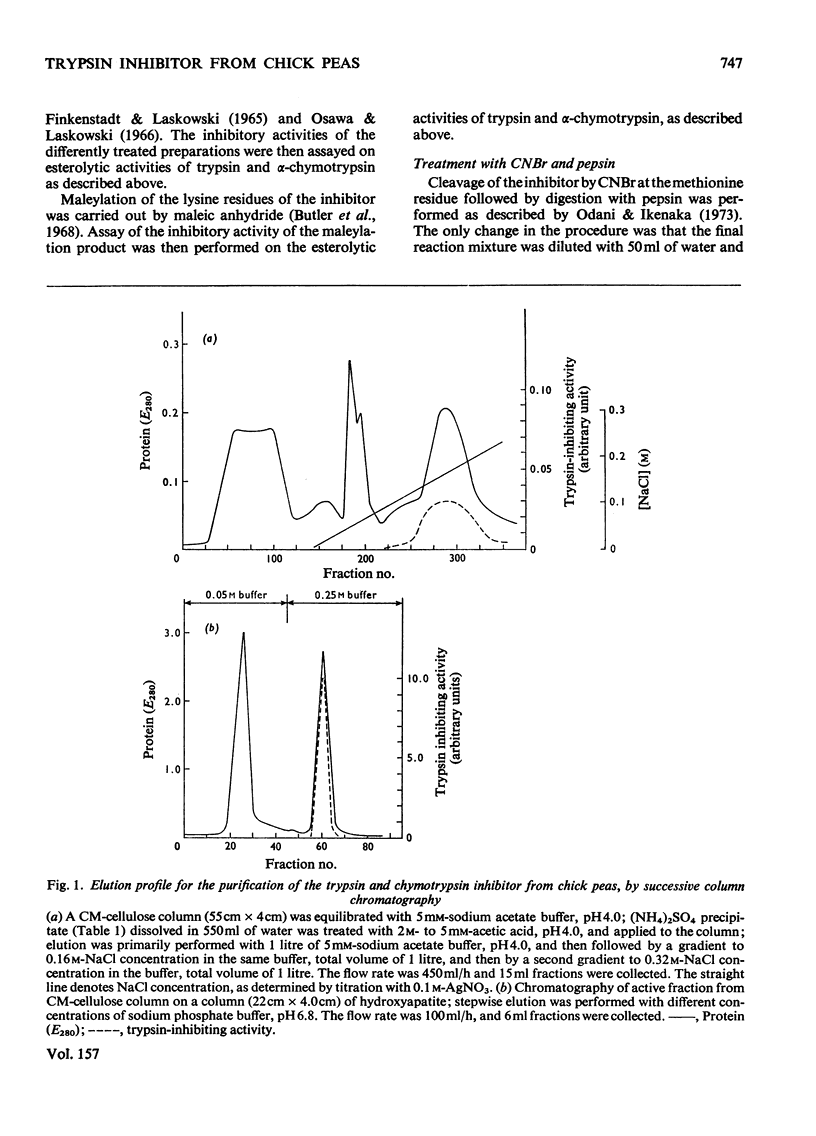
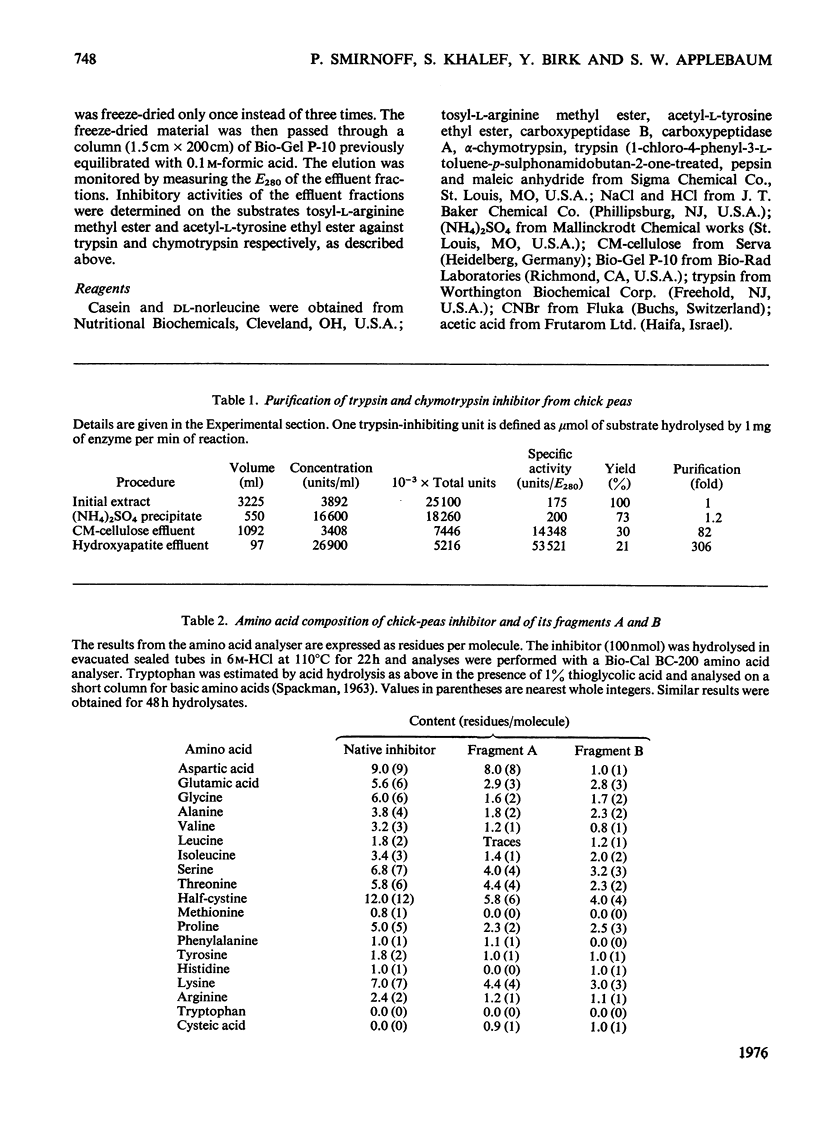
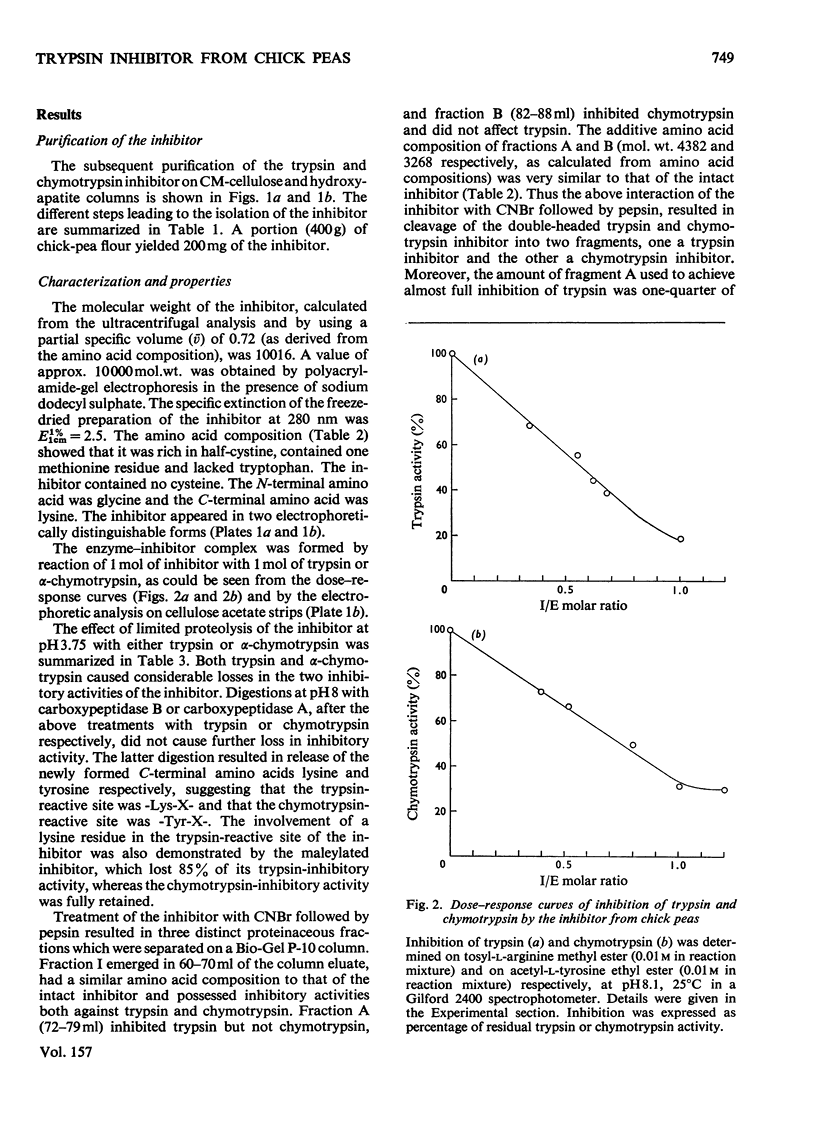
1. A trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor was isolated by extraction of chick-pea meal at pH8.3, followed by (NH4)2SO4 precipitation and successive column chromatography on CM-cellulose and calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite). 2. The inhibitor was pure by polyacrylamide-gel and cellulose acetate electrophoresis and by isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. 3. The inhibitor had a molecular weight of approx. 10000 as determined by ultracentrifugation and by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. A molecular weight of 8300 was resolved from its amino acid composition. 4. The inhibitor formed complexes with trypsin and chymotrypsin at molar ratios of 1:1. 5. Limited proteolysis of the inhibitor with trypsin at pH3.75 resulted in hydrolysis of a single-Lys-X-bond and in consequent loss of 85% of the trypsin inhibitory activity and 60% of the chymotrypsin inhibitory activity. Limited proteolysis of the inhibitor with chymotrypsin at pH3.75 resulted in hydrolysis of a single-Tyr-X-bond and in consequent loss of 70% of the trypsin inhibitory activity and in complete loss of the chymotrypsin inhibitory activity. 