Abstract
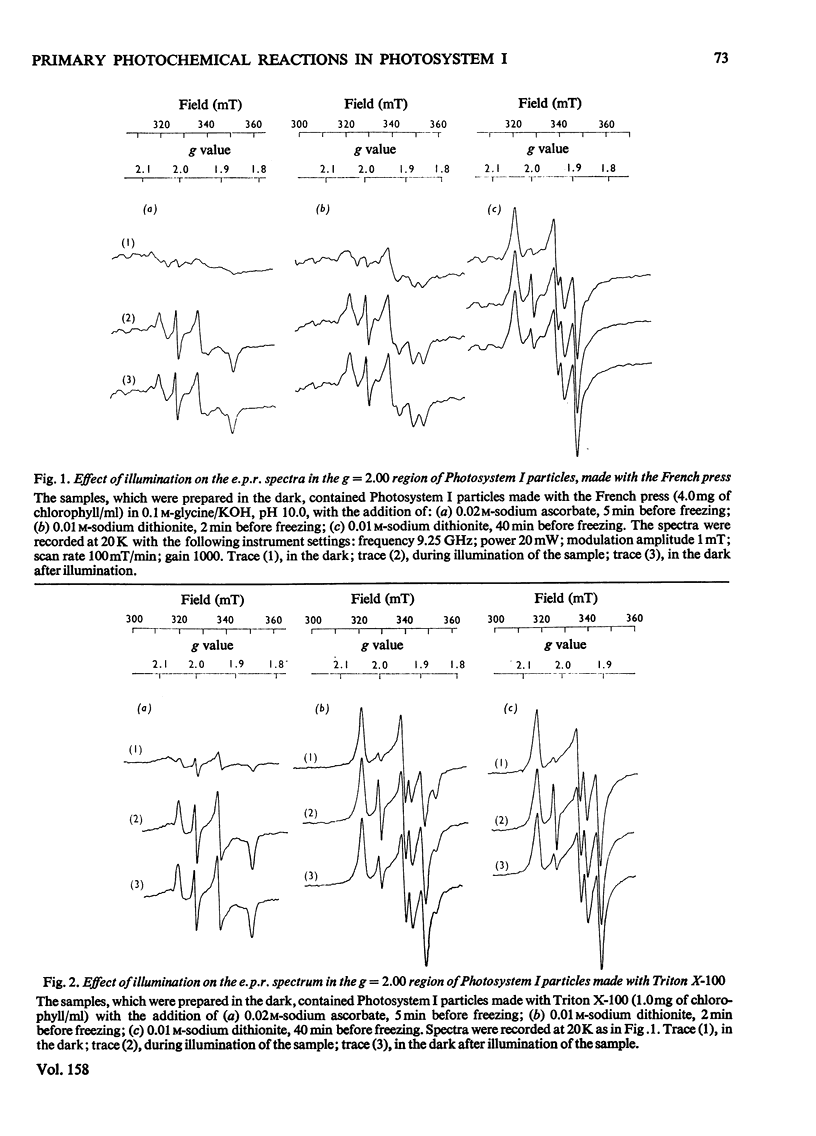
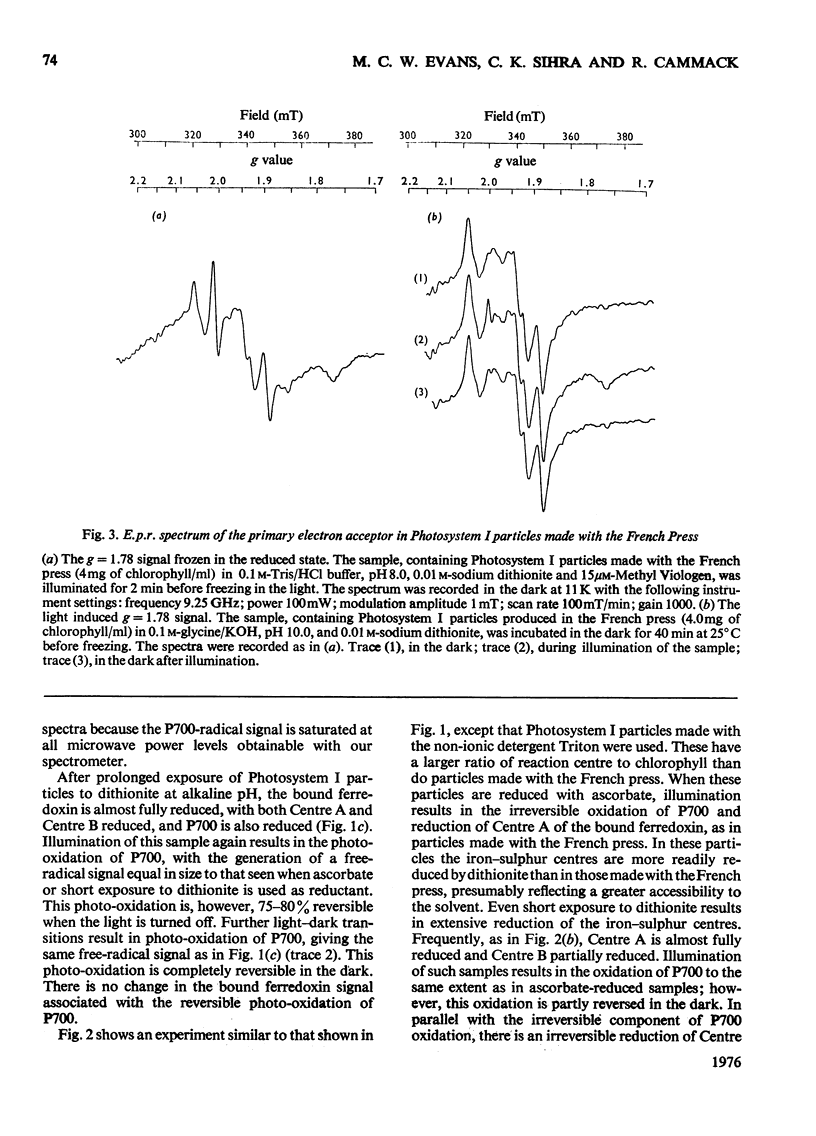
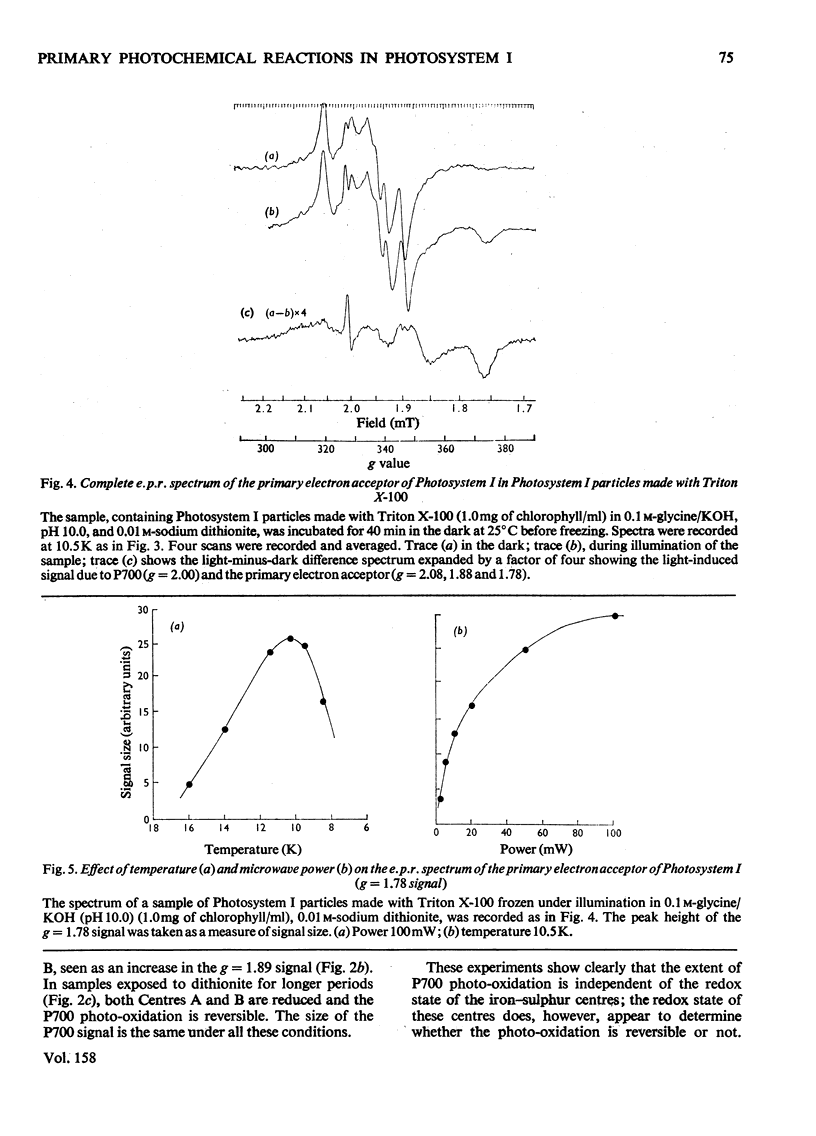
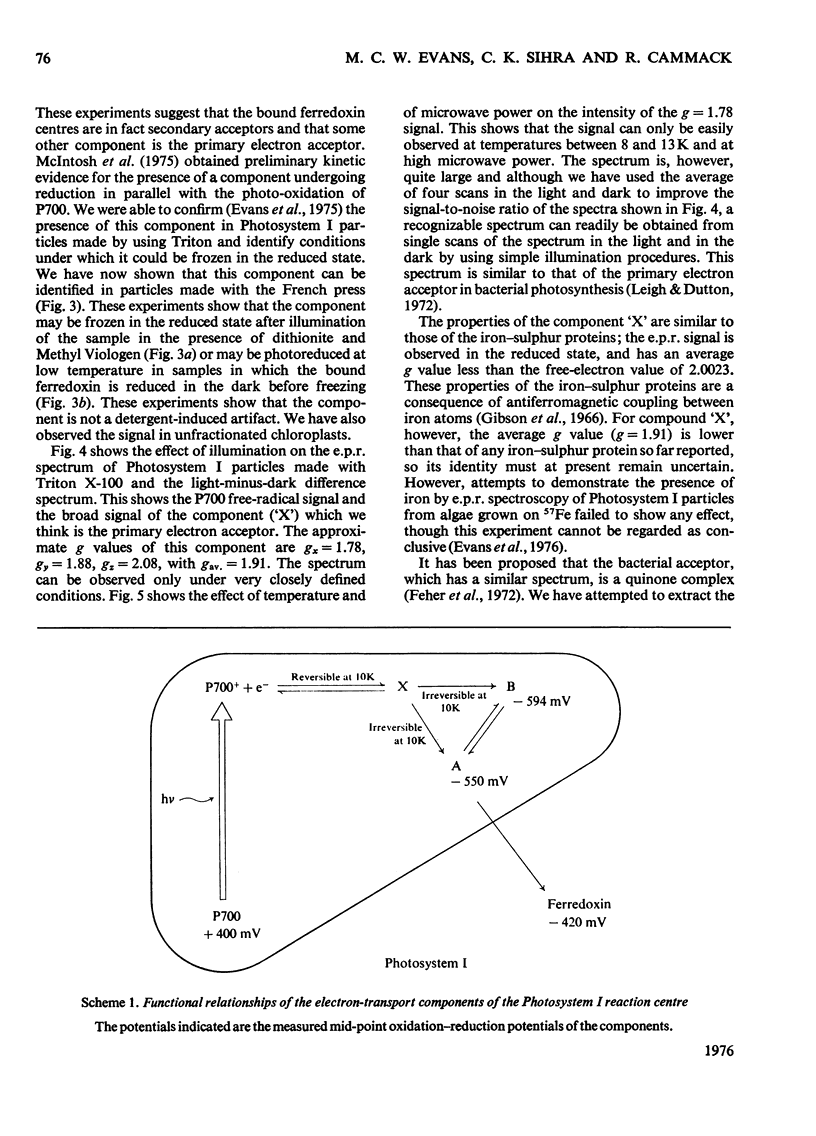
The properties of the component 'X' identified as the primary electron acceptor of Photosystem I in spinach was investigated by electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy and the complete spectrum obtained for the first time. Component 'X' has gx = 1.78, gy = 1.88 and gz = 2.08; it can be observed only at very low temperatures (8--13K) and high microwave powers. Component X was identified in Photosystem I particles prepared with the French press or with Triton X-100. In samples reduced with ascorbate, illumination at low temperatures results in the photo-oxidation of P700 and reduction of a bound iron-sulphur protein; this is irreversible at low temperature. In samples in which the iron-sulphur proteins are reduced by sodium dithionite, illumination at low temperature results in the oxidation of P700 and the reduction of component 'X'; this is reversible at low temperature. The light-induced P700 signal is the same size with either ascorbate or dithionite as reducing agent, showing that all of the P700 involved in reduction of bound ferredoxin also functions in the reduction of component 'X'.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearden A. J., Malkin R. Primary photochemical reactions in chloroplast photosynthesis. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 May;7(2):131–177. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin M., Sogo P. B. Primary Quantum Conversion Process in Photosynthesis: Electron Spin Resonance. Science. 1957 Mar 15;125(3246):499–500. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3246.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R., Evans M. C. E.P.R. spectra of iron-sulphur proteins in dimethylsulphoxide solutions: evidence that chloroplast photosystem I particles contain 4Fe-4S centres. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 17;67(2):544–549. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90846-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commoner B., Heise J. J., Townsend J. LIGHT-INDUCED PARAMAGNETISM IN CHLOROPLASTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):710–718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. H., Cammack R. Properties of the primary electron acceptor complex of photosystem I in the blue green alga Chlorogloea fritschii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1212–1218. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Cammack R. The effect of the redox state of the bound iron-sulphur centres in spinach chloroplasts on the reversibility of P700 photooxidation at low temperatures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 3;63(1):187–193. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Reeves S. G., Cammack R. Determination of the oxidation-reduction potential of the bound iron-sulphur proteins of the primary electron acceptor complex of photosystem I in spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1974 Dec 1;49(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Lord A. V. Evidence for the role of a bound ferredoxin as the primary electron acceptor of photosystem I in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher G., Okamura M. Y., McElroy J. D. Identification of an electron acceptor in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. F., Hall D. O., Thornley J. H., Whatley F. R. The iron complex in spinach ferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):987–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. Oxidation-reduction potentials of bound iron-sulfur proteins of photosystem I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B. The primary electron acceptor of photosystem. I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):1–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. S., Jr, Dutton P. L. The primary electron acceptor in photosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):414–421. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Bearden A. J. Primary reactions of photosynthesis: photoreduction of a bound chloroplast ferredoxin at low temperature as detected by EPR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):16–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh A. R., Chu M., Bolton J. R. Flash photolysis electron spin resonance studies of the electron acceptor species at low temperatures in photosystem I of spinach subchloroplast particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 17;376(2):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


