Abstract
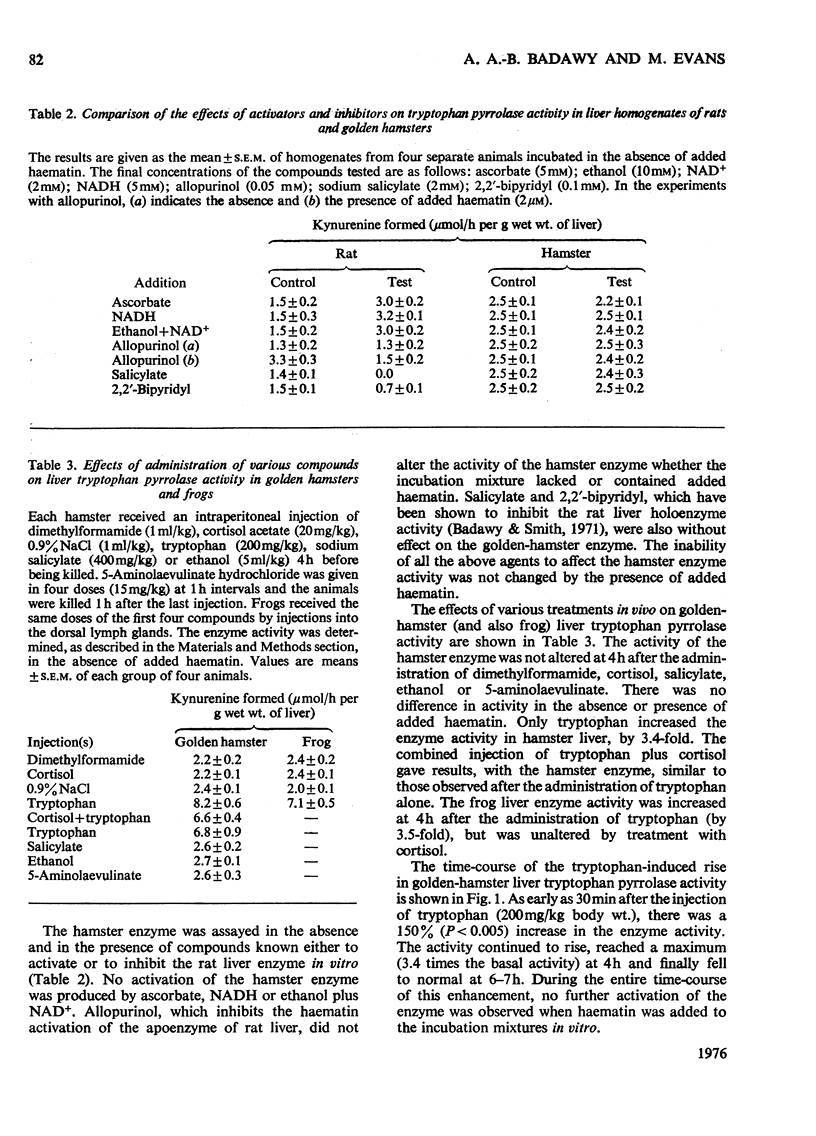
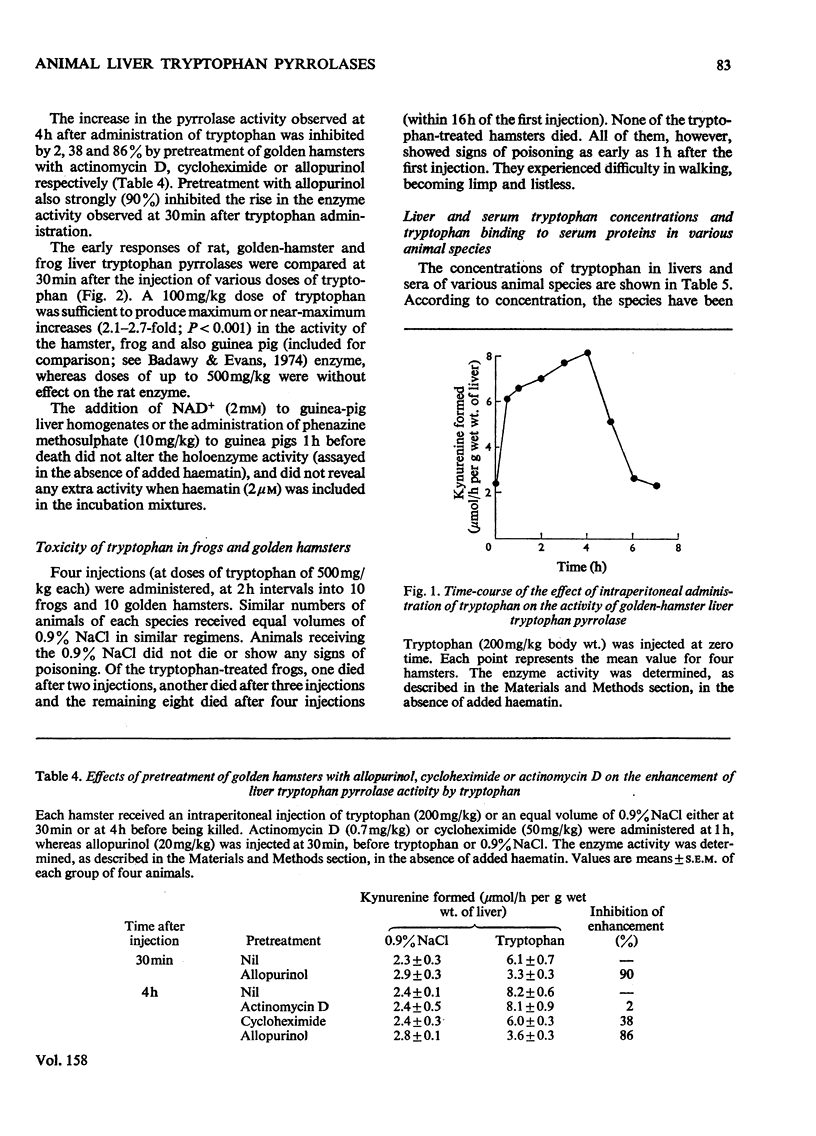
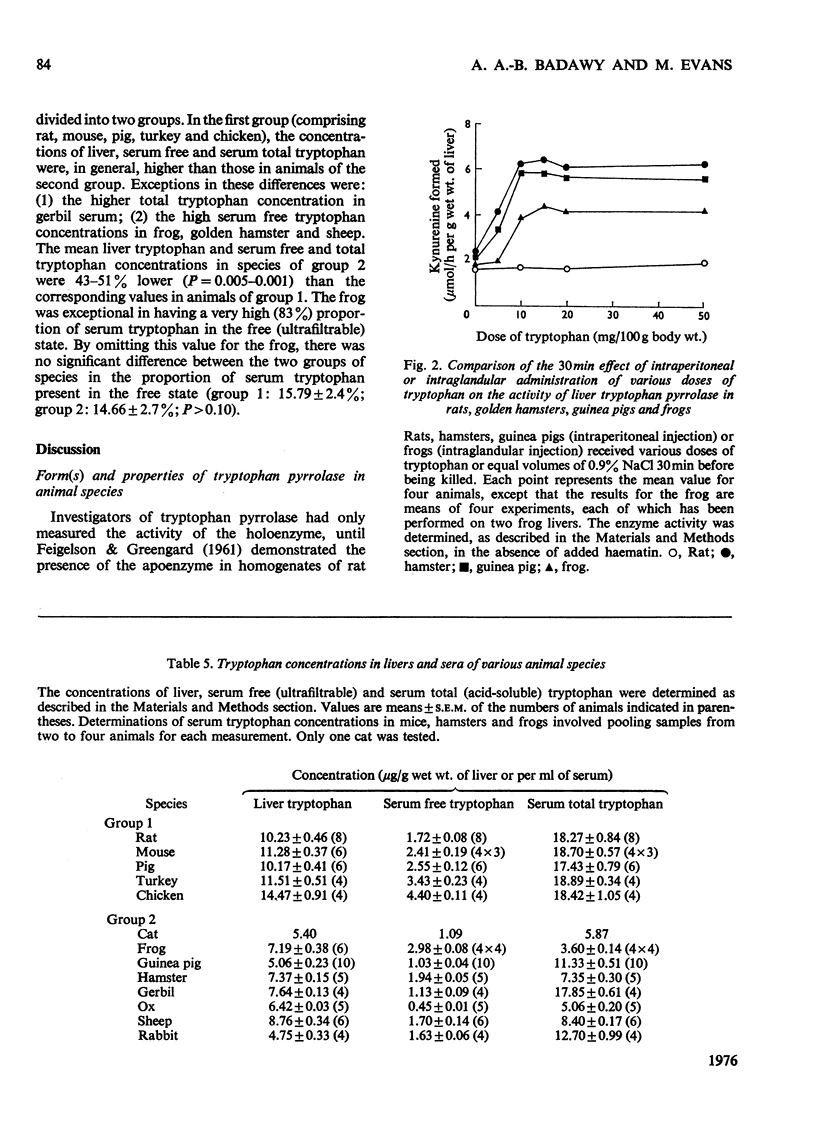
1. Liver tryptophan pyrrolase exists as holoenzyme and apoenzyme in rat, mouse, pig, turkey, chicken and possibly man. 2. The apoenzyme is absent from cat, frog, gerbil, guinea pig, hamster, ox, sheep and rabbit. 3. The hormonal mechanism of induction of the pyrrolase is absent from species lacking the apoenzyme. 4. The concentrations of tryptophan in livers and sera of these species are lower than in species possessing the apoenzyme. 5. Species lacking the apoenzyme or the hormonal induction mechanism have a deficient kynurenine pathway and are sensitive to the toxicity of tryptophan. 6. It is suggested that these species are not suitable as models for studying human tryptophan metabolism. 7. The possible significance of these findings in relation to veterinary and human neonatal care is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUERBACH V. H., WAISMAN H. A. Tryptophan peroxidase-oxidase, histidase, and transaminase activity in the liver of the developing rat. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):304–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AURICCHIO S., QUAGLIARIELLO E., RUBINO A. [Research on the interrelations of tryptophan and nicotinic acid in newborn infants during the first month of life]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1959 Dec 31;35:2206–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman K., Greengard O. Correlation of kynurenine excretion with liver tryptophan pyrrolase levels in disease and after hydrocortisone induction. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1527–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI105459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Guinea-pig liver tryptophan pyrrolase. Absence of detectable apoenzyme activity and of hormonal induction by cortisol and possible regulation by tryptophan. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):445–451. doi: 10.1042/bj1380445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Regulation of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase by its cofactor haem: Experiments with haematin and 5-aminolaevulinate and comparison with the substrate and hormonal mechanisms. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):511–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1500511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The effects of acute and chronic nicotine hydrogen (+)-tartrate administration and subsequent withdrawal on rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity and their comparison with those of morphine, phenobarbitone and ethanol. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):425–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1480425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The effects of ethanol on tryptophan pyrrolase activity and their comparison with those of phenobarbitone and morphine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;59:229–251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0632-1_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The mechanism of inhibition of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by 4-hydroxypyrazolo(3,4-d)pyrimidine (Allopurinol). Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj1330585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The regulation of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (phosphate). Experiments with glucose and nicotinamide. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1560381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Smith M. J. Changes in liver tryptophan and tryptophan pyrrolase activity after administration of salicylate and tryptophan to the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Jan;21(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Smith M. J. The effects of salicylate on the activity of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1230171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloxam D. L., Warren W. H. Error in the determination of tryptophan by the method of Denkla and Dewey. A revised procedure. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):621–625. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Faivre-Bauman A., Benda P., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Plasma tryptophan and 5-HT metabolism in the CNS of the newborn rat. J Neurochem. 1974 Aug;23(2):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra P., Rampichini L., Severini M. Tryptophan--niacin and tryptophan--serotonin pathways in weaning pigs with porphyria experimentally induced. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol. 1972;26(3):69–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R., Dyer I. A. A comparison of tryptophan pyrrolase adaptation in cattle, sheep, and rats. J Nutr. 1970 Jan;100(1):94–100. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S., Pitot H. C. Feedback control of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase. I. End product inhibition of trytophan pyrrolase activity. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1192–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGELSON P., GREENGARD O. A microsomal iron-porphyrin activator of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Roush B. W. Binding of tryptophan to plasma proteins in several species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1973 Oct 15;46(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(73)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., FEIGELSON P. RELATIONSHIPS OF THE APO-ENZYME AND COENZYME OF TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE IN DEVELOPING AND REGENERATING RAT LIVER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;111:227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb36963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Sourkes T. L., Young S. N. Liver and brain tryptophan metabolism following hydrocortisone administration to rats and gerbils. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankes L. V., Brown R. R., Lippincott S., Schmaeler M. Effects of L-tryptophan load on the metabolism of tryptophan-2-C14 in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Feb;69(2):313–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortia A., Carino M. A. Modification of the toxic actions of l-tryptophan by pargyline and p-chlorophenylalanine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;19(4):1521–1524. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvitefelt J., Santti R. S. Tryptophan pyrrolase in the liver of guinea pig: the absence of hydrocortisone induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Dyer I. A. Effect of orally administered tryptophan on tryptophan pyrrolase activity in ovine and bovine. Life Sci. 1966 Jun;5(12):1121–1124. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Wals P. A. Effect of phenazine methosulfate on lipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2546–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox W. E. The regulation of tryptophan pyrrolase activity by tryptophan. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:287–297. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leklem J. E., Woodford J., Brown R. R. Comparative tryptophan metabolism in cats and rats: differences in adaptation of tryptophan oxygenase and in vivo metabolism of tryptophan, kynurenine and hydroxykynurenine. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)92171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madras B. K., Sourkes T. L. Effects of drugs on the metabolism of tryptophan. Alpha-hydrazinotryptophan and other amino acid analogs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Jun;17(6):1037–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90362-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMENAMY R. H., LUND C. C., ONCLEY J. L. Unbound amino acid concentrations in human blood plasmas. J Clin Invest. 1957 Dec;36(12):1672–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI103568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe C. B. Induction of tryptophan oxygenase and tyrosine aminotransferase in mice. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jun;214(6):1410–1414. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.6.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMETH A. M. Mechanisms controlling changes in tryptophan peroxidase activity in developing mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2921–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMETH A. M., NACHMIAS V. T. Changes in tryptophan peroxidase activity developing liver. Science. 1958 Oct 31;128(3331):1085–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3331.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. N., Carlson J. R. Effects of high tryptophan doses and two experimental rations on the excretion of urinary tryptophan metabolites in cattle. J Nutr. 1972 Dec;102(12):1655–1665. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.12.1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Sourkes T. L. Antidepressant action of tryptophan. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):897–898. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