6. Cleavage of the inhibitor with CNBr followed by pepsin and consequent separation of the products on a Bio Gel P-10 column, yielded two active fragments, A and B. Fragment A inhibited trypsin but not chymotrypsin, and fragment B inhibited chymotrypsin but not trypsin. The specific trypsin inhibitory activity, on a molar ratio, of fragment A was twice that of the native inhibitor, suggesting the unmasking of another trypsin inhibitory site as a result of the cleavage. On the other hand, the specific chymotrypsin inhibitory activity of fragment B was about one-half of that of the native inhibitor, indicating the occurrence of a possible conformational change.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRK Y., GERTLER A., KHALEF S. A pure trypsin inhibitor from soya beans. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj0870281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk Y. Chemistry and nutritional significance of proteinase inhibitors from plant sources. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 28;146(2):388–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk Y., Gertler A., Khalef S. Further evidence for a dual, independent, activity against trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin of inhibitor AA from soybeans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):402–404. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Harris J. I., Hartley B. S., Lebeman R. The use of maleic anhydride for the reversible blocking of amino groups in polypeptide chains. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):679–689. doi: 10.1042/bj1120679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernikov M. P., Abramova E. P., Liaiman M. E., Chernikova L. G., Shuliak A. I., Chebotarev A. K. Ingibitory proteinaz semian nekotorykh rastenii, ikh svoistva i vliianie na usvoenie belka. Vestn Akad Med Nauk SSSR. 1966;21(10):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertler A., Birk Y., Bondi A. A comparative study of the nutritional and physiological significance of pure soybean trypsin inhibitors and of ethanol-extracted soybean meals in chicks and rats. J Nutr. 1967 Mar;91(3):358–370. doi: 10.1093/jn/91.3_Suppl.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn A. M., Biek Y., Guggenheim K. Pancreatic enzyme pattern in rats as affected by dietary soybean flour. J Nutr. 1970 Mar;100(3):361–368. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn A. M., Birk Y., Guggenheim K. In vitro synthesis of pancreatic enzymes: effect of soybean trypsin inhibitor. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1113–1117. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahn J., Stevens F. C. Lima bean trypsin inhibitor. Limited proteolysis by trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2646–2652. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., LASKOWSKI M., Jr Naturally occurring trypsin inhibitors. Adv Protein Chem. 1954;9:203–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky H., Smirnoff P., Khalef S., Birk Y., Applebaum S. W. Proceedings: Trypsin-like enzymes and trypsin inhibitors. Isr J Med Sci. 1975 Nov;11(11):1170–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madar Z., Birk Y., Gertler A. Native and modified Bowman-Birk trypsin inhibitor--comparative effect on pancreatic enzymes upon ingestion by quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1974 Jun 15;48(2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(74)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odani S., Ikenaka T. Scission of soybean Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor into two small fragments having either trypsin or chymotrypsin inhibitory activity. J Biochem. 1973 Oct;74(4):857–860. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Laskowski M., Jr The reactive site of trypsin inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3955–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Sanger F. The free amino groups of haemoglobins. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0420287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai A. Trypsin inhibitors of plant origin, their chemistry and potential role in animal nutrition. Nutr Abstr Rev. 1967 Jan;37(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
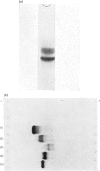
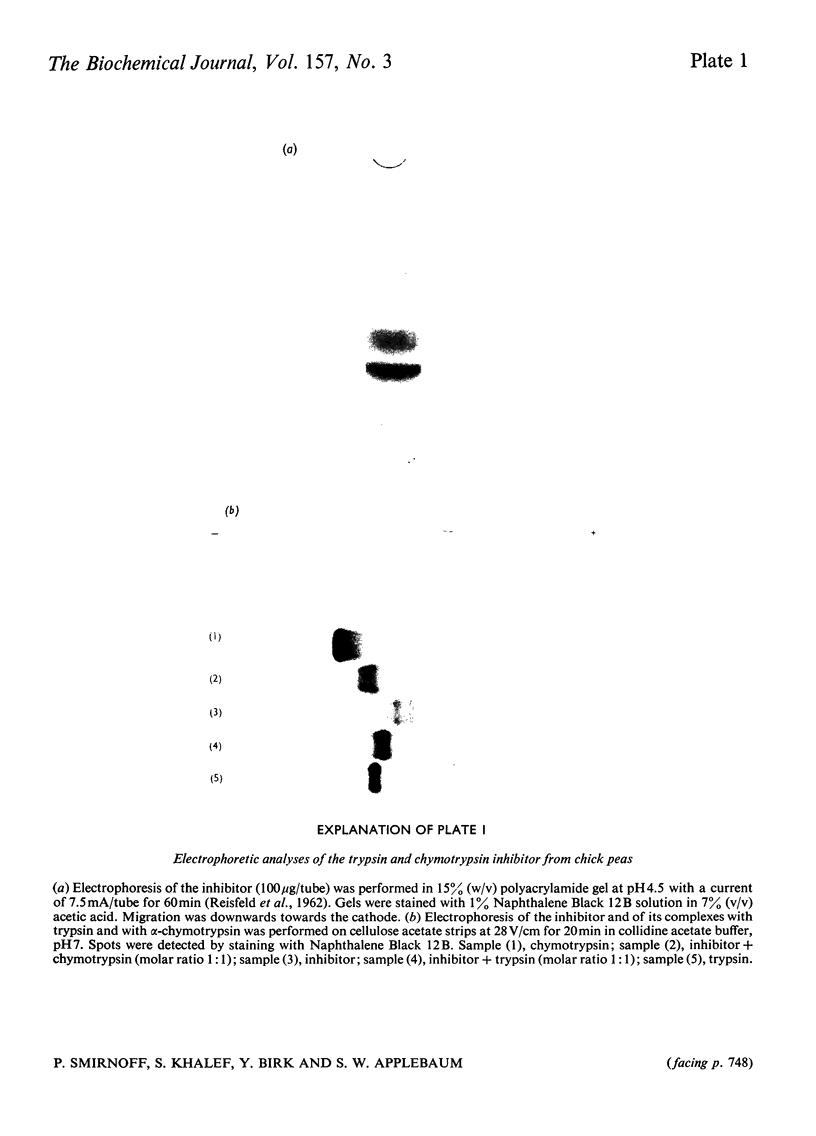
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANSTIS D. A. Rapid determination of molecular weights of peptides and preteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Aug 31;88:586–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]